Abstract
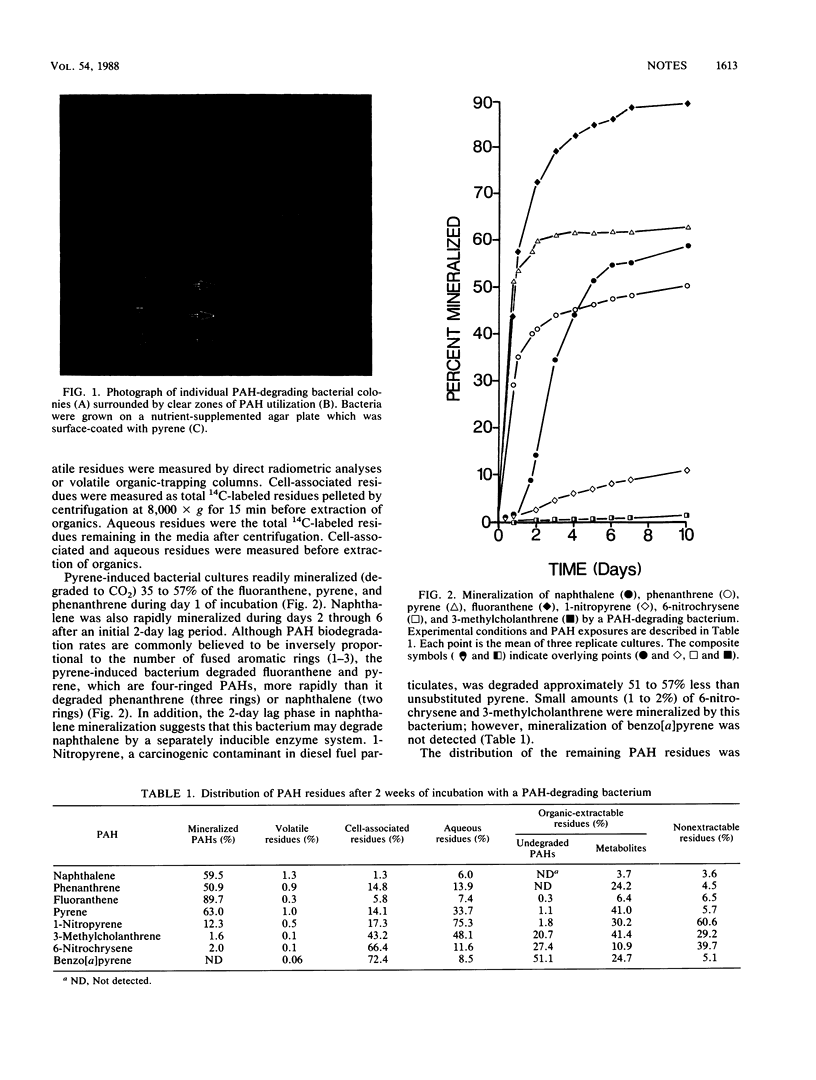
Microbiological analyses of sediments chronically exposed to petrogenic hydrocarbons resulted in the isolation of a gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium which mineralized naphthalene (59.5% of the original amount), phenanthrene (50.9%), fluoranthene (89.7%), pyrene (63.0%), 1-nitropyrene (12.3%), 3-methylcholanthrene (1.6%), and 6-nitrochrysene (2.0%) to carbon dioxide when grown for 2 weeks in pure culture with organic nutrients. The bacterium tolerated salt concentrations up to 4% and grew well at 24 to 30 degrees C. The use of this bacterium may be an attractive alternative to existing physicochemical methods for the remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerniglia C. E. Microbial metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1984;30:31–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitkamp M. A., Freeman J. P., Cerniglia C. E. Naphthalene biodegradation in environmental microcosms: estimates of degradation rates and characterization of metabolites. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.129-136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Searches for ultimate chemical carcinogens and their reactions with cellular macromolecules. Cancer. 1981 May 15;47(10):2327–2345. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810515)47:10<2327::aid-cncr2820471003>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]