Abstract
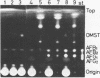
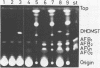
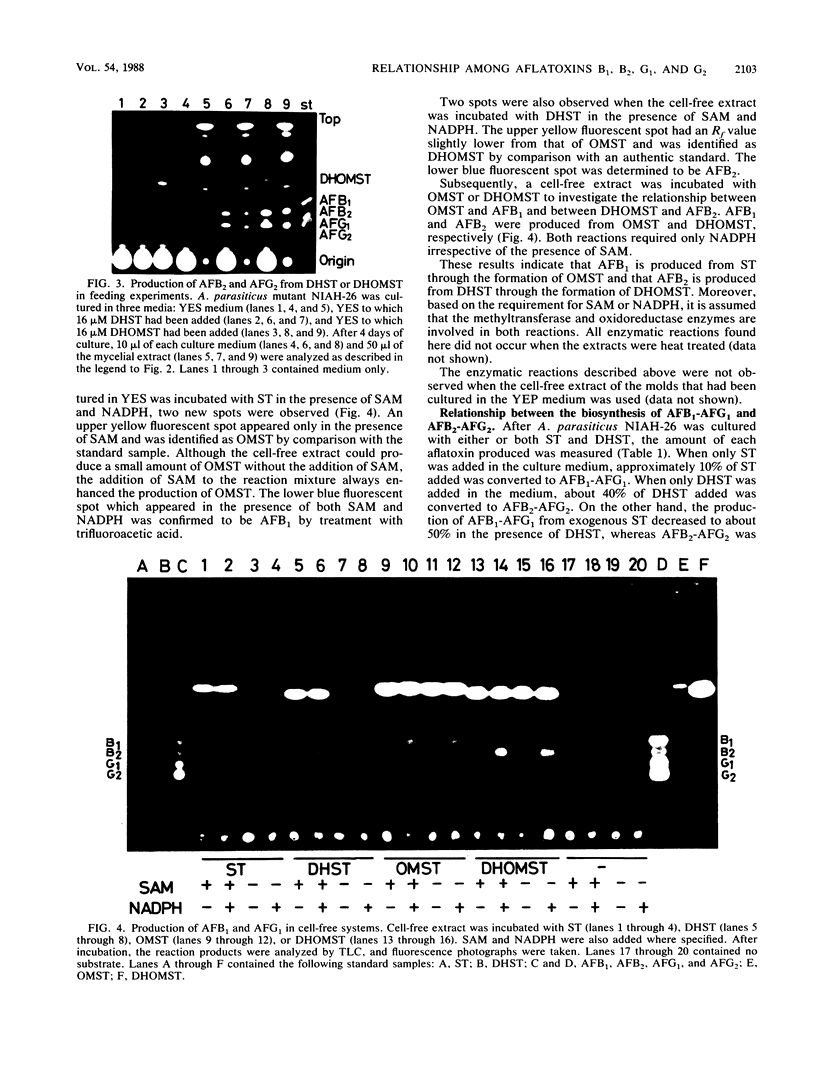
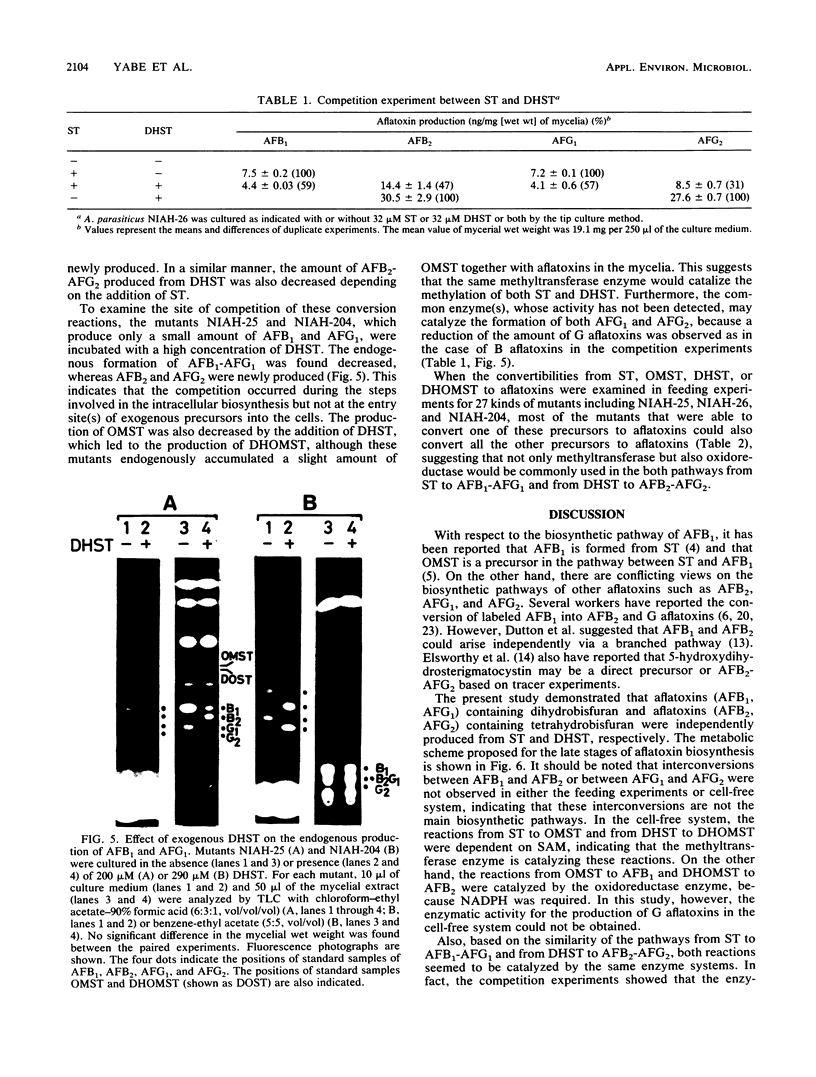
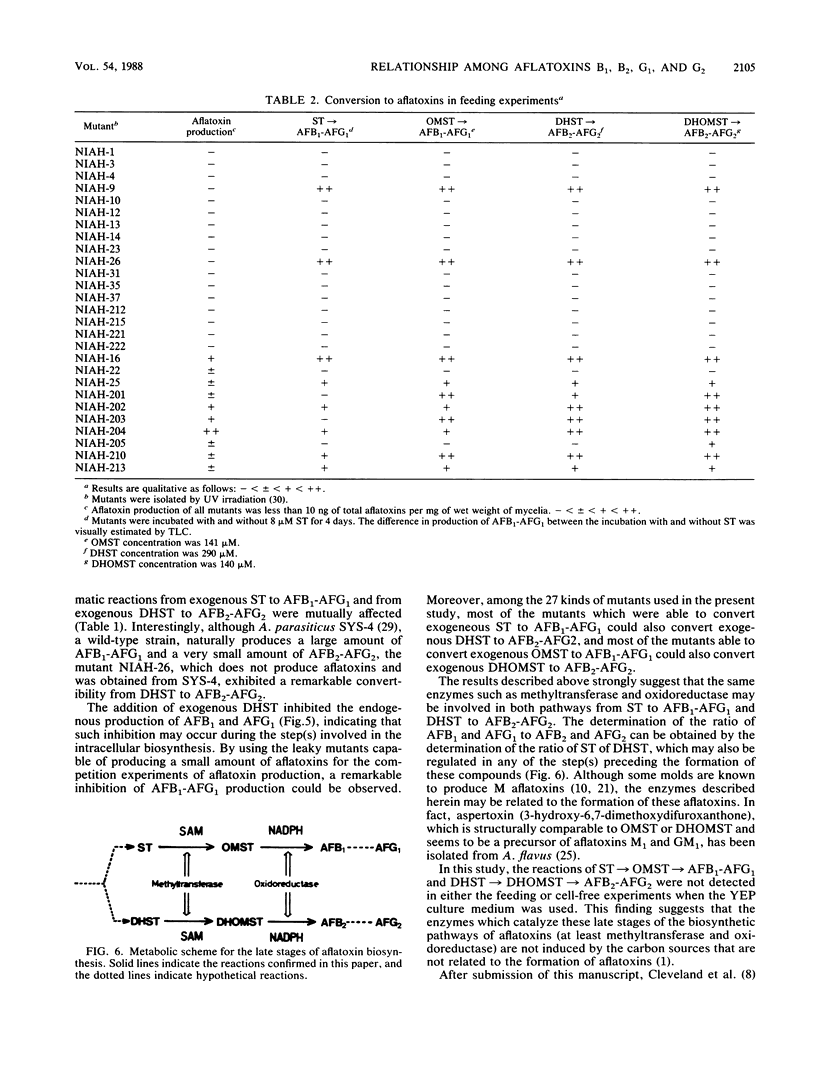
Aspergillus parasiticus NIAH-26, a UV-irradiated mutant of A. parasiticus SYS-4 (NRRL 2999), produces neither aflatoxins nor precursors. When sterigmatocystin (ST) or O-methylsterigmatocystin was fed to this mutant in YES medium, aflatoxins B1 (AFB1) and G1 (AFG1) were produced. When dihydrosterigmatocystin (DHST) or dihydro-O-methylsterigmatocystin was fed to this mold, aflatoxins B2 (AFB2) and G2 (AFG2) were produced. The reactions from ST to AFB1 and DHST to AFB2 were also observed in the cell-free system and were catalyzed stepwise by the methyltransferase and oxidoreductase enzymes. In the feeding experiments of strain NIAH-26, the convertibility from ST to AFB1-AFG1 was found to be remarkably suppressed by the coexistence of DHST in the medium, and the convertibility from DHST to AFB2-AFG2 was also suppressed by the presence of ST. When some other mutants which endogenously produce a small amount of aflatoxins (mainly AFB1 and AFG1) were cultured with DHST, the amounts of AFB1 and AFG1 produced were significantly decreased, whereas AFB2 and AFG2 were newly produced. In similar feeding experiments in which 27 kinds of mutants including these mutants were used, most of the mutants which were able to convert exogenous ST to AFB1-AFG1 were also found to convert exogenous DHST to AFB2-AFG2. These results suggest that the same enzymes may be involved in the both biosynthetic pathways from ST to AFB1-AFG1 and DHST to AFB2-AFG2. The reactions described herein were not observed when the molds had been cultured in the YEP medium.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. The use of cell free extracts derived from fungal protoplasts in the study of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Experientia. 1979 Jan 15;35(1):21–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01917850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. W., Christensen S. B. New perspectives on aflatoxin biosynthesis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:53–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., McCormick S. P., Lee L. S., Hill R. A. Identification of O-methylsterigmatocystin as an aflatoxin B1 and G1 precursor in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1028-1033.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biollaz M., Büchi G., Milne G. The biosynthesis of the aflatoxins. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Feb 25;92(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1021/ja00707a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland T. E., Bhatnagar D., Foell C. J., McCormick S. P. Conversion of a new metabolite to aflatoxin B2 by Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2804–2807. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2804-2807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland T. E., Lax A. R., Lee L. S., Bhatnagar D. Appearance of enzyme activities catalyzing conversion of sterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B1 in late-growth-phase Aspergillus parasiticus cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1711–1713. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1711-1713.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F., Ehrlich K., Bennett J. W. Biosynthetic relationship among aflatoxins B1, B2, M1, and M2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1392–1395. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1392-1395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Bennett J. W., Dunn J. J., Fine J. S. Growth of high aflatoxin B2 mutants on defined and complex media and with ethoxyquin. Microbios. 1982;35(139):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Gupta S. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):822–855. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.822-855.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Metabolism of aflatoxins B1 and G1 by Aspergillus parasiticus. Experientia. 1973 Oct 15;29(10):1210–1211. doi: 10.1007/BF01935075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. P., Bhatnagar D., Lee L. S. Averufanin is an aflatoxin B1 precursor between averantin and averufin in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):14–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.14-16.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodricks J. V., Lustig E., Campbell A. D., Stoloff L. Aspertoxin, a hydroxy derivative of O-methylsterigmatocystin from aflatoxin-producing cultures of Aspergillus flavus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968 May;(25):2975–2978. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)89626-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic conversion of sterigmatocystin into aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):743–745. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.743-745.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan N. C., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic formation of the bisfuran structure in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):109–112. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.109-112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Ito M., Terakado N. Simple method for screening aflatoxin-producing molds by UV photography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.230-234.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura H., Ando Y., Terakado N., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T. Isolation and characterization of Aspergillus parasiticus mutants with impaired aflatoxin production by a novel tip culture method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2096–2100. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2096-2100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]