Abstract
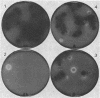
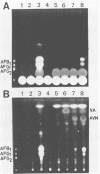
A convenient procedure consisting of UV photography (K. Yabe, Y. Ando, M. Ito, and N. Terakado, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53:230-234, 1987) and a tip culture method has been devised for the isolation and characterization of Aspergillus parasiticus mutants relating to aflatoxin production. With the latter procedure, the production of aflatoxins excreted into the culture medium and precursors in the mycelium were easily measured quantitatively or semiquantitatively. A total of 38 mutants in which the aflatoxigenicity was decreased or lost were obtained by UV radiation; 3 were found to be blocked mutants, which accumulated the aflatoxin precursors versicolorin A or averantin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. W., Christensen S. B. New perspectives on aflatoxin biosynthesis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:53–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. W., Goldblatt L. A. The isolation of mutants of Aspergillus flavus and A.parasiticus with altered aflatoxin producing ability. Sabouraudia. 1973 Nov;11(3):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. W., Lee L. S., Shoss S. M., Boudreaux G. H. Identification of averantin as an aflatoxin B1 precursor: placement in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):835–839. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.835-839.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkinshaw J. H., Roberts J. C., Roffey P. Studies in mycological chemistry. XIX. "Product B" (averantin) [1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2-(1-hydroxyhexyl)anthraquinone], a pigment from Aspergillus versicolor (Vuillemin) Tiraboschi. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;9:855–857. doi: 10.1039/j39660000855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. D., Diener U. L., Eldridge D. W. Production of aflatoxins B1 and G1 by Aspergillus flavus in a semisynthetic medium. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):378–380. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.378-380.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. D., Diener U. L. Growth and aflatoxin production by Aspergillus parasiticus from various carbon sources. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):158–159. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.158-159.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detroy R. W., Freer S., Ciegler A. Aflatoxin and anthraquinone biosynthesis by nitrosoguanidine-derived mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1373–1378. doi: 10.1139/m73-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donkersloot J. A., Mateles R. I., Yang S. S. Isolation of averufin from a mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus impaired in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaich L. L., Papa K. E. Aflatoxins in mutants of Aspergillus flavus. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Apr 30;52(3):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02198747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Bennett J. W., Goldblatt L. A., Lundin R. E. Norsolorinic acid from a mutant strain of Aspergillus parasiticus. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1971 Feb;48(2):93–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02635696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillard H. S., Hanlin R. T., Lillard D. A. Aflatoxigenic isolates of Aspergillus flavus from pecans. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.128-130.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Gupta S. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):822–855. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.822-855.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. P., Bhatnagar D., Lee L. S. Averufanin is an aflatoxin B1 precursor between averantin and averufin in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):14–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.14-16.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons W. A., Jr, Cucullu A. F., Franz A. O., Jr, Goldblatt L. A. Improved objective fluorodensitometric determination of aflatoxins in cottonseed products. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1968 Oct;45(10):694–699. doi: 10.1007/BF02541260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway: elucidation by using blocked mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Biosynthetic relationship among aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2101–2106. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2101-2106.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Ito M., Terakado N. Simple method for screening aflatoxin-producing molds by UV photography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.230-234.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]