Abstract
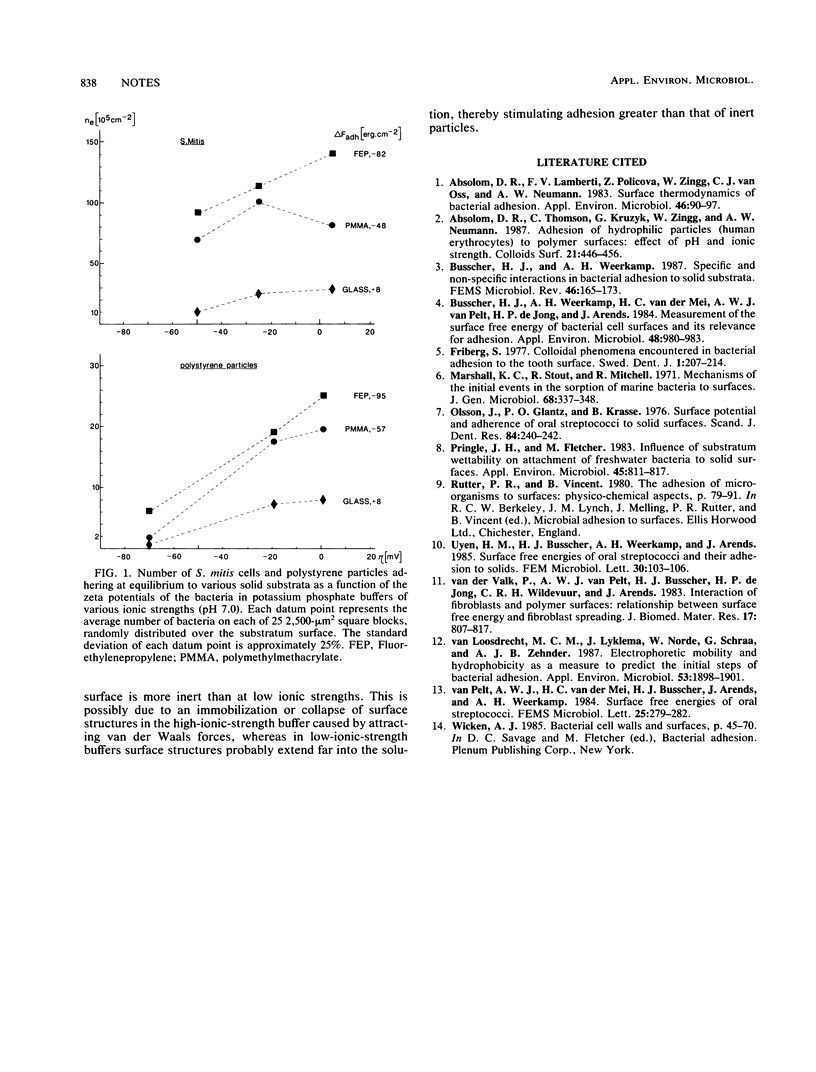
The adhesion of Streptococcus mitis to solid substrata from phosphate suspensions with various ionic strengths was studied and compared with the adhesion of polystyrene particles. At all ionic strengths, the interfacial free energy of adhesion governed the relative number of bacteria or polystyrene particles adhering at equilibrium, except that in a low-ionic-strength buffer, adhesion occurred less frequently because of increased electrostatic repulsion. Large differences between bacterial and polystyrene particle adhesion were observed, as indicated by the ratio of bacteria to polystyrene particles adhering, which decreased from 30 to 4 with a change from low to high ionic strength.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R., Lamberti F. V., Policova Z., Zingg W., van Oss C. J., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.90-97.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberg S. Colloidal phenomena encountered in the bacterial adhesion to the tooth surface. Swed Dent J. 1977;1(6):207–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Glantz P. O., Krasse B. Surface potential and adherence of oral streptococci to solid surfaces. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jul;84(4):240–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. H., Fletcher M. Influence of substratum wettability on attachment of freshwater bacteria to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):811–817. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.811-817.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1898–1901. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1898-1901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., van Pelt A. W., Busscher H. J., de Jong H. P., Wildevuur C. R., Arends J. Interaction of fibroblasts and polymer surfaces: relationship between surface free energy and fibroblast spreading. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983 Sep;17(5):807–817. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820170508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


