Abstract
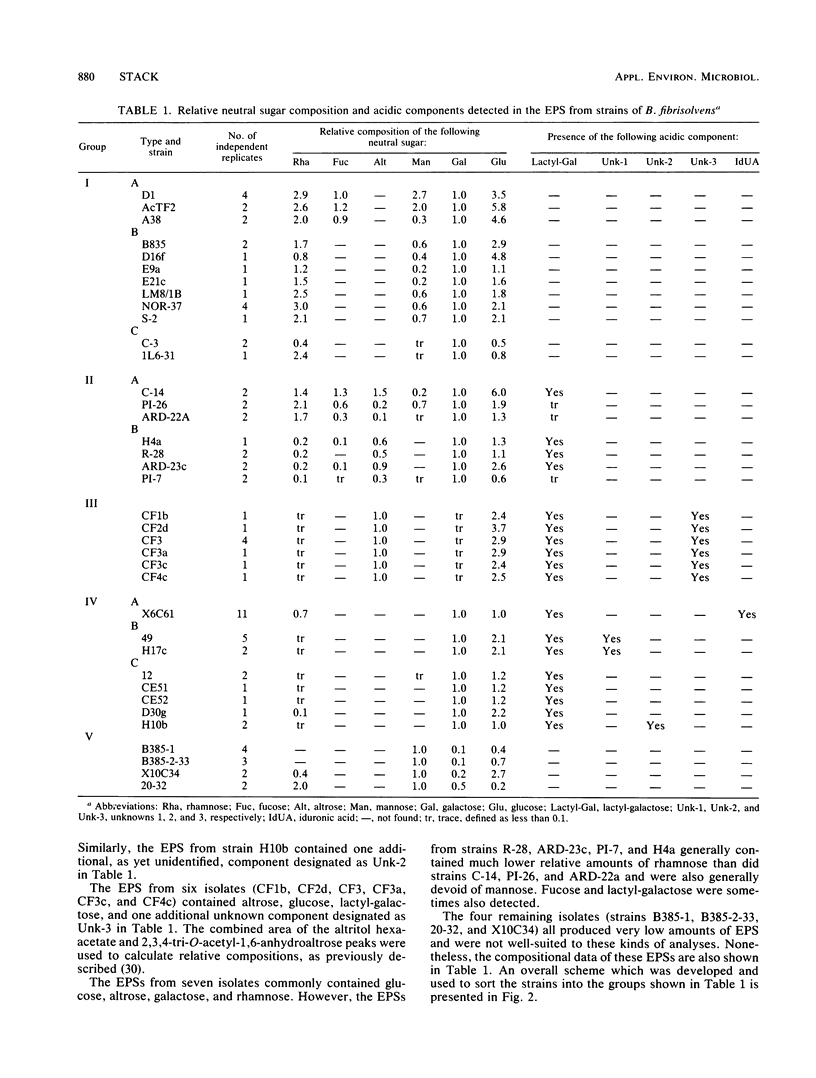
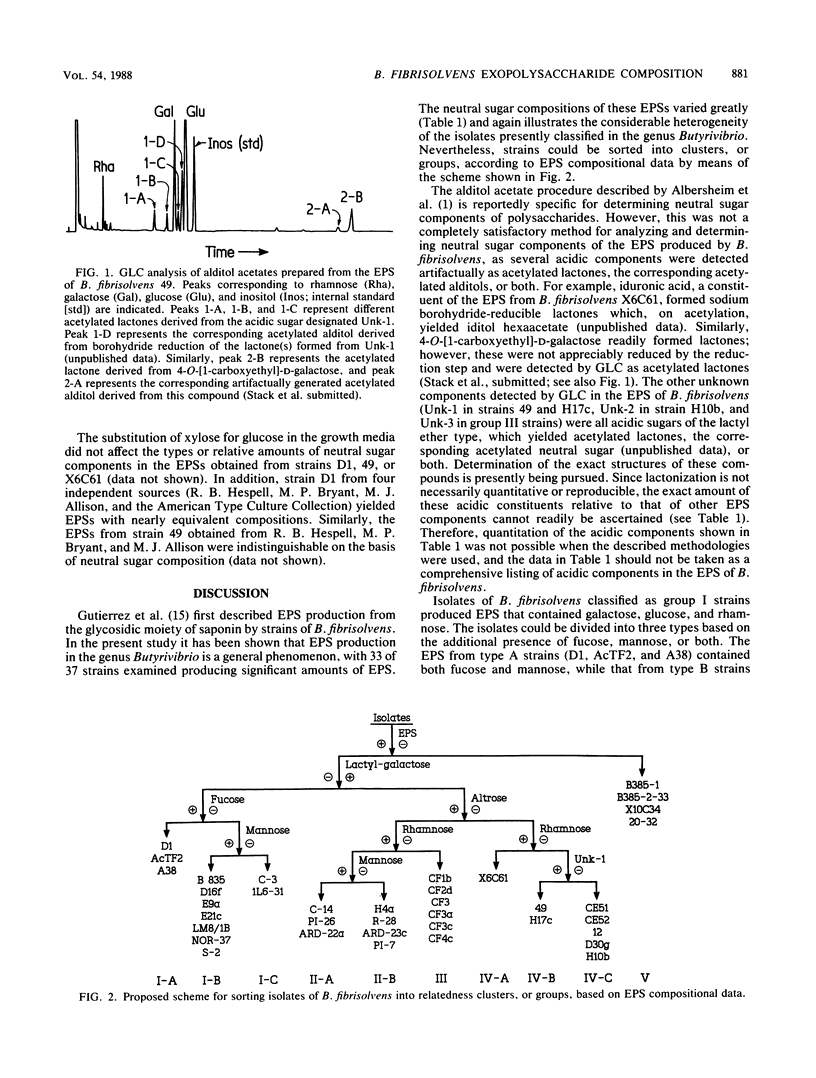
The extracellular polysaccharides (EPSs) produced by 37 isolates presently classified as Butyrivibrio species (or more specifically as Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens) were purified from glucose-grown cultures. The neutral sugar compositions of these EPSs were determined by both thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatographic techniques. Results showed that while the neutral sugar composition of the EPS was constant for a given strain, it varied considerably between strains. In addition, several acidic components in the EPS, of both known and unknown structure, were detected artifactually as acetylated lactones, the acetylated alditols derived from these lactone(s), or both. Two novel components, L-altrose and the acidic sugar 4-O-[1-carboxyethyl]-D-galactose, were common constituents of the EPS from some strains of B. fibrisolvens. These and other EPS compositional features were used to sort isolates of B. fibrisolvens into groups which may have taxonomic significance. A scheme for sorting isolates into these groups, and the relative relationships between groups, is proposed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. The characteristics of strains of Selenomonas isolated from bovine rumen contents. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):162–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.162-167.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnicki-Garcia S. Cell wall chemistry, morphogenesis, and taxonomy of fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Ultrastructure of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens: a gram-positive bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1506-1512.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Jones G. A., Simpson F. J., Bryant M. P. Isolation and identification of rumen bacteria capable of anaerobic rutin degradation. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1365–1371. doi: 10.1139/m69-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotta M. A., Hespell R. B. Proteolytic activity of the ruminal bacterium Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.51-58.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Characterization of several bovine rumen bacteria isolated with a xylan medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1724–1729. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1724-1729.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Grubb J. A. Characterization of the predominant bacteria occurring in the rumen of goats (Capra hircus). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1030–1036. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1030-1036.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Pectin-fermenting bacteria isolated from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.189-196.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULGHUM R. S., MOORE W. E. ISOLATION, ENUMERATION, AND CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTEOLYTIC RUMINAL BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:808–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.808-815.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTIERREZ J., DAVIS R. E., LINDAHL I. L. Characteristics of saponin-utilizing bacteria from the rumen of cattle. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Sep;7:304–308. doi: 10.1128/am.7.5.304-308.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood G., Dawson R. M. Characteristics of a lipolytic and fatty acid-requiring Butyrivibrio sp. isolated from the ovine rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning P. A. Examination of methods for enumerating hemicellulose-utilizing bacteria in the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):13–17. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.13-17.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Dehority B. A. Microbiology and ration digestibility in the hindgut of the ovine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.356-363.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGHERITA S. S., HUNGATE R. E. SEROLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF BUTYRIVIBRIO FROM THE BOVINE RUMEN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:855–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.855-860.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGHERITA S. S., HUNGATE R. E., STORZ H. VARIATION IN RUMEN BUTYRIVIBRIO STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1304–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1304-1308.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roché C., Albertyn H., van Gylswyk N. O., Kistner A. The growth response of cellulolytic acetate-utilizing and acetate-producing butyruvibrios to volatile fatty acids and other nutrients. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shane B. S., Gouws L., Kistner A. Cellulolytic bacteria occurring in the rumen of sheep conditioned to low-protein teff hay. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):445–457. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. E., Brock J. H., Phillips B. A. Glycerol teichoic acid as an antigenic determinant in a Gram-negative bacterium Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jun;88(2):355–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-2-355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. E., Reiter B. Common antigenic determinant in a rumen organism and in salmonellae containing the antigen O4. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):613–617. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.613-617.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Biosynthesis and composition of gram-negative bacterial extracellular and wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:243–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gylswyk N. O., Roché C. E. Characteristics of ruminococcus and cellulolytic butyrivibrio species from the rumens of sheep fed differently supplemented teff (Eragrostis tef) hay diets. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;64(1):11–17. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


