Abstract
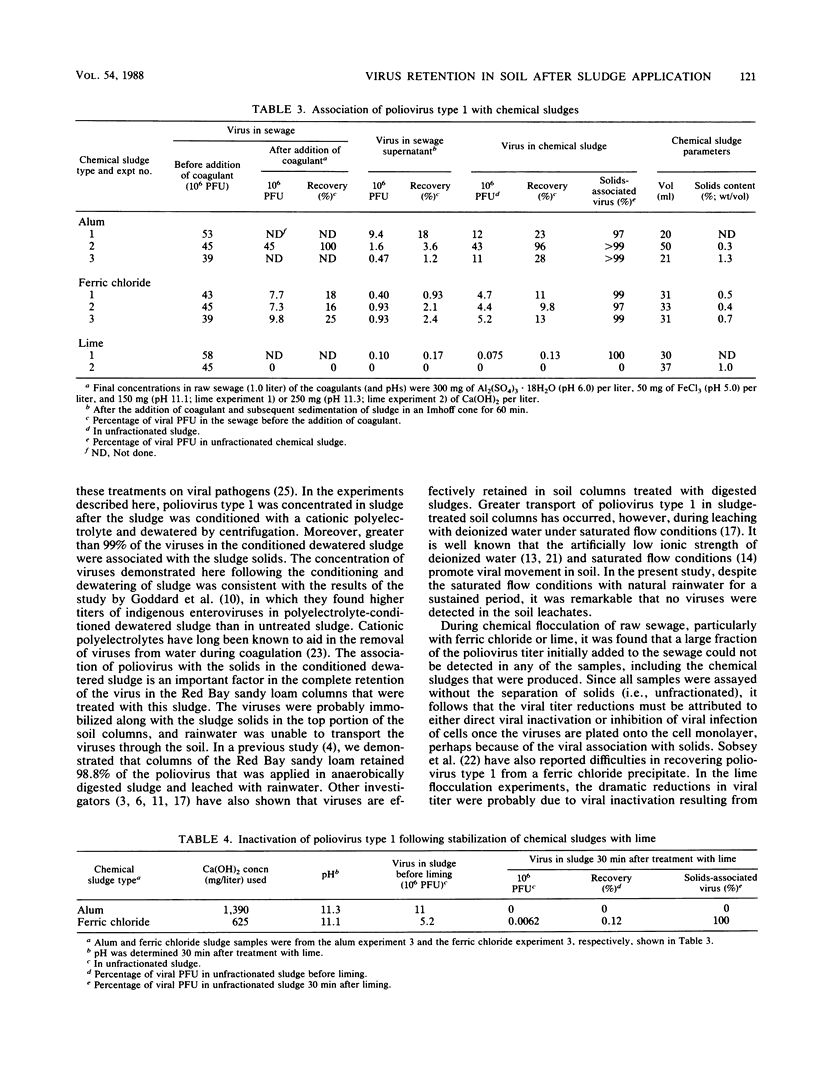
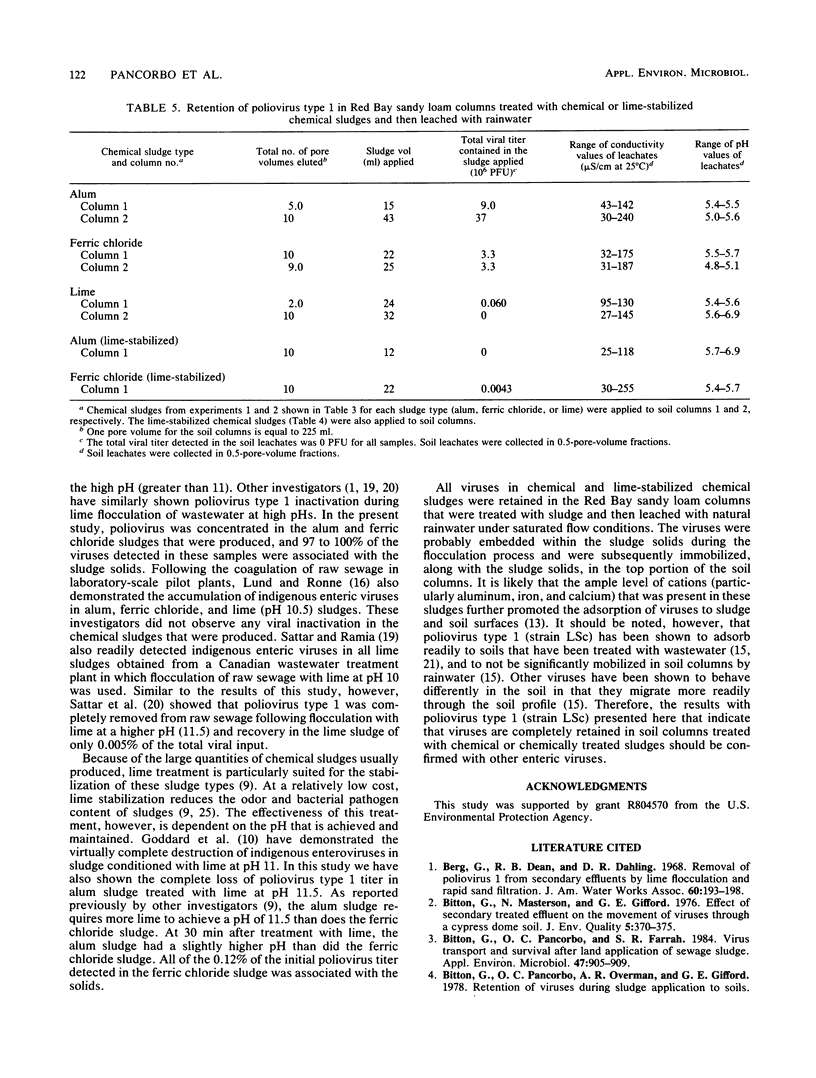
The transport of poliovirus type 1 (strain LSc) was studied in Red Bay sandy loam columns that were treated with chemical- or polyelectrolyte-conditioned dewatered sludges and then leached with natural rainwater under saturated flow conditions. Poliovirus was concentrated in the alum and ferric chloride sludges that were produced following the flocculation of virus-seeded raw sewage. Virtually complete inactivation of the virus was observed following the flocculation of raw sewage or the stabilization of alum and ferric chloride sludges with lime at pH 11.5. Poliovirus was also concentrated in polyelectrolyte-conditioned dewatered sludge that was produced from virus-seeded, anaerobically digested sludge. Despite the saturated flow conditions for a sustained period, no viruses were detected in the leachates of the soil columns that were treated with these chemical and chemically treated sludges. Since the viruses were mostly associated with the solids in these sludge samples, it is believed that they were immobilized along with the sludge solids in the top portion of the soil columns.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitton G., Pancorbo O. C., Farrah S. R. Virus transport and survival after land application of sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):905–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.905-909.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Bitton G., Hoffmann E. M., Lanni O., Pancorbo O. C., Lutrick M. C., Bertrand J. E. Survival of enteroviruses and coliform bacteria in a sludge lagoon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):459–465. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.459-465.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J. B., Smith J. E., Jr, Hathaway S. W., Dean R. B. Lime stabilization of primary sludges. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1974 Jan;46(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard M. R., Bates J., Butler M. Isolation of indigenous enteroviruses from chemically treated and dewatered sludge samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1042-1046.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. C., Gerba C. P. Effect of ionic composition of suspending solution on virus adsorption by a soil column. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):484–488. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. C., Gerba C. P. Virus movement in soil during saturated and unsaturated flow. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):335–337. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.335-337.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry E. F., Vaughn J. M., Thomas M. Z., Beckwith C. A. Adsorption of enteroviruses to soil cores and their subsequent elution by artificial rainwater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):680–687. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.680-687.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancorbo O. C., Scheuerman P. R., Farrah S. R., Bitton G. Effect of sludge type on poliovirus association with and recovery from sludge solids. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Mar;27(3):279–287. doi: 10.1139/m81-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar S. A., Ramia S. Viruses in sewage: effect of phosphate removal with calcium hydroxide (lime). Can J Microbiol. 1978 Aug;24(8):1004–1006. doi: 10.1139/m78-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar S. A., Ramia S., Westwood J. C. Calcium hydroxide (lime) and the elimination of human pathogenic viruses from sewage: studies with experimentally-contaminated (poliovirus type 1, Sabin) and pilot plant samples. Can J Public Health. 1976 May-Jun;67(3):221–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Dean C. H., Knuckles M. E., Wagner R. A. Interactions and survival of enteric viruses in soil materials. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.92-101.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of turbid estuary water. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):770–778. doi: 10.1139/m77-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


