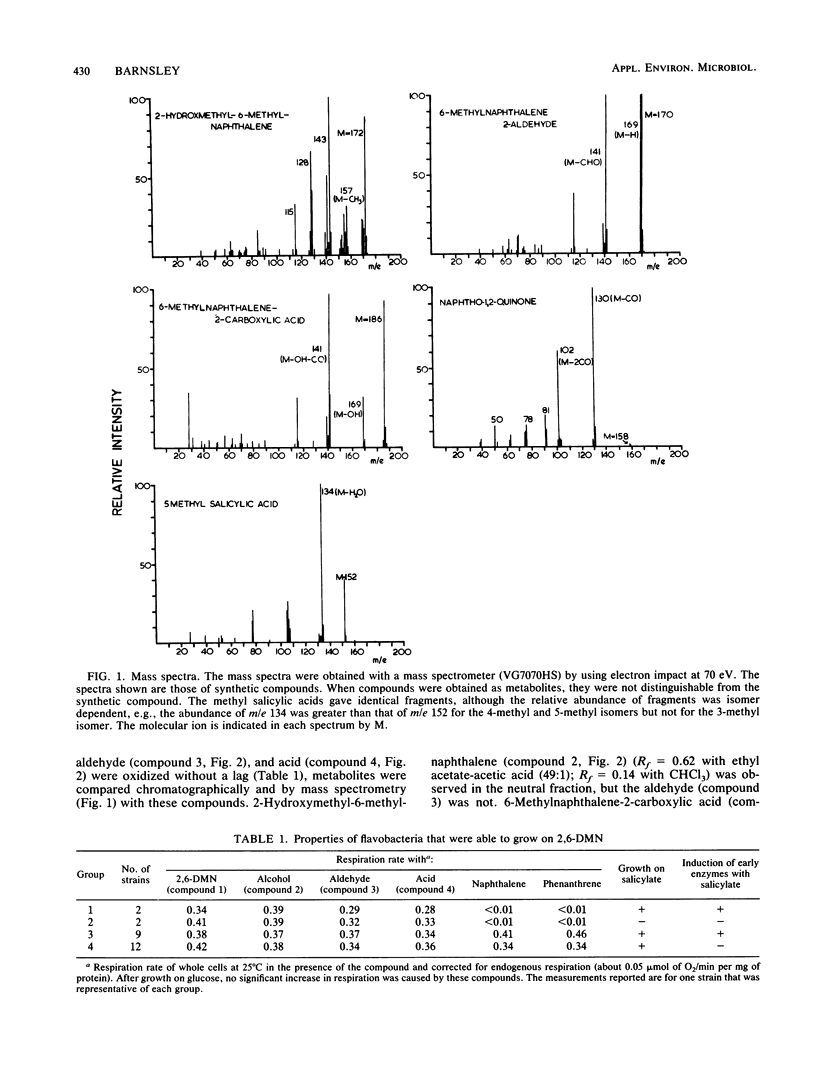
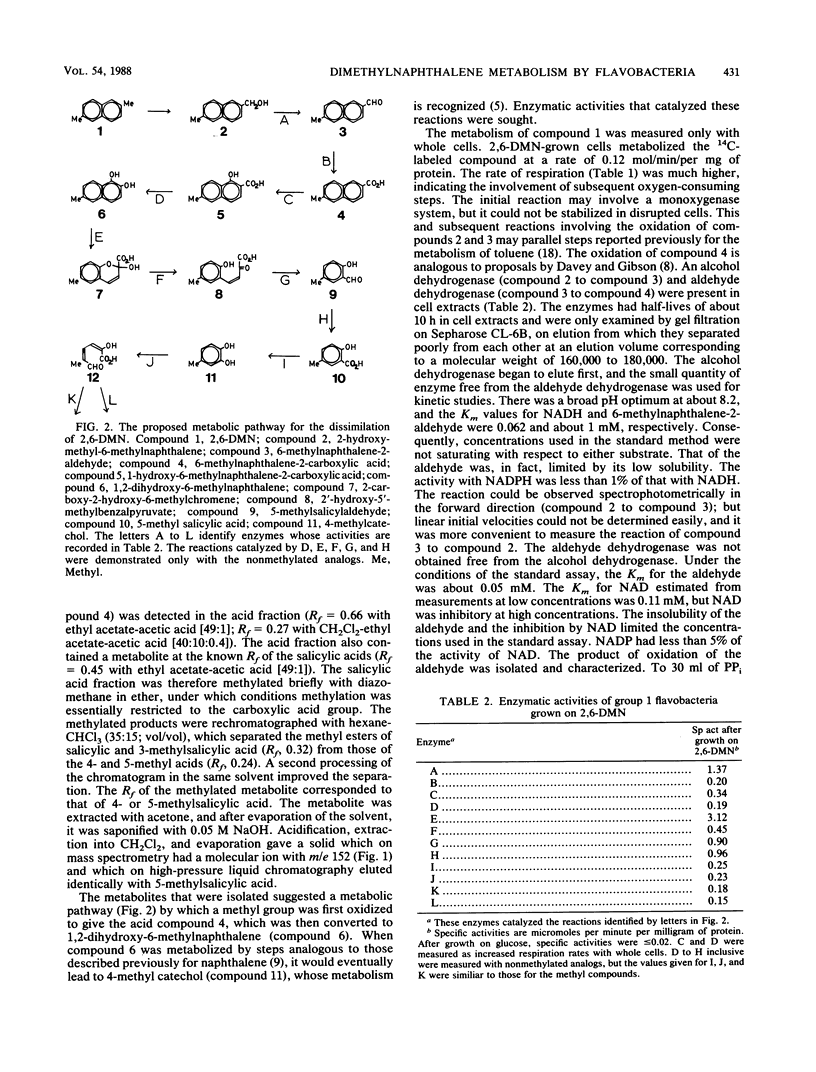
Abstract
Flavobacteria that were able to grow on 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene (2,6-DMN) were isolated from soil. Most were able to oxidize a broad range of aromatic hydrocarbons after growth on 2,6-DMN at rates comparable to that of the oxidation of 2,6-DMN itself. One small group was neither able to grow on naphthalene nor able to oxidize this compound after growth on 2,6-DMN, but metabolized 2,6-DMN by a pathway which converged with that previously described for naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads. These organisms could also grow on salicylate or methylsalicylate, and in so doing, early enzymes for 2,6-DMN metabolism were induced.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnsley E. A. Bacterial oxidation of naphthalene and phenanthrene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1069–1071. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1069-1071.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnsley E. A. Naphthalene metabolism by pseudomonads: the oxidation of 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene to 2-hydroxychromene-2-carboxylic acid and the formation of 2'-hydroxybenzalpyruvate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):1116–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnsley E. A. The induction of the enzymes of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads by salicylate and 2-aminobenzoate. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):193–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Bacterial metabolism of para- and meta-xylene: oxidation of a methyl substituent. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):923–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.923-929.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Gibson D. T., Laborde A. L. Oxidation of naphthalene by a multicomponent enzyme system from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):948–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.948-954.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorak P. M., Westlake D. W. Microbial degradation of aromatics and saturates in Prudhoe Bay crude oil as determined by glass capillary gas chromatography. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Apr;27(4):432–443. doi: 10.1139/m81-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin K. A., Johnson C. B., Breger R. K., Franklin R. B. Pulmonary toxicity of 2-methylnaphthalene: lack of a relationship between toxicity, dihydrodiol formation and irreversible binding to cellular macromolecules in DBA/2J mice. Toxicology. 1983 Mar-Apr;26(3-4):213–230. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(83)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison V. W., Raymond R. L., Hudson J. O. Microbial Hydrocarbon Co-oxidation. III. Isolation and Characterization of an alpha, alpha'-Dimethyl-cis, cis-Muconic Acid-producing Strain of Nocardia corallina. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):853–856. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.853-856.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. Z., Leighton F. A., Peakall D. B., Norstrom R. J., O'Brien P. J., Payne J. F., Rahimtula A. D. Effects of ingestion of hibernia and Prudhoe Bay crude oils on hepatic and renal mixed function oxidase in nestling herring gulls (Larus argentatus). Environ Res. 1985 Feb;36(1):248–255. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(85)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield C. I., Inniss W. E. A rapid, simple method for staining bacterial flagella. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1311–1313. doi: 10.1139/m77-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. R., Barnsley E. A. Naphthalene metabolism by pseudomonads: purification and properties of 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene oxygenase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):668–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.668-673.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond R. L., Jamison V. W., Hudson J. O. Microbial hydrocarbon co-oxidation. I. Oxidation of mono- and dicyclic hydrocarbons by soil isolates of the genus Nocardia. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):857–865. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.857-865.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):582–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene oxygenase in pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvestre M. Isolation Method for Bacterial Isolates Capable of Growth on p-Chlorobiphenyl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1223–1224. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1223-1224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


