Abstract
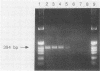
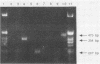
A procedure for the detection of enteric viral nucleic acid in oysters by the polymerase chain reaction was developed. Known quantities of poliovirus type 1 were seeded into oysters. Virus was extracted and concentrated by using organic flocculation and polyethylene glycol precipitation. Inhibitors of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction were present in the oyster extracts, preventing amplification of target viral nucleic acid. The use of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide precipitation sufficiently removed inhibitors to allow detection of as few as 10 PFU of poliovirus. Norwalk virus also could be detected after being seeded into oysters. This methodology may be useful for the detection of these and other shellfish-borne viral pathogens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bemiss J. A., Logan M. M., Sample J. D., Richards G. P. A method for the enumeration of poliovirus in selected molluscan shellfish. J Virol Methods. 1989 Nov;26(2):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cova L., Kopecka H., Aymard M., Girard M. Use of cRNA probes for the detection of enteroviruses by molecular hybridization. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):11–18. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desenclos J. C., Klontz K. C., Wilder M. H., Nainan O. V., Margolis H. S., Gunn R. A. A multistate outbreak of hepatitis A caused by the consumption of raw oysters. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1268–1272. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gama R. E., Horsnell P. R., Hughes P. J., North C., Bruce C. B., al-Nakib W., Stanway G. Amplification of rhinovirus specific nucleic acids from clinical samples using the polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1989 Jun;28(2):73–77. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Gingeras T. R., Richman D. D. Nucleic acid amplification in vitro: detection of sequences with low copy numbers and application to diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):217–226. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Keasler S. P., Trucksess M. W., Feng P., Kaysner C. A., Lampel K. A. Polymerase chain reaction identification of Vibrio vulnificus in artificially contaminated oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):707–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.707-711.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES A. S. USE OF ALKYLTRIMETHYLAMMONIUM BROMIDES FOR THE ISOLATION OF RIBO- AND DESOXYRIBO-NUCLEIC ACIDS. Nature. 1963 Jul 20;199:280–282. doi: 10.1038/199280b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Siegl G., Lemon S. M. Molecular epidemiology of human hepatitis A virus defined by an antigen-capture polymerase chain reaction method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2867–2871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Estes M. K., Metcalf T. G. Detection of hepatitis A virus by hybridization with single-stranded RNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2487–2495. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2487-2495.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Estes M. K., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Detection of hepatitis A virus in seeded estuarine samples by hybridization with cDNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.711-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Wang J., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2529–2534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2529-2534.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. D., Metcalf T. G. Polyethylene glycol precipitation for recovery of pathogenic viruses, including hepatitis A virus and human rotavirus, from oyster, water, and sediment samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1983–1988. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1983-1988.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf T. G., Xi J. A., Estes M. K., Melnick J. L. Nucleic acid probes and molecular hybridization for detection of viruses in environmental samples. Prog Med Virol. 1988;35:186–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Guzewich J. J., Hanrahan J. P., Stricof R., Shayegani M., Deibel R., Grabau J. C., Nowak N. A., Herrmann J. E., Cukor G. Widespread outbreaks of clam- and oyster-associated gastroenteritis. Role of Norwalk virus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):678–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A. Enzymatic RNA amplification of the enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):438–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.438-442.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERDT C. E., FOGH J. The ratio of physical particles per infectious unit observed for poliomyelitis viruses. Virology. 1957 Aug;4(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. Epidemiology of foodborne illness: North America. Lancet. 1990 Sep 29;336(8718):788–790. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93250-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde J., Eiden J., Yolken R. Removal of inhibitory substances from human fecal specimens for detection of group A rotaviruses by reverse transcriptase and polymerase chain reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1300-1307.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi J. N., Graham D. Y., Wang K. N., Estes M. K. Norwalk virus genome cloning and characterization. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1580–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2177224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. J., Estes M. K., Jiang X., Metcalf T. G. Concentration and detection of hepatitis A virus and rotavirus from shellfish by hybridization tests. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2963–2968. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2963-2968.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]