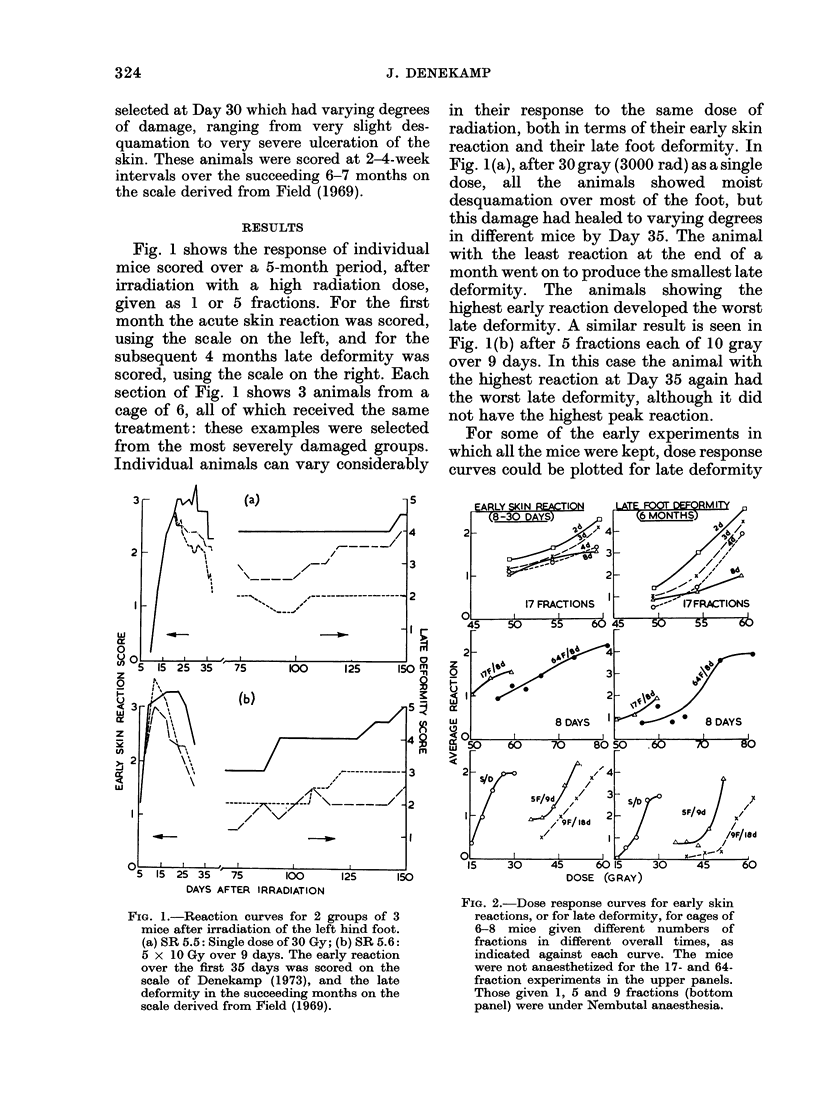
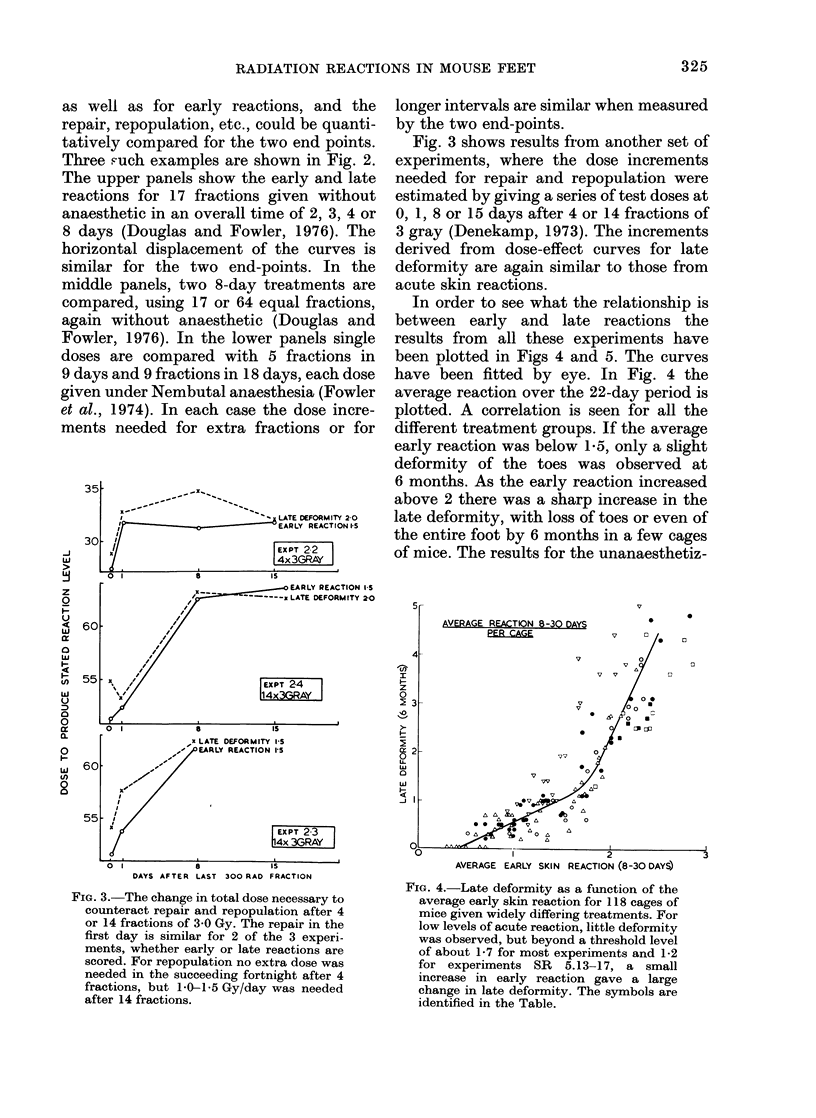
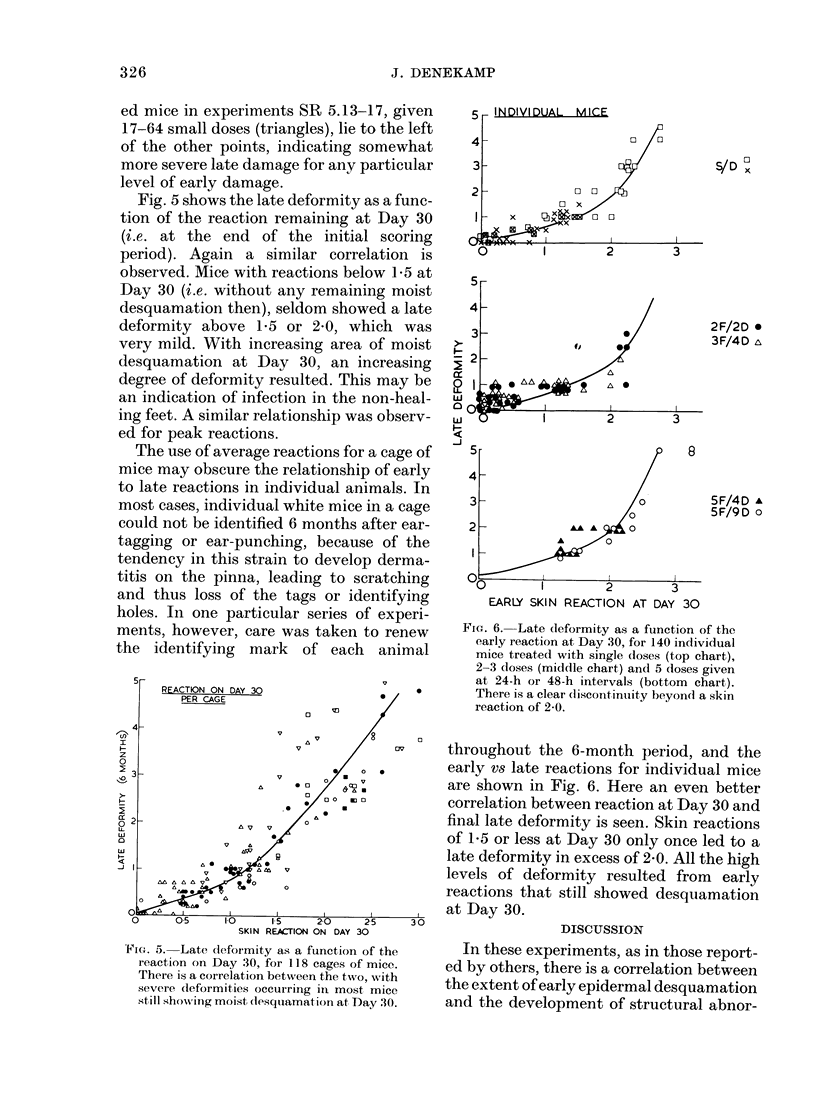
Abstract
The relationship between early and late radiation damage has been analysed by comparing the early skin reaction (desquamation in the first month) with the late foot deformity seen at 6 months, for mice from a wide variety of different fractionation experiments. A close correlation was observed between the early and late reactions in each experiment and the relationship was the same for all the experiments except for 17-64 fractions given over a short time. The fractionation schemes included single doses and 2-64 fractions, and the overall times ranged from 1 day to 6 months. This close correlation for such a wide variety of treatments suggests that the two end points are not necessarily independent responses of different tissues and that late damage in the mouse foot can result secondarily from depletion of the basal layer of the epidermis. Late foot deformity is therefore not a reliable model for the response of a slowly proliferating tissue.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. M., Probert J. C. Early and late radiation changes following a second course of irradiation. Radiology. 1975 Jun;115(3):711–716. doi: 10.1148/15.3.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denekamp J. Changes in the rate of repopulation during multifraction irradiation of mouse skin. Br J Radiol. 1973 May;46(545):381–387. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-545-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B., Law M. P. The relationship between early and late radiation damage in rodents' skin. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1976 Dec;30(6):557–564. doi: 10.1080/09553007614551411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. F., Denekamp J., Delapeyre C., Harris S. R., Sheldon P. W. Skin reactions in mice after multifraction x-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Mar;25(3):213–223. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsey S., Kutsutani Y., Field S. B. Damage to mouse lung with fractionated neutrons and x rays. Radiology. 1975 Jul;116(1):171–174. doi: 10.1148/116.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. E., Fischer J. J., Casey A. Dose-time relationships for skin reactions and structural damage in rat feet exposed to 250-kVp x rays. Radiology. 1975 May;115(2):465–470. doi: 10.1148/115.2.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wara W. M., Phillips T. L., Margolis L. W., Smith V. Radiation pneumonitis: a new approach to the derivation of time-dose factors. Cancer. 1973 Sep;32(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197309)32:3<547::aid-cncr2820320306>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kogel A. J., Barendsen G. W. Late effects of spinal cord irradiation with 300 kV X rays and 15 MeV neutrons. Br J Radiol. 1974 Jul;47(559):393–398. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-559-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


