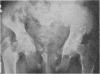
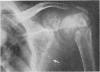
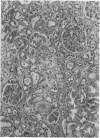
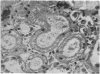
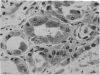
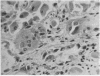
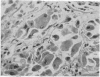
Full text
PDF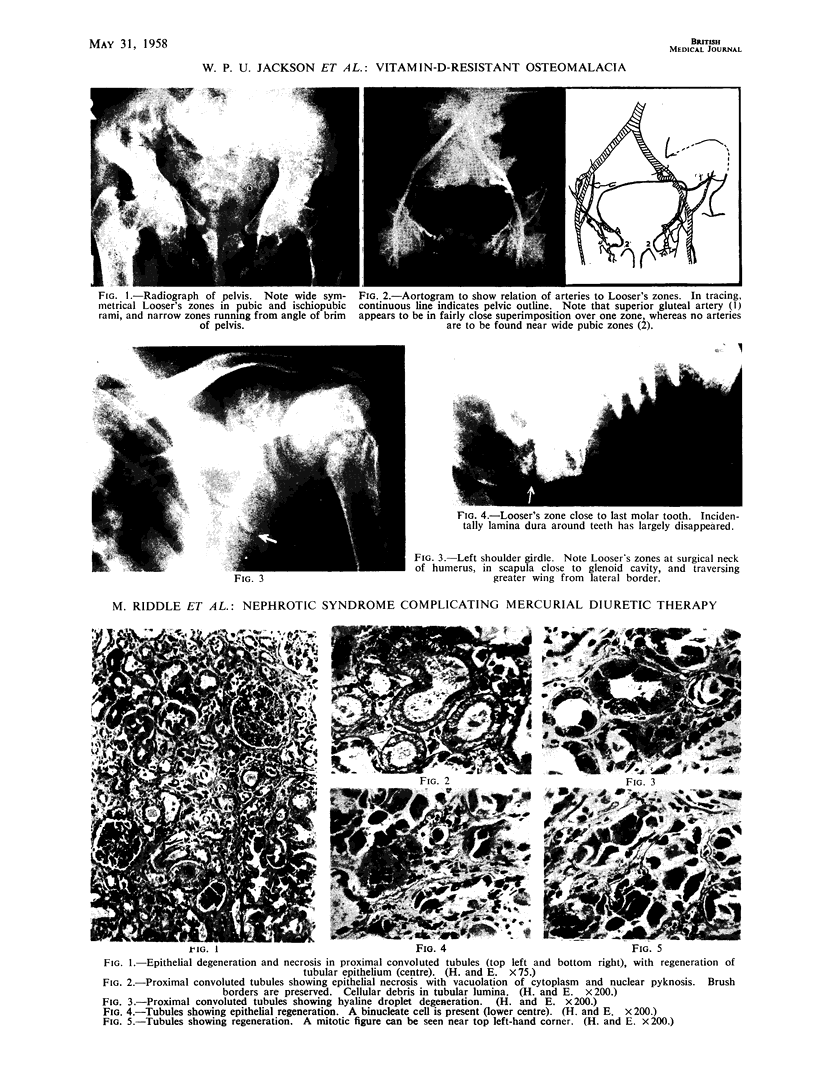




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIENGOTT D. Dangers in the use of mercurial diuretics, with emphasis on the importance of hypoalbuminemia in the etiology of complication; review and presentation of a case. Harefuah. 1953 May 15;44(10):227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., HANDLEY C. A., SEIBERT R. A., SYNDER H. B. Electrolyte, water, and mercury excretion after oral administration of neohydrin; observations on experimental use of neohydrin (1347ex), a chloro derivative, and two thiol (1353ex and 1431ex) derivatives of 2-methoxy-propylurea. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1953 Dec;92(6):847–855. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1953.00240240083006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNCK O., NISSEN N. I. Development of nephrotic syndrome during treatment with mercurial diuretics. Acta Med Scand. 1956 Jan 25;153(4):307–313. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1955.tb18231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREEDY J. R., RUSSELL D. S. Acute salt depletion associated with the nephrotic syndrome developing during treatment with a mercurial diuretic. Lancet. 1953 Dec 5;265(6797):1181–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90730-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]