Abstract
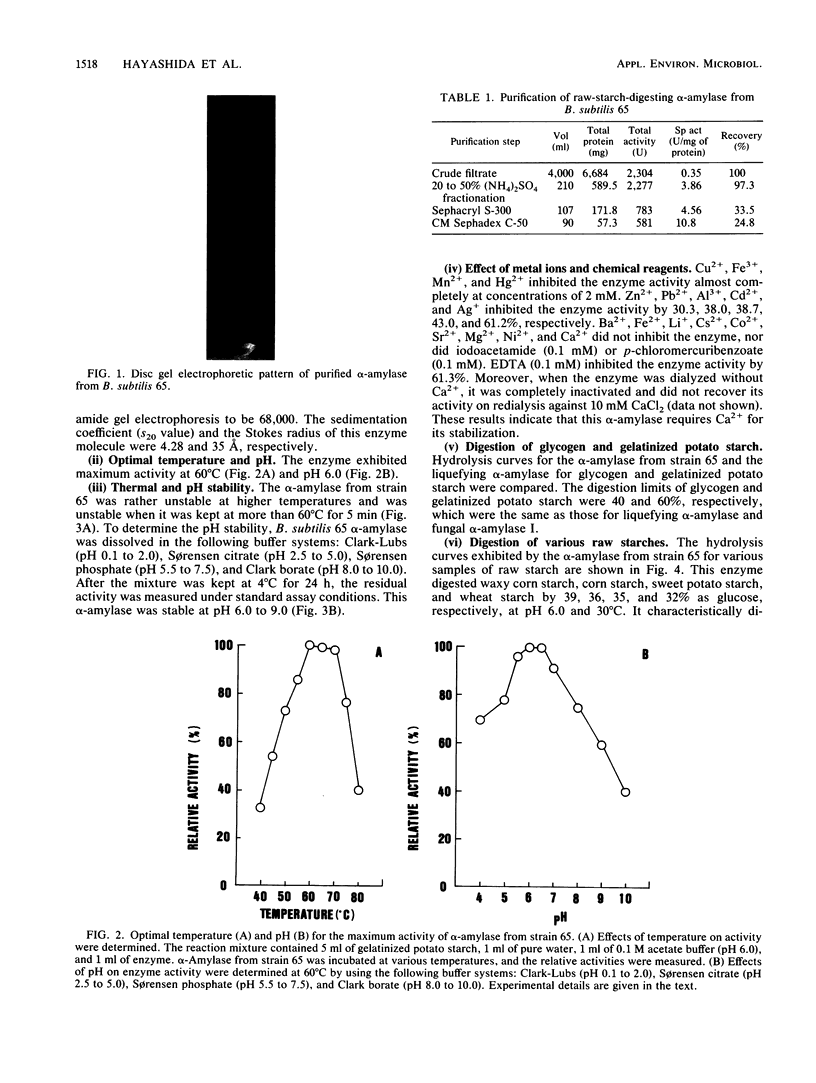
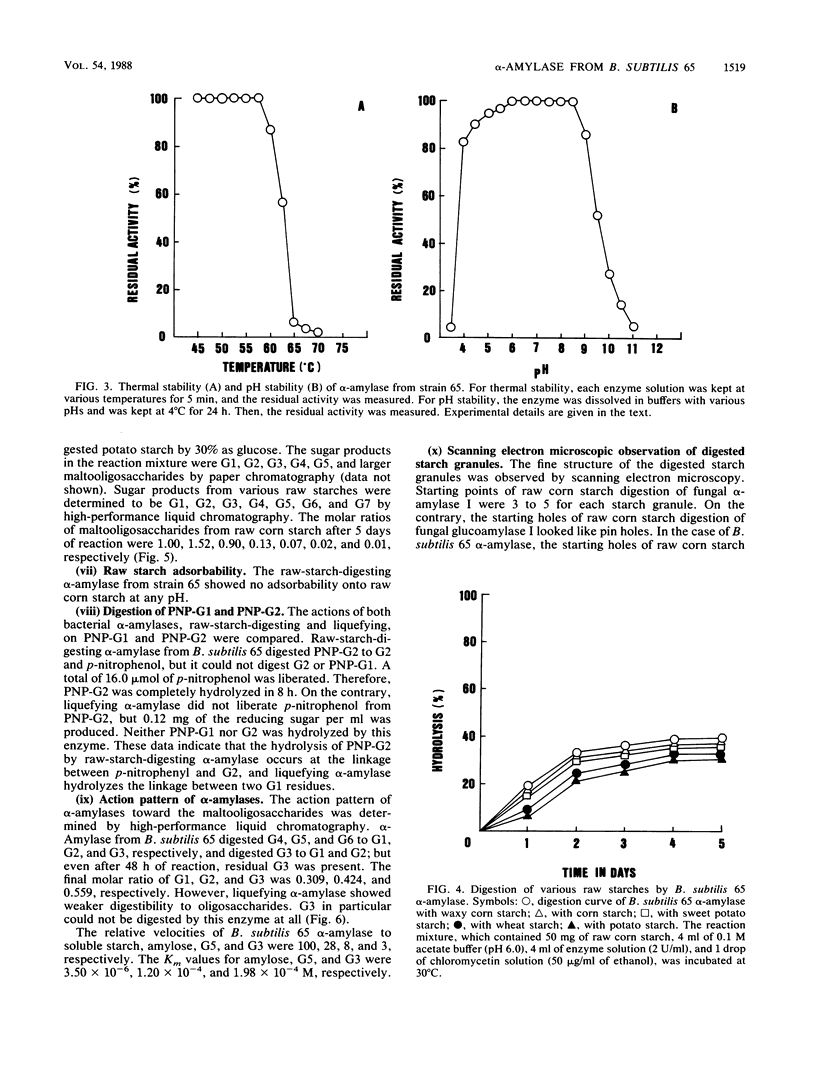
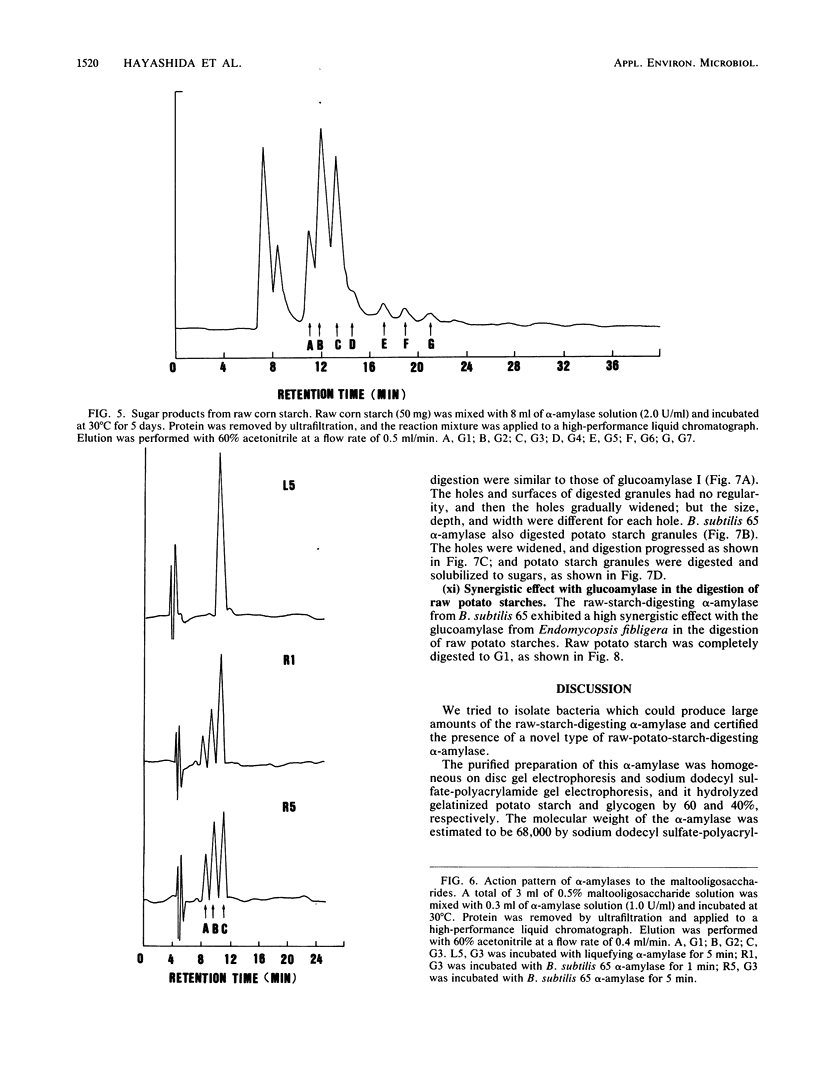
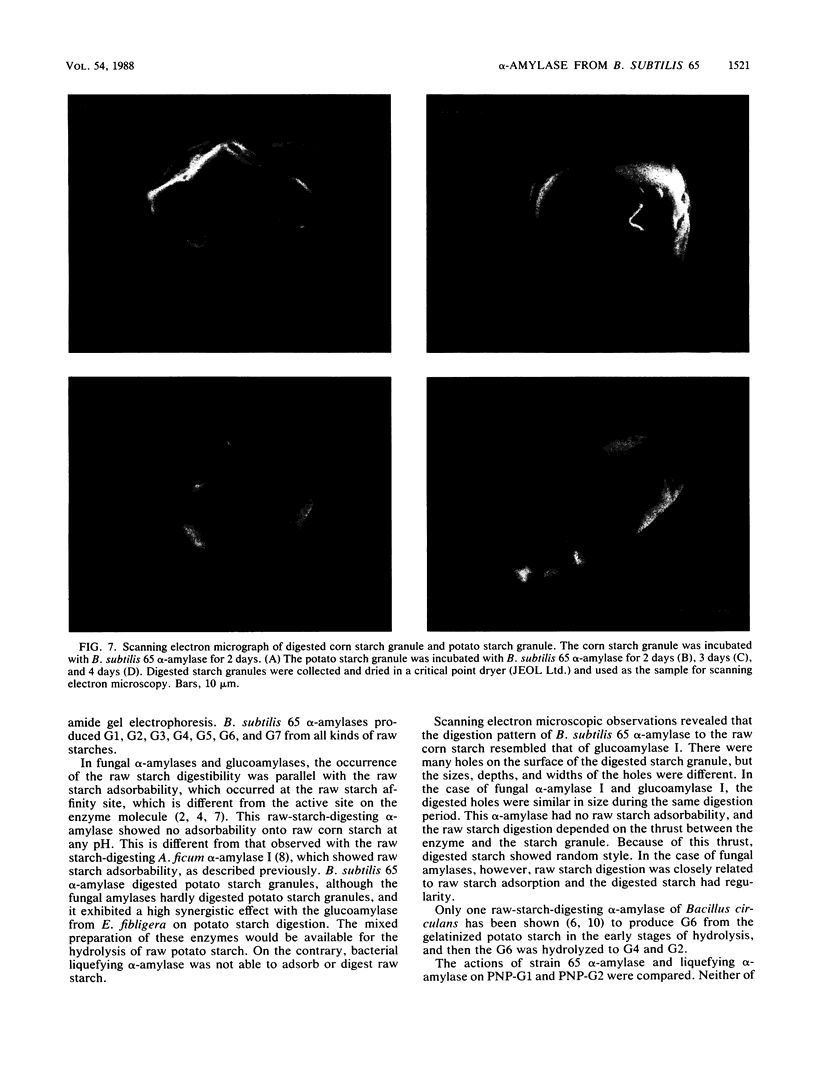
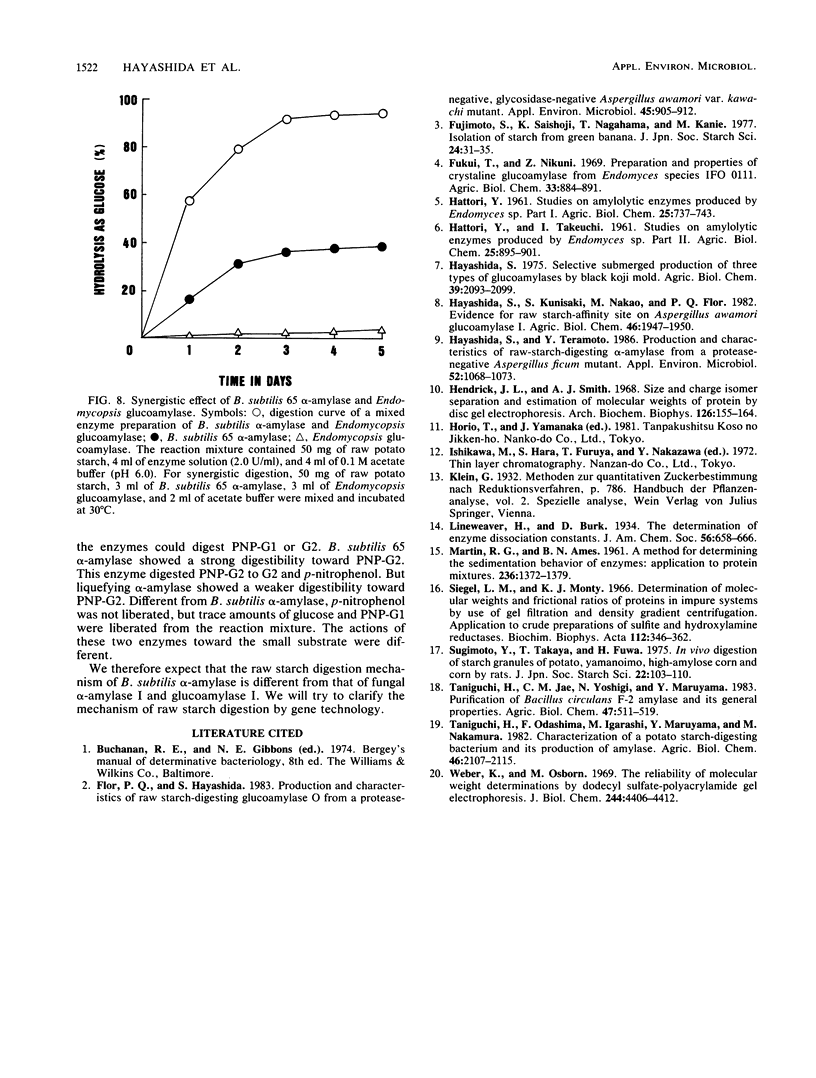
A newly isolated bacterium, identified as Bacillus subtilis 65, was found to produce raw-starch-digesting α-amylase. The electrophoretically homogeneous preparation of enzyme (molecular weight, 68,000) digested and solubilized raw corn starch to glucose and maltose with small amounts of maltooligosaccharides ranging from maltotriose to maltoheptaose. This enzyme was different from other amylases and could digest raw potato starch almost as fast as it could corn starch, but it showed no adsorbability onto any kind of raw starch at any pH. The mixed preparation with Endomycopsis glucoamylase synergistically digested raw potato starch to glucose at 30°C. The raw-potato-starch-digesting α-amylase showed strong digestibility to small substrates, which hydrolyzed maltotriose to maltose and glucose, and hydrolyzed p-nitrophenyl maltoside to p-nitrophenol and maltose, which is different from the capability of bacterial liquefying α-amylase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayashida S., Teramoto Y. Production and Characteristics of Raw-Starch-Digesting alpha-Amylase from a Protease-Negative Aspergillus ficum Mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1068-1073.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]