Abstract
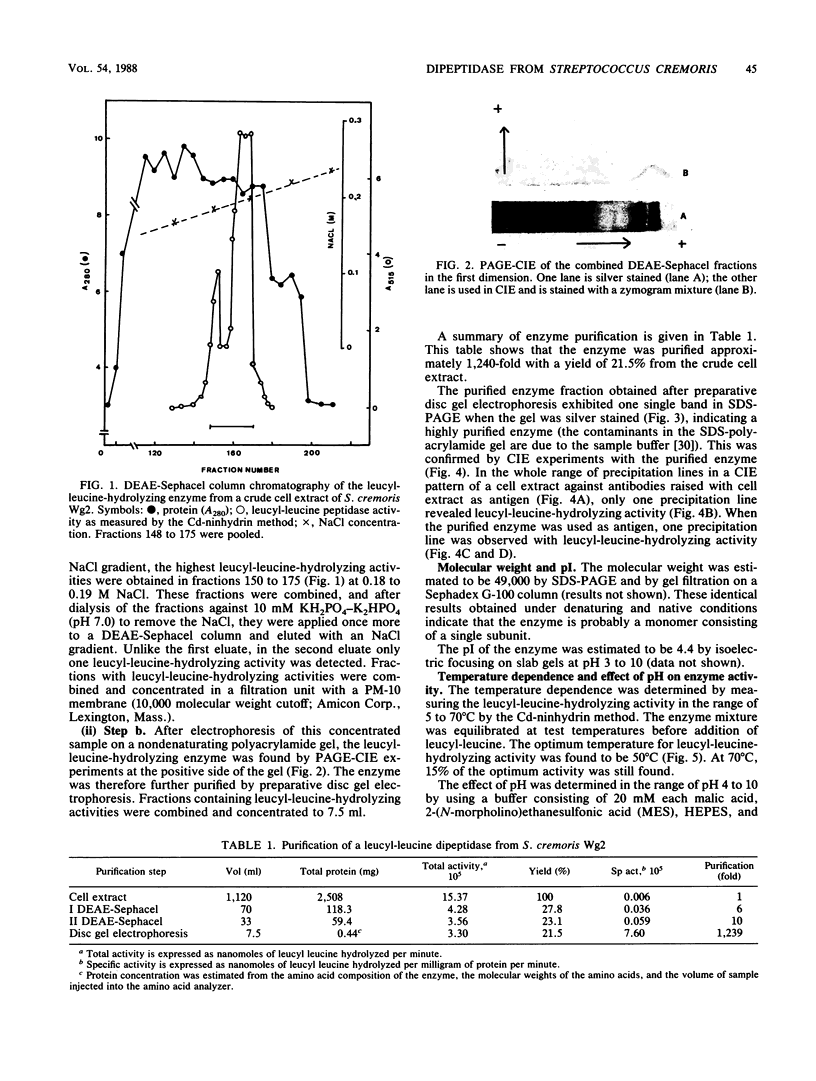
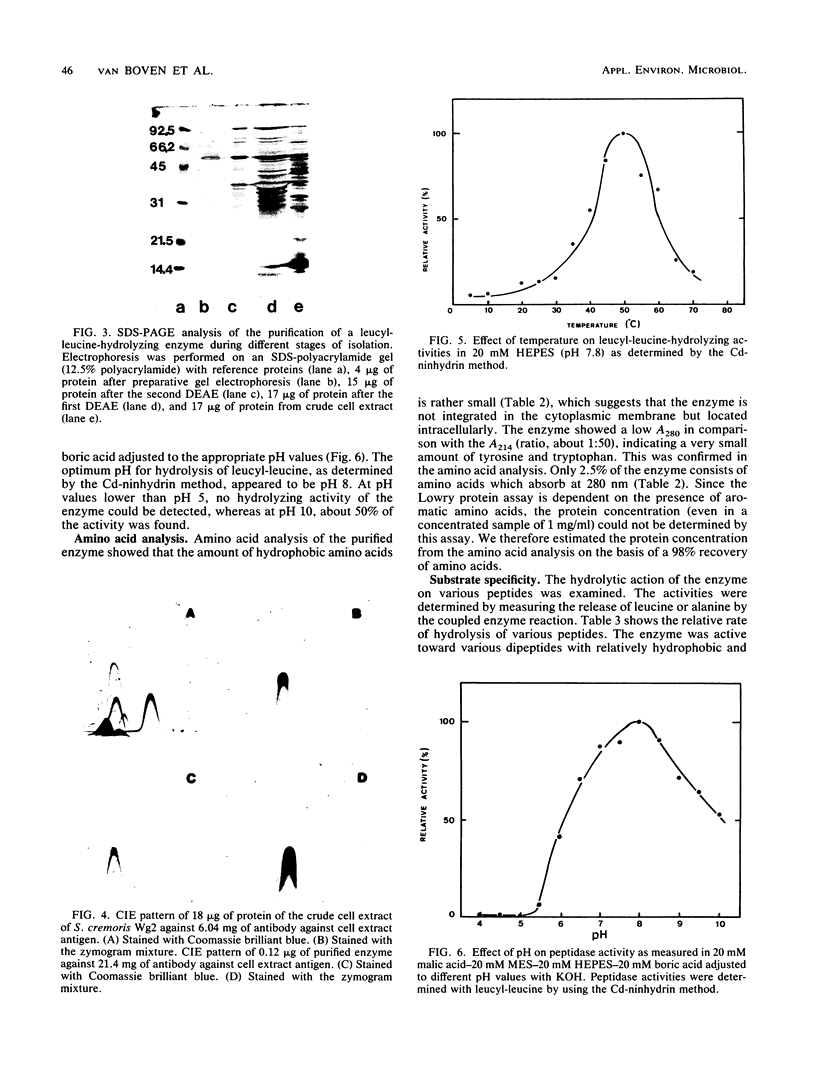
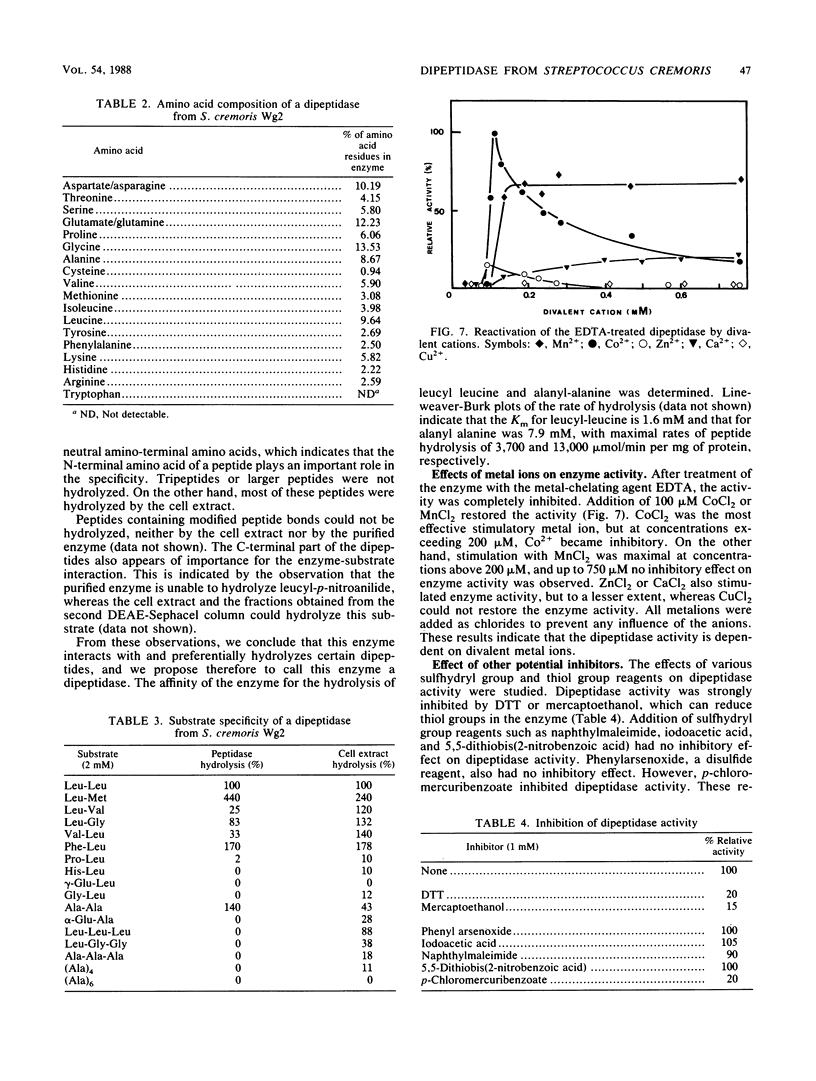
A dipeptidase was purified to homogeneity from a crude cell extract of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2 by DEAE-Sephacel column chromatography followed by preparative disc gel electrophoresis. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified enzyme showed a single protein band with a molecular weight of 49,000. The dipeptidase is capable of hydrolyzing a range of dipeptides, but not peptides with longer chains. The enzyme was shown to be a metallo-Mn2+ enzyme with a pH optimum of 8 and a temperature optimum of 50°C. The enzyme is strongly inhibited by thiol-reducing reagents but not by sulfhydryl reagents. Kinetic studies indicated that the enzyme has a relatively low affinity for leucyl-leucine and alanyl-alanine (Km, 1.6 and 7.9 mM, respectively) but can hydrolyze these substrates at very high rates (Vmax, 3,700 and 13,000 μmol/min per mg of protein, respectively).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doi E., Shibata D., Matoba T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Seÿen H. G., Konings W. N. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles and chromatophoresis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Location of Peptidases Outside and Inside the Membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.177-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., Exterkate F., Konings W. N. The Proteolytic Systems of Streptococcus cremoris: an Immunological Analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1105–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1105-1110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., van Sinderen D., Kok J., Konings W. N. Cell Wall-Associated Proteases of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):853–859. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.853-859.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolstad J., Law B. A. Comparative peptide specificity of cell wall, membrane and intracellular peptidases of group N streptococci. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 May;58(5):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A., Kolstad J. Proteolytic systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):225–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00399500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A. Peptide utilization by group N streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Mar;105(1):113–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Bioenergetic consequences of lactose starvation for continuously cultured Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1460-1468.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. H., Morris H. A., Castberg H. B., McKay L. L. Hydrolysis of milk proteins by bacteria used in cheese making. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Nov-Dec;24(6):1106–1113. doi: 10.1021/jf60208a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasheva B., Dessev G. Artifacts in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis due to 2-mercaptoethanol. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boven A., Konings W. N. Energetics of Leucyl-Leucine Hydrolysis in Streptococcus cremoris Wg(2). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):95–100. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.95-100.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plas J., Hellingwerf K. J., Seijen H. G., Guest J. R., Weiner J. H., Konings W. N. Identification and localization of enzymes of the fumarate reductase and nitrate respiration systems of escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1027–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1027-1037.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





