Abstract
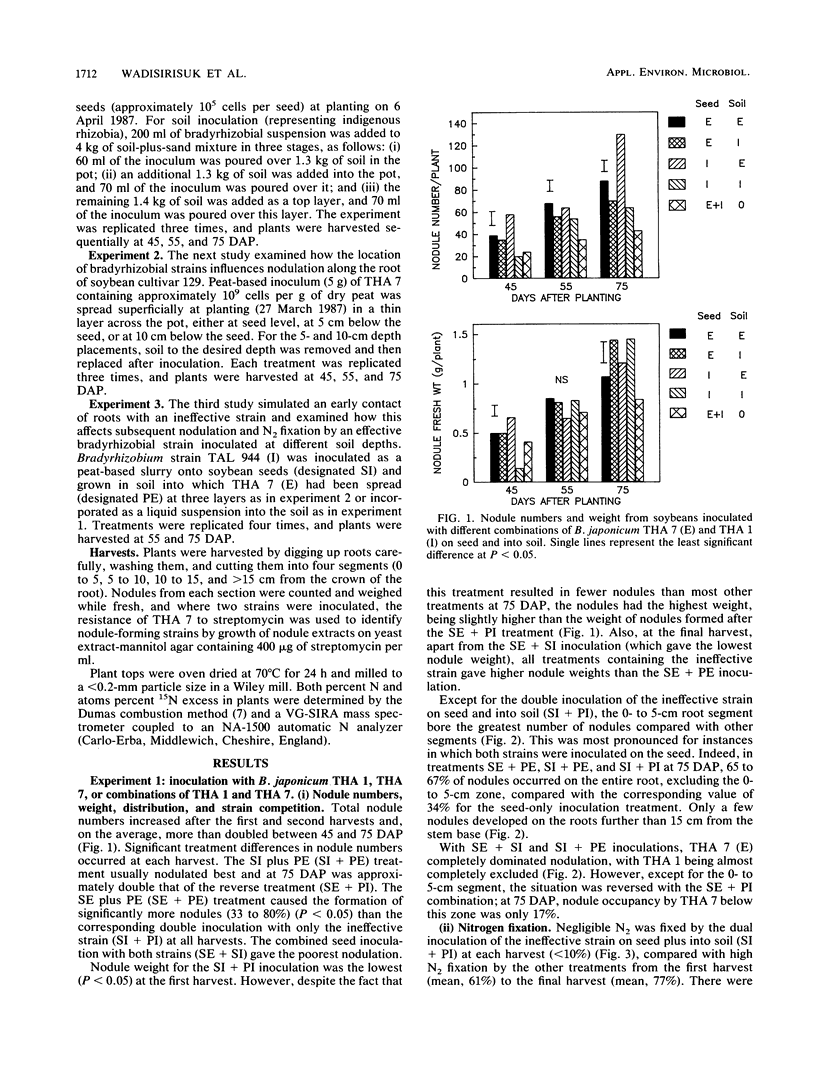
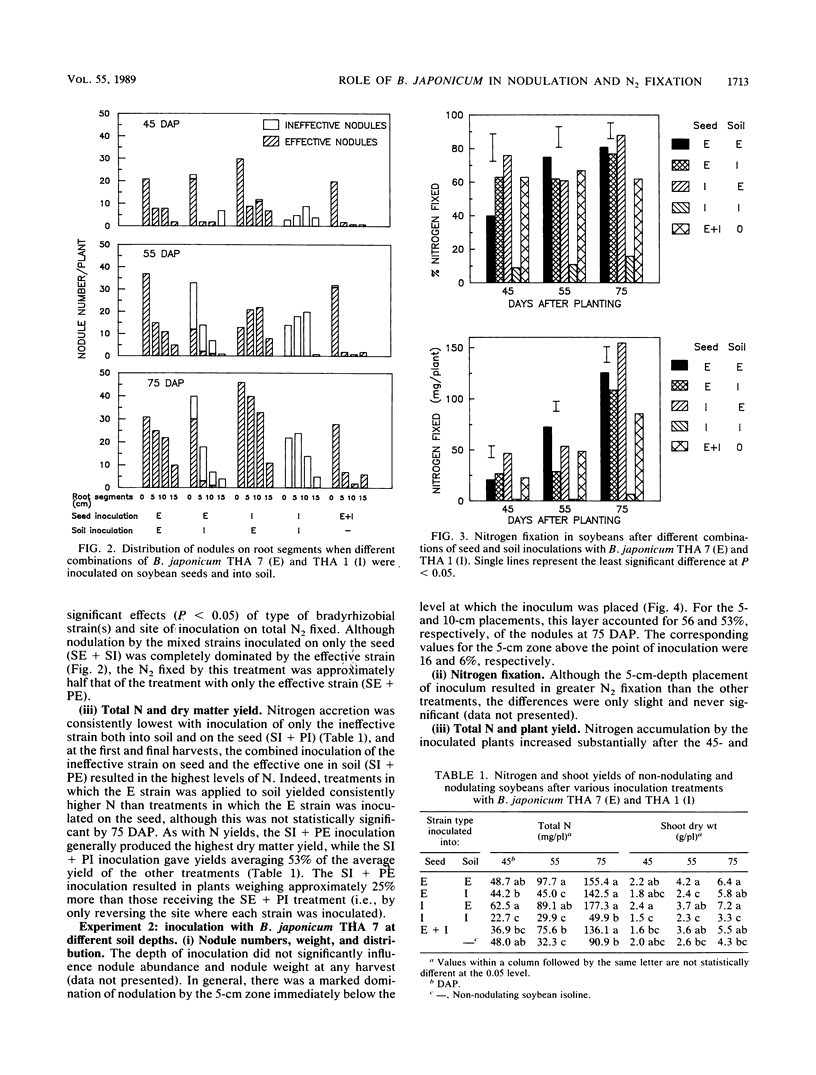
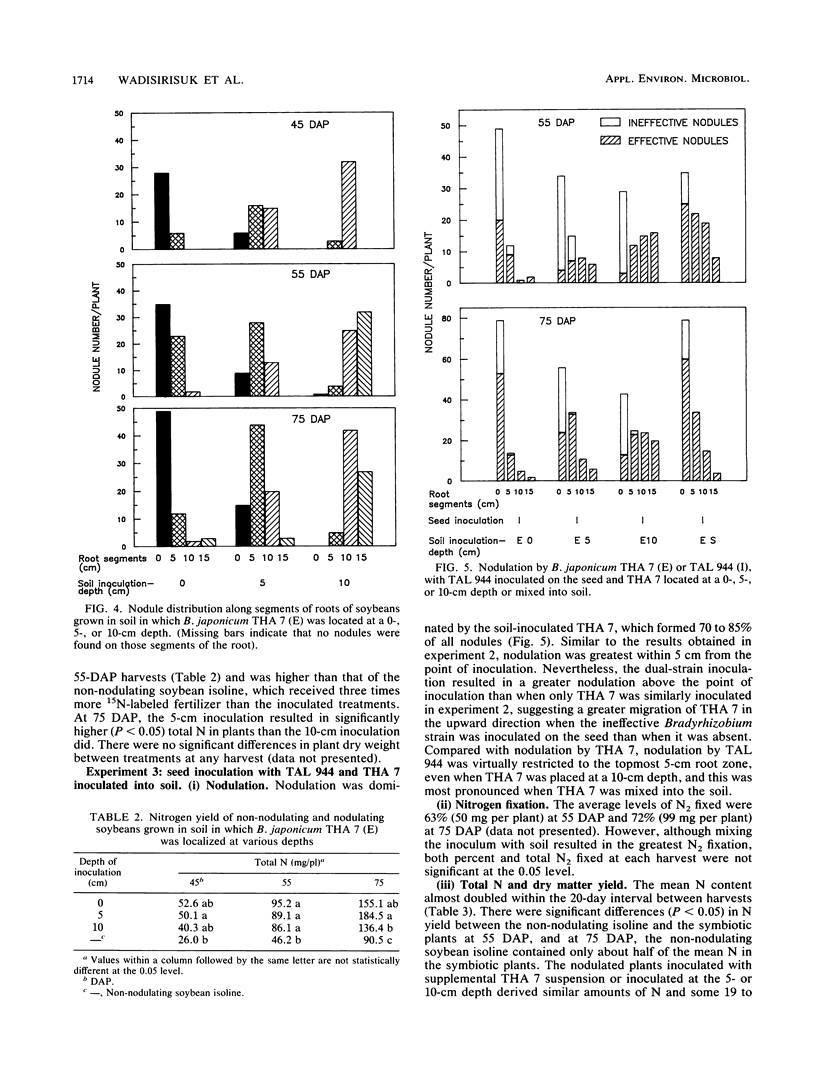
The influence of seed and soil inoculation on bradyrhizobial migration, nodulation, and N2 fixation was examined by using two Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains of contrasting effectiveness in N2 fixation. Seed-inoculated strains formed fewer nodules on soybeans (mostly restricted to the tap and crown roots within 0 to 5 cm from the stem base) than did bradyrhizobia distributed throughout the soil or inoculated at specific depths. Nodulation was greater below the depths at which bradyrhizobial cells were located rather than above, even though watering was done from below to minimize passive bradyrhizobial migration with percolating water. The most profuse nodulation occurred within approximately 5 cm below the point of placement and was generally negligible below 10 cm. These and other results suggest that bradyrhizobial migration from the initial point of placement was very limited. Nevertheless, the more competitive strain, effective strain THA 7, migrated into soil to a greater extent than the ineffective strain THA 1 did. Nitrogen fixation resulting from the dual-strain inoculations differed depending on the method of inoculation. For example, the amount of N2 fixed when both strains were slurried together onto the seed was about half that obtained from mixing the effective strain into the soil with the ineffective strain on the seed. The results indicate the importance of rhizobial distribution or movement into soil for nodulation, nodule distribution, strain competitiveness, and N2 fixation in soil-grown legumes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bhagwat A. A., Bauer W. D. Transient susceptibility of root cells in four common legumes to nodulation by rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. M., Quail G. Movement of bacteria in moist, particulate systems. Aust J Biol Sci. 1968 Jun;21(3):579–582. doi: 10.1071/bi9680579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B. Suppression of nodule development of one side of a split-root system of soybeans caused by prior inoculation of the other side. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):125–130. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moawad H. A., Ellis W. R., Schmidt E. L. Rhizosphere Response as a Factor in Competition Among Three Serogroups of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum for Nodulation of Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):607–612. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.607-612.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M., Bauer W. D. A rapid regulatory response governing nodulation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):286–290. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton P. W., Tavares J. W. Inoculation response of legumes in relation to the number and effectiveness of indigenous Rhizobium populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1013–1018. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1013-1018.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


