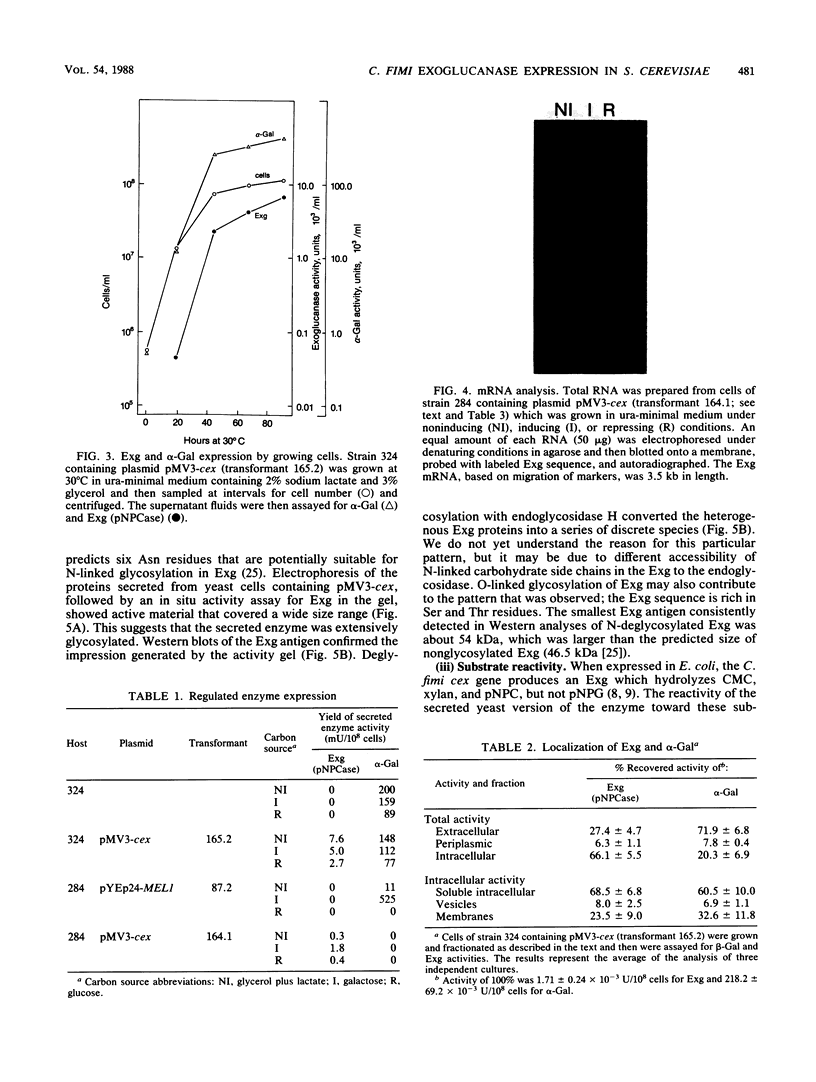
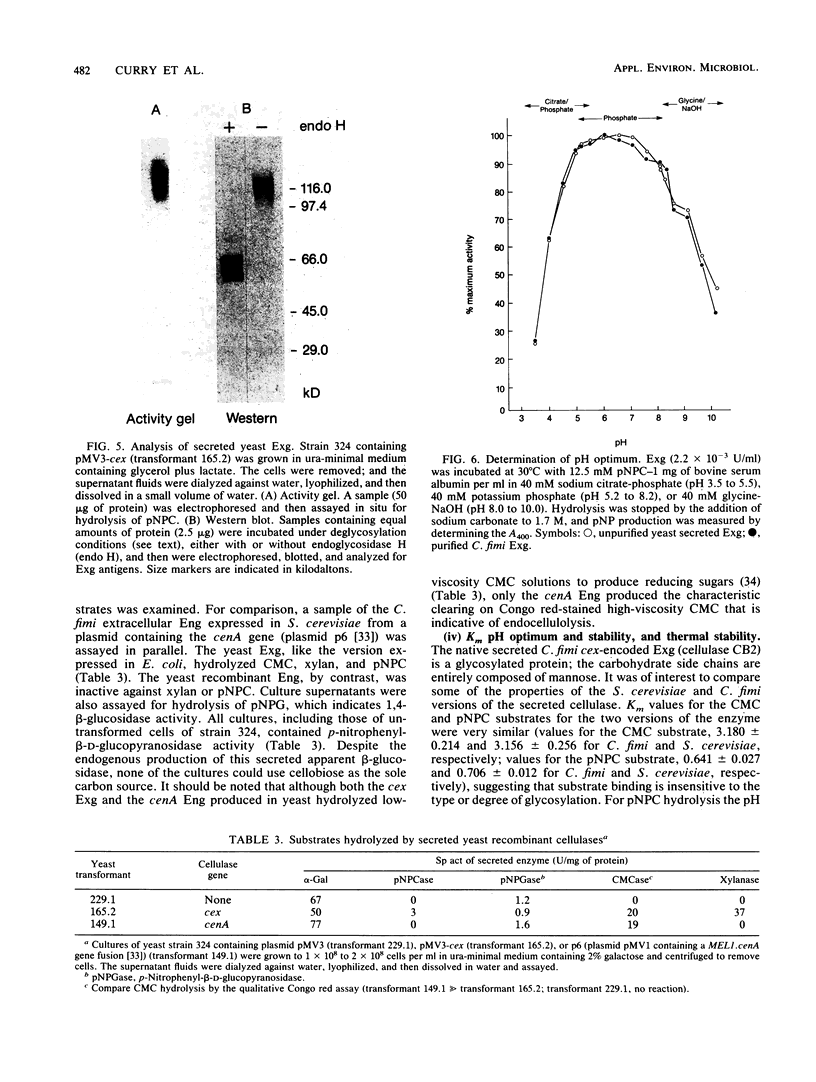
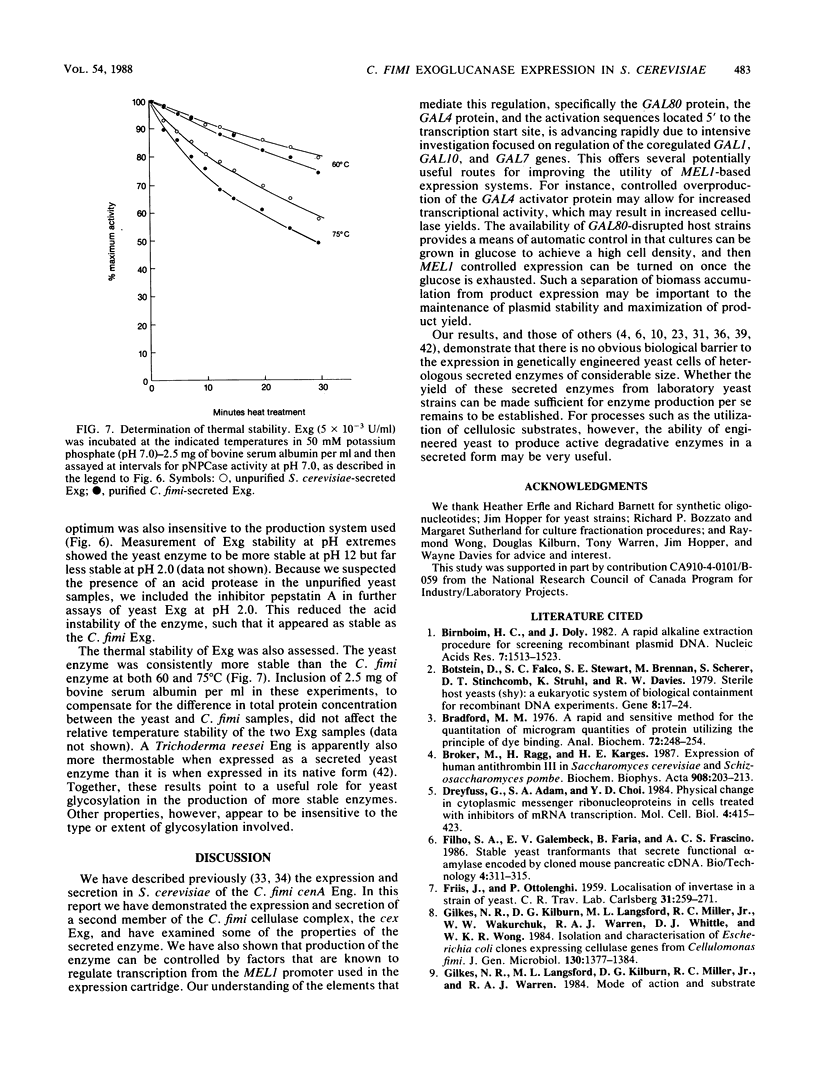
Abstract
We used the yeast MEL1 gene for secreted α-galactosidase to construct cartridges for the regulated expression of foreign proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The gene for a Cellulomonas fimi β-1,4-exoglucanase was inserted into one cartridge to create a fusion of the α-galactosidase signal peptide to the exoglucanase. Yeast transformed with plasmids containing this construction produced active extracellular exoglucanase when grown under conditions appropriate to MEL1 promoter function. The cells also produced active intracellular enzyme. The secreted exoglucanase was N-glycosylated and was produced continuously during culture growth. It hydrolyzed xylan, carboxymethyl cellulose, 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-d-cellobiose, and p-nitrophenyl-β-d-cellobiose. A comparison of the recombinant S. cerevisiae enzyme with the native C. fimi enzyme showed the yeast version to have an identical Km and pH optimum but to be more thermostable.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröker M., Ragg H., Karges H. E. Expression of human antithrombin III in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 29;908(3):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of invertase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:259–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Holland M. J., McCabe P. C., Cole G. E., Wittman V. P., Tal R., Watt K. W., Gelfand D. H., Holland J. P., Meade J. H. Expression, Glycosylation, and Secretion of an Aspergillus Glucoamylase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):21–26. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4695.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Skory S., Lecocq J. P. Linker tailing: unphosphorylated linker oligonucleotides for joining DNA termini. DNA. 1984;3(2):173–182. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. S., Ochoa A. G., Gascón S. alpha-Galactosidase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Cellular localization, and purification of the external enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):375–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever M. Colorimetric and fluorometric carbohydrate determination with p-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide. Biochem Med. 1973 Apr;7(2):274–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P. L. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast MEL1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7257–7268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemans W. A., Boer P., Elbers P. F. Localization of acid phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a clue to cell wall formation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):638–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.638-644.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Sato T., Emi M., Miyanohara A., Nishide T., Matsubara K. Expression of human salivary alpha-amylase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its secretion using the mammalian signal sequence. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y. GAL3 gene product is required for maintenance of the induced state of the GAL cluster genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.101-106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G., Goh S. H., Warren R. A., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr Structure of the gene encoding the exoglucanase of Cellulomonas fimi. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O., Cannon L. E. Presecretory and cytoplasmic invertase polypeptides encoded by distinct mRNAs derived from the same structural gene differ by a signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):781–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. Distinct repressible mRNAs for cytoplasmic and secreted yeast invertase are encoded by a single gene. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Hamilton R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulation of basal and induced levels of the MEL1 transcript in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1238–1245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Tsunasawa S., Nakamura Y., Emi M., Sakiyama F., Matsubara K. Expression of the human salivary alpha-amylase gene in yeast and characterization of the secreted protein. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipper N., Sutherland M., Davies R. W., Kilburn D., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren A., Wong R. Secretion of a bacterial cellulase by yeast. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):958–960. doi: 10.1126/science.230.4728.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Bozzato R. P., Skipper N., Davies R. W., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the inducible MEL1 gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and its secreted product, alpha-galactosidase (melibiase). Gene. 1985;36(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Wood P. J. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.777-780.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hamilton R. W., Cano C. L., Hopper J. E. Disruption of regulatory gene GAL80 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on carbon-controlled regulation of the galactose/melibiose pathway genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1521–1527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the GAL3 gene in the expression of the galactose/melibiose regulon of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):229–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. K., Gerhard B., Guo Z. M., Kilburn D. G., Warren A. J., Miller R. C., Jr Characterization and structure of an endoglucanase gene cenA of Cellulomonas fimi. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]