Abstract
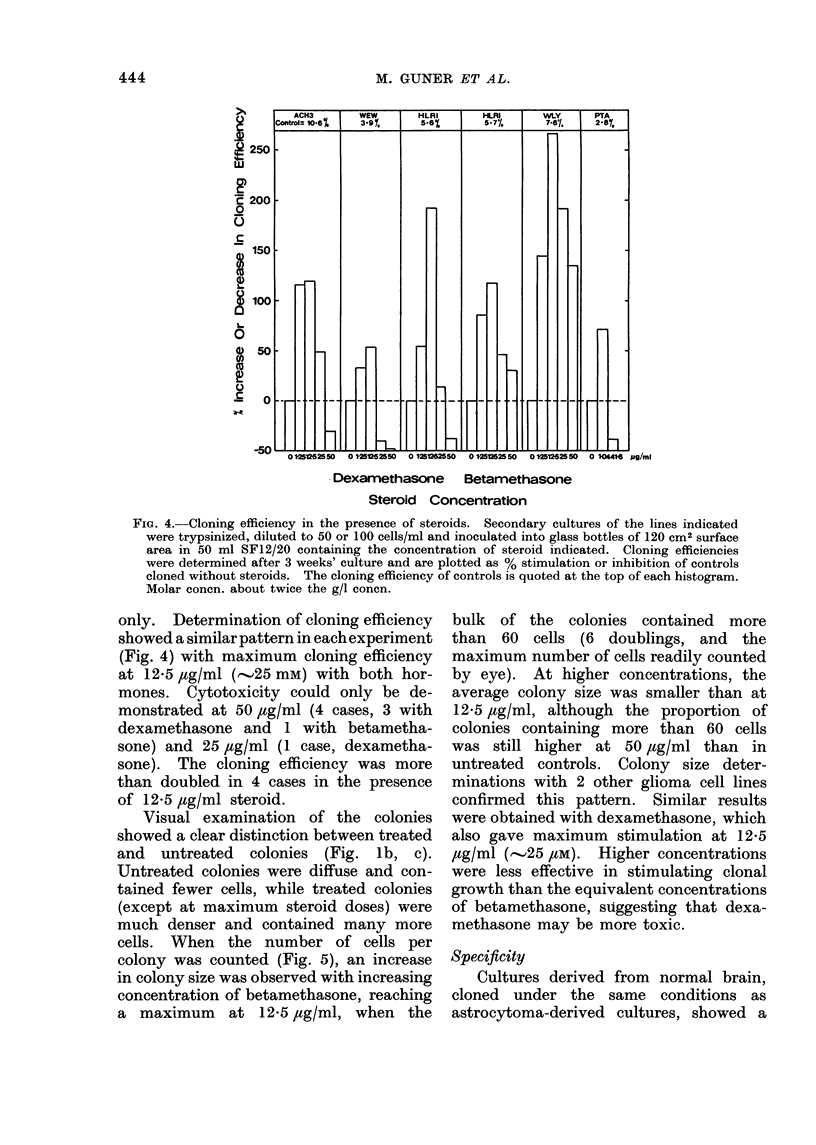
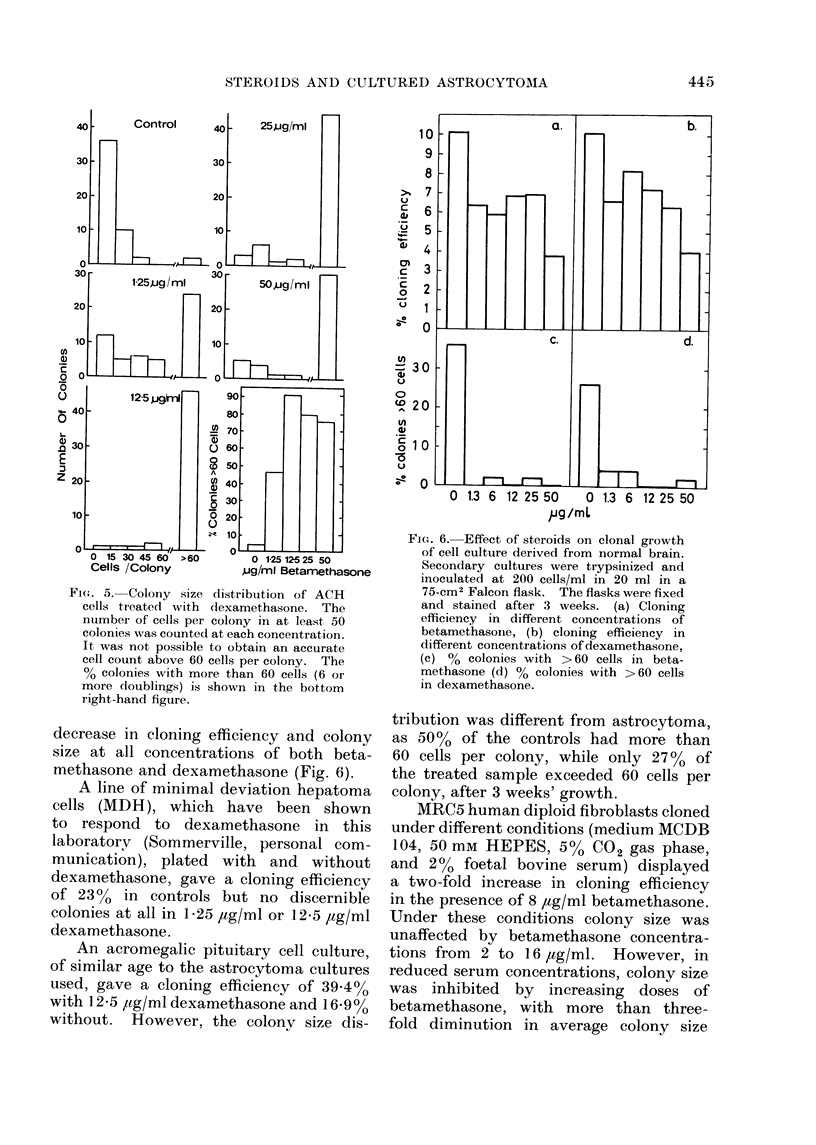
Cultures of human astrocytoma have been derived by collagenase digestion and are presumed, from their aneuploid karyotypes, to be predominantly neoplastic. Early passage cultures in proliferative phase have been cloned in the presence of dexamethasone and betamethasone, both commonly used in management of patients with brain tumours. These steroids raise both the cloning efficiency and the proliferative capacity of cells within each clone. Inhibition was detected only in very high steroid concentrations (25-50 microng/ml). Since these concentrations are unlikely to be attained in vivo it is concluded that anticipated physiological levels of these steroids enhance cell survival at low densities in culture. The significance of this in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker D. P., Young H. F., Vries J. K., Sakalas R. Monitoring in patients with brain tumors. Clin Neurosurg. 1975;22:364–388. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/22.cn_suppl_1.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei E., 3rd Combination cancer therapy: Presidential address. Cancer Res. 1972 Dec;32(12):2593–2607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freshney R. I. Tumour cells disaggregated in collagenase. Lancet. 1972 Sep 2;2(7775):488–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91885-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutin P. H. Corticosteroid therapy in patients with cerebral tumors: benefits, mechanisms, problems, practicalities. Semin Oncol. 1975 Mar;2(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura J., Kamijyo Y., Sunaga T., Nelson E. Tubular bodies in vascular endothelium of a cerebellar neoplasm. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):358–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B. B., Tomkins G. M., Stellwagen R. H. The regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis. Studies in HTC cells with inhibitors of ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6297–6302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson I., Bryden A. Mitomycin C treated cells as feeders. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Nov;69(1):240–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mealey J., Jr, Chen T. T., Schanz G. P. Effects of dexamethasone and methylprednisolone on cell cultures of human glioblastomas. J Neurosurg. 1971 Mar;34(3):324–334. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.34.3.0324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. HEPATOMAS IN TISSUE CULTURE COMPARED WITH ADAPTING LIVER IN VIVO. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 Apr;13:229–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLINGS S. R., MOON H. D. Morphologic and functional effects of hydrocortisone in tissue culture. Lab Invest. 1961 May-Jun;10:539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLINGTON J. S., MOON H. D. Effect of hydrocortisone on human cells in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:556–559. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. L., Shaumba B., Keller J. The effect of glucocorticosteroids on growth and metabolism of experimental glial tumors. J Neurosurg. 1969 Feb;30(2):140–145. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.30.2.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]