Abstract
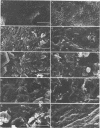
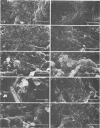
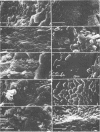
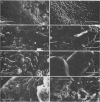
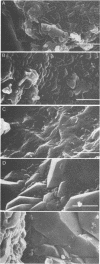
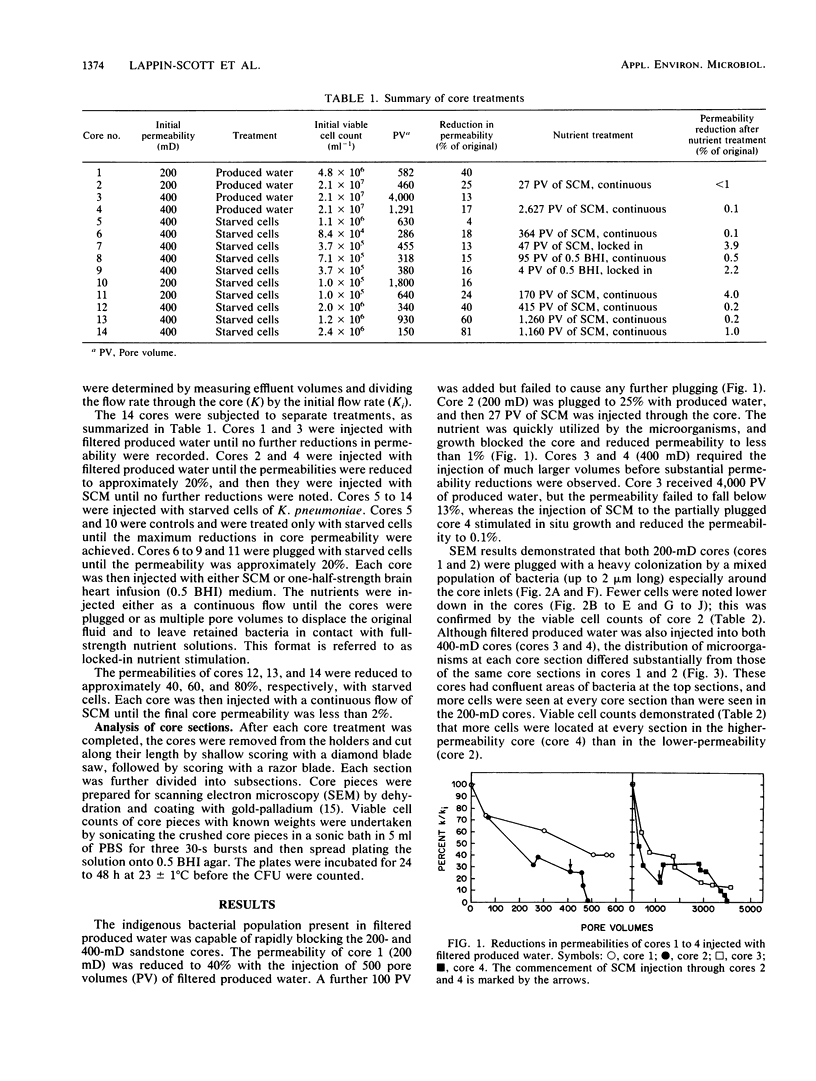
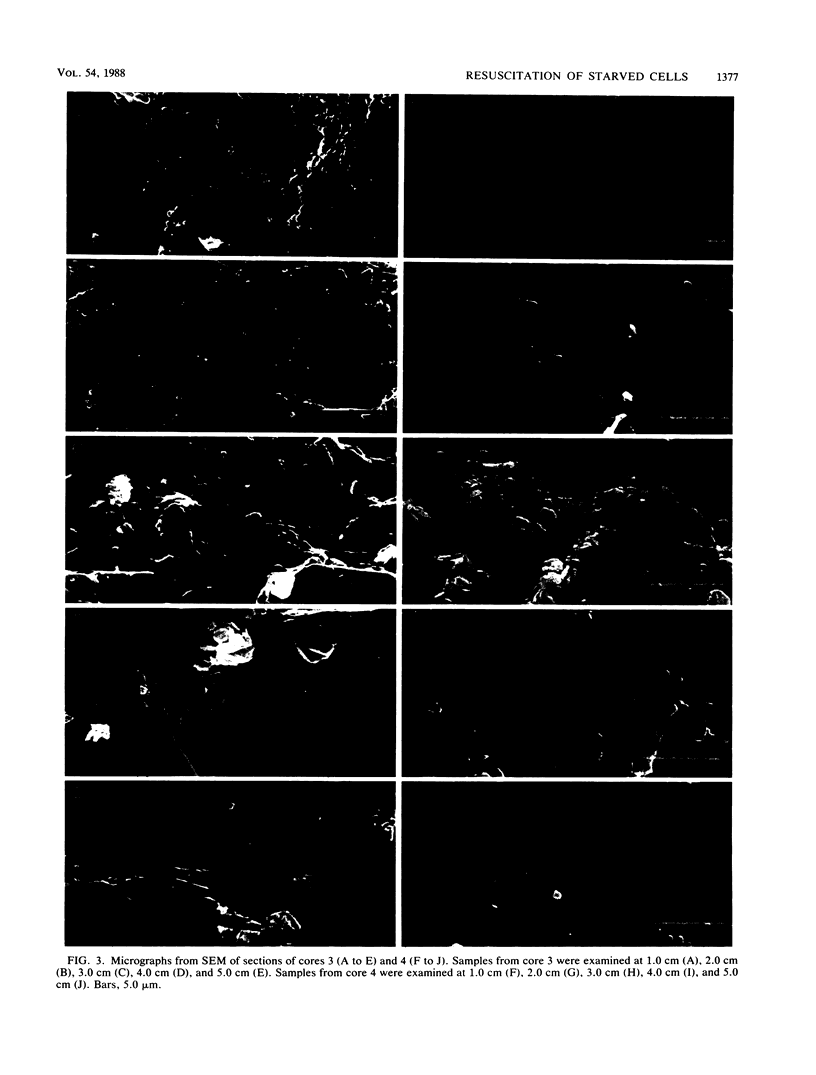
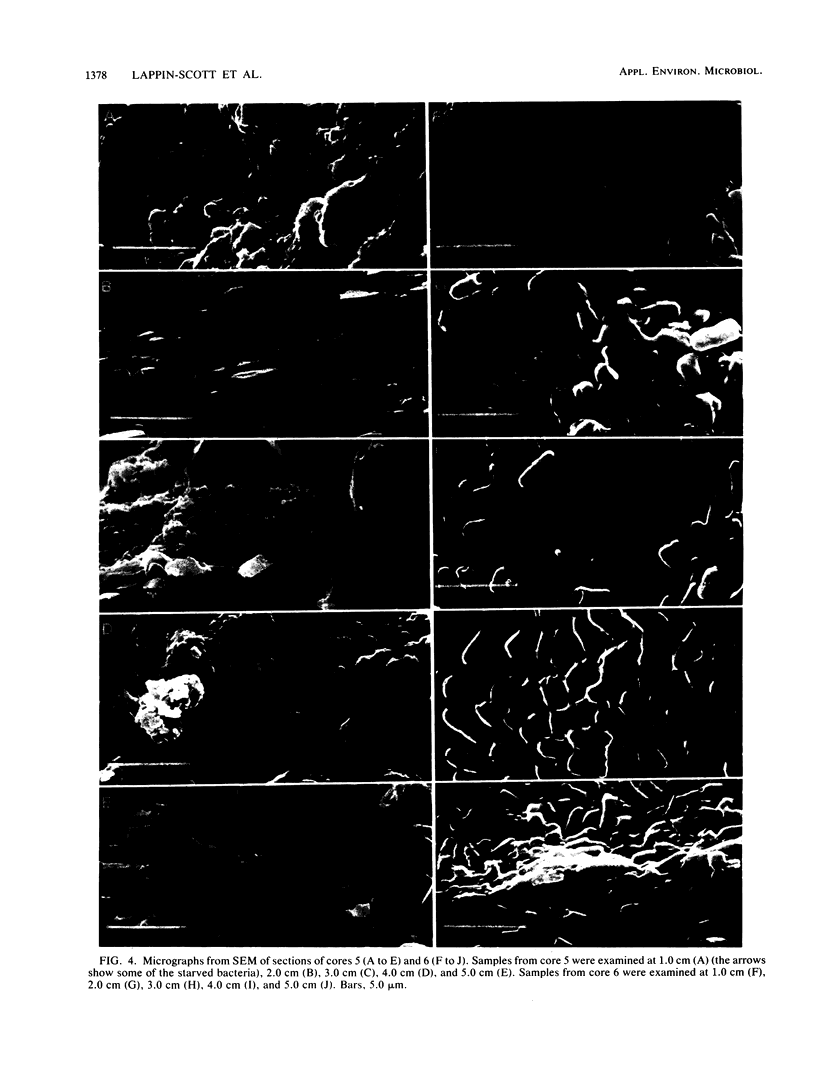
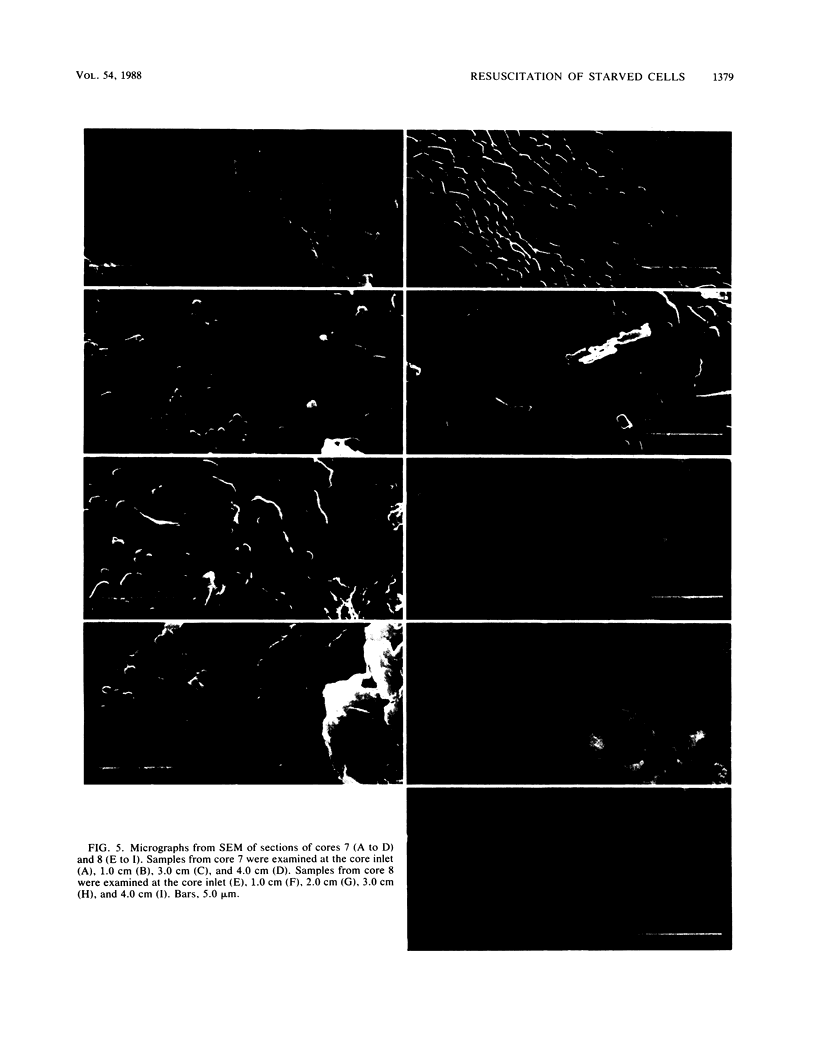
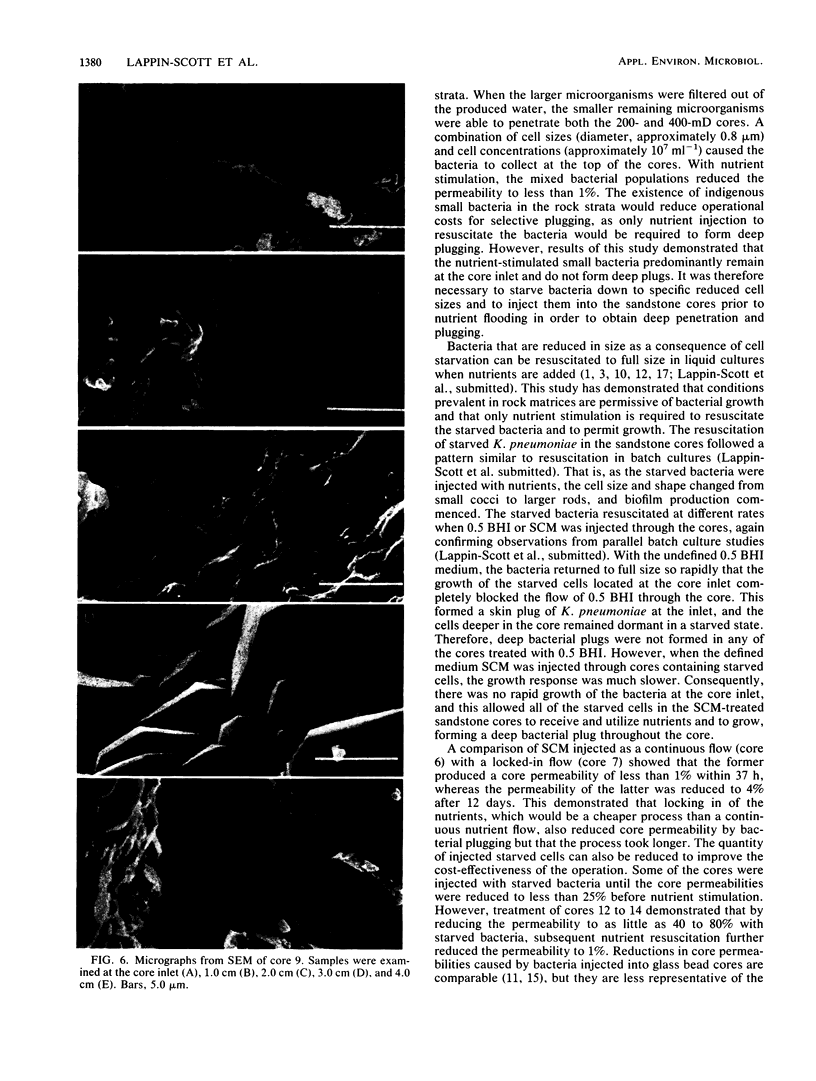
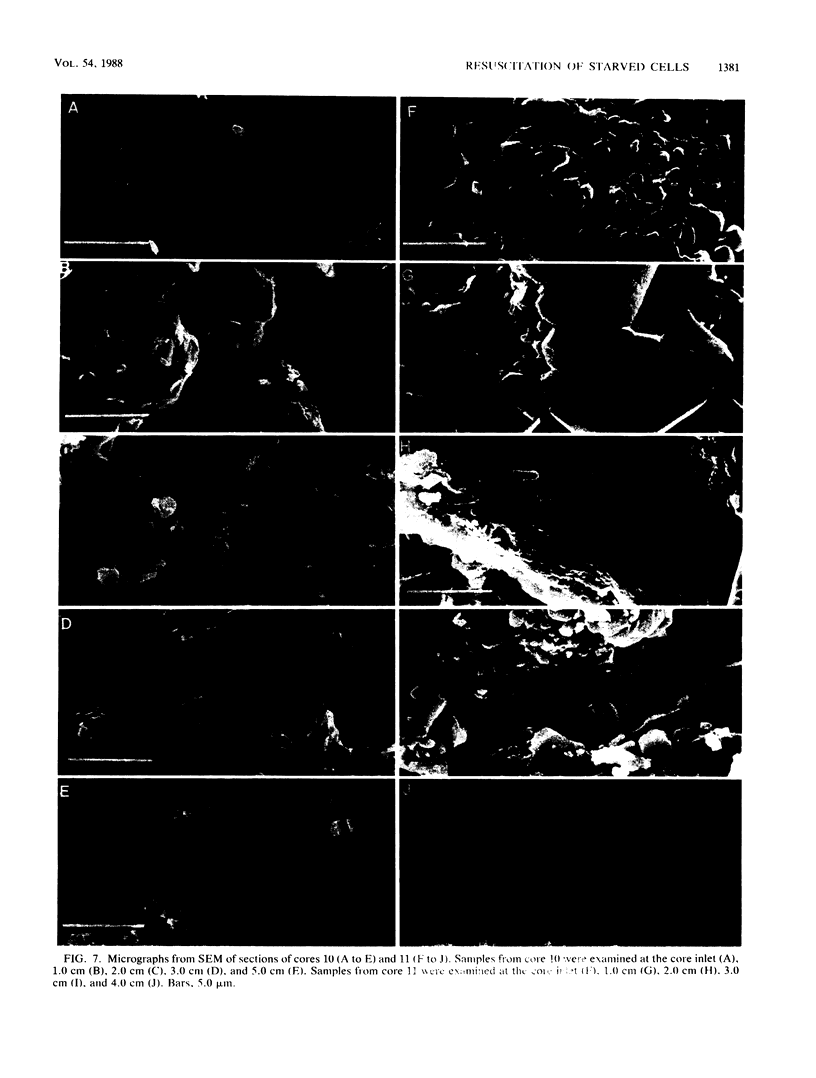
Klebsiella pneumoniae, which was reduced in size (0.25 by 0.5 μm) by carbon deprivation, was injected into a series of sandstone cores and subjected to separate treatments. Scanning electron microscopy of 400-mD cores showed these small starved cells in nearly every core section. The cells were a mixture of small rods and cocci with little or no biofilm production. Continuous or dose stimulation with sodium citrate allowed the cells to grow throughout the sandstone and completely plug the length of the core. The resuscitated cells were larger than the starved cells (up to 1.7 μm) and were encased in glycocalyx. Scanning electron microscopic results of resuscitation in situ with half-strength brain heart infusion broth showed that a shallow “skin” plug of cells formed at the core inlet and that fewer cells were located in the lower sections. Starved cells also penetrated 200-mD cores and were successfully resuscitated in situ with sodium citrate, so that the entire core was plugged. Nutrient resuscitation of injected starved cells to produce full-size cells which grow and block the rock pores may be successfully applied to selective plugging and may effectively increase oil recovery.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Pauling C., Morita R. Y. Recovery from nutrient starvation by a marine Vibrio sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1685–1690. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1685-1690.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae H. C., Cota-Robles E. H., Casida L. E. Microflora of soil as viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):637–648. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.637-648.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. M., Singleton F. L., Hood M. A. Effects of nutrient deprivation on Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):930–940. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.930-940.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASIDA L. E., Jr ABUNDANT MICROORGANISM IN SOIL. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:327–334. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.327-334.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonell M. T., Hood M. A. Isolation and characterization of ultramicrobacteria from a gulf coast estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):566–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.566-571.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod F. A., Lappin-Scott H. M., Costerton J. W. Plugging of a model rock system by using starved bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1365–1372. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1365-1372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky J. A., Morita R. Y. Morphological characterization of small cells resulting from nutrient starvation of a psychrophilic marine vibrio. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):617–622. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.617-622.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. C., Bramhill B., Wardlaw N. C., Costerton J. W. Bacterial fouling in a model core system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.693-701.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyndham R. C., Costerton J. W. Heterotrophic potentials and hydrocarbon biodegradation potentials of sediment microorganisms within the athabasca oil sands deposit. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):783–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.783-790.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]