Abstract
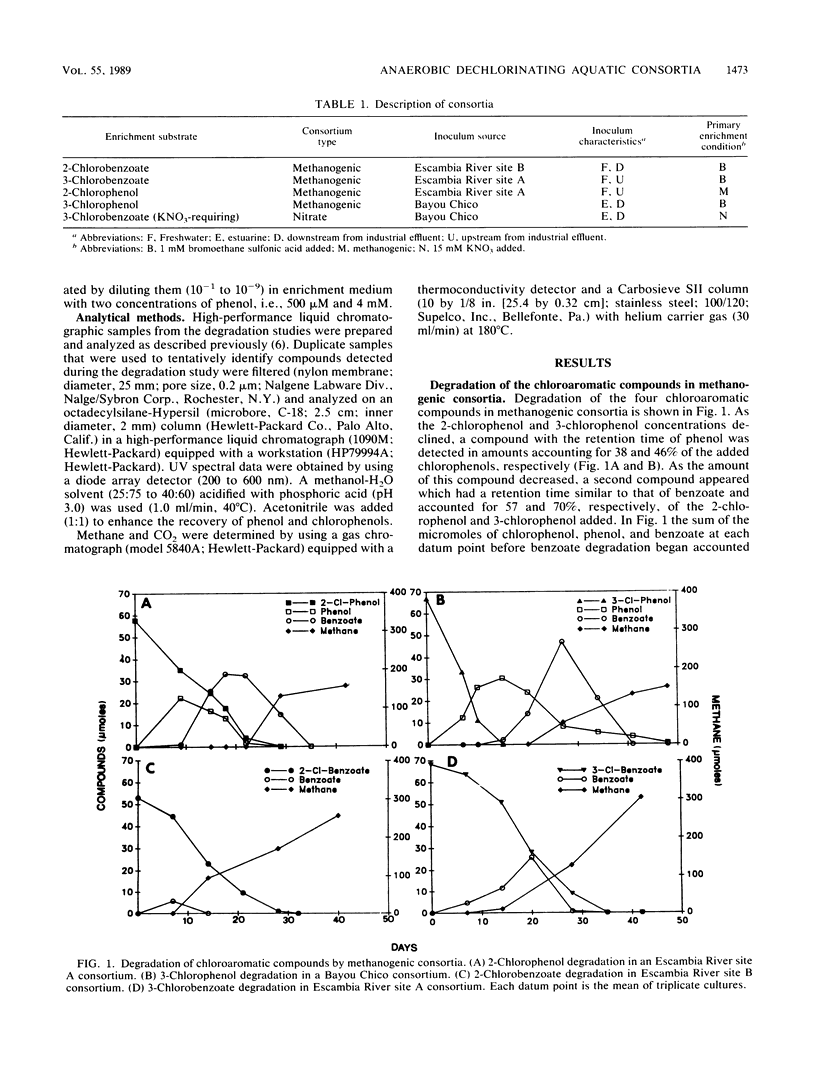
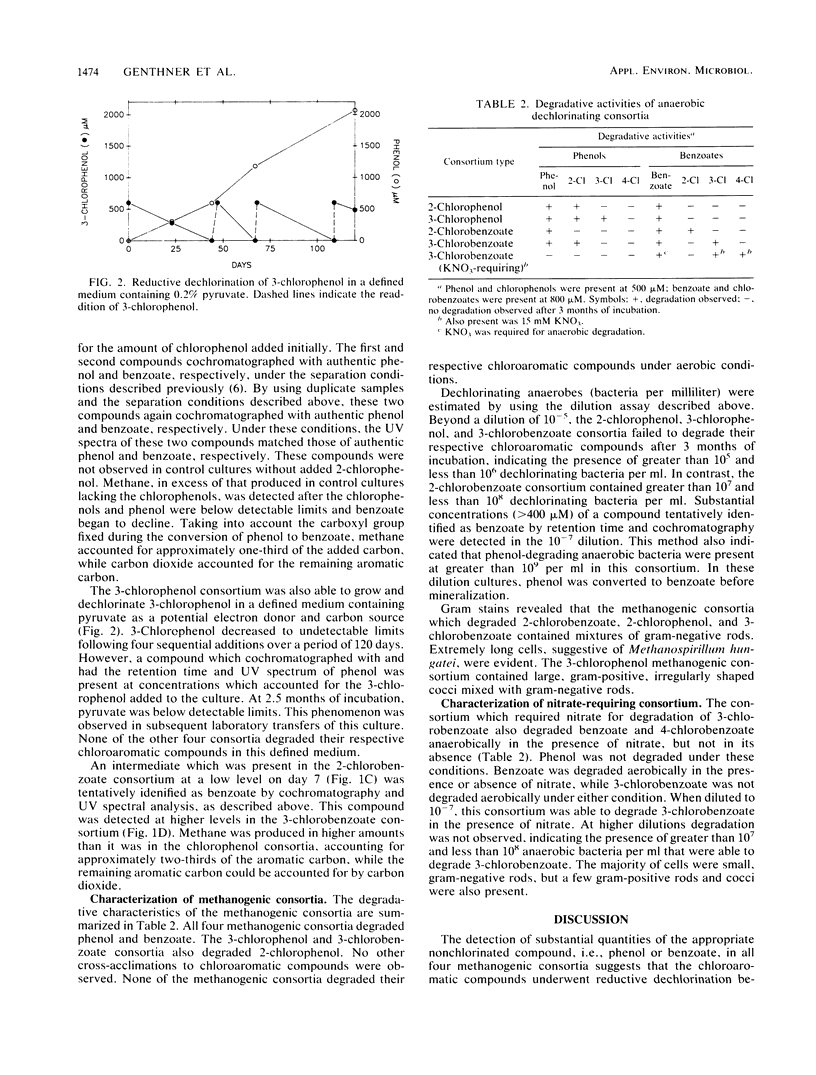
Four methanogenic consortia which degraded 2-chlorophenol, 3-chlorophenol, 2-chlorobenzoate, and 3-chlorobenzoate, respectively, and one nitrate-reducing consortium which degraded 3-chlorobenzoate were characterized. Degradative activity in these consortia was maintained by laboratory transfer for over 2 years. In the methanogenic consortia, the aromatic ring was dechlorinated before mineralization to methane and carbon dioxide. After dechlorination, the chlorophenol consortia converted phenol to benzoate before mineralization. All methanogenic consortia degraded both phenol and benzoate. The 3-chlorophenol and 3-chlorobenzoate consortia also degraded 2-chlorophenol. No other cross-acclimation to monochlorophenols or monochlorobenzoates was detected in the methanogenic consortia. The consortium which required nitrate for the degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate degraded benzoate and 4-chlorobenzoate anaerobically in the presence of KNO3, but not in its absence. This consortium also degraded benzoate, but not 3-chlorobenzoate, aerobically.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R., Berry D., Tiedje J. M. Anaerobic biodegradation of phenolic compounds in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.50-54.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. G., Wolfe R. S. Anaerobic degradation of benzoate to methane by a microbial consortium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00427864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Anaerobic Degradation of Chloroaromatic Compounds in Aquatic Sediments under a Variety of Enrichment Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1466–1471. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1466-1471.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Extrapolation of biodegradation results to groundwater aquifers: reductive dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.681-688.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Reductive dehalogenations of halobenzoates by anaerobic lake sediment microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1459-1465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy N. B., Kaufman D. D., Fries G. F. Degradation of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in aerobic and anaerobic soil. J Environ Sci Health B. 1979;14(1):1–14. doi: 10.1080/03601237909372110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schennen U., Braun K., Knackmuss H. J. Anaerobic degradation of 2-fluorobenzoate by benzoate-degrading, denitrifying bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):321–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.321-325.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. F., Hearn W. L., Pincus S. Metabolism of monofluoro- and monochlorobenzoates by a dentrifying bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Sep;122(3):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00411295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


