Abstract
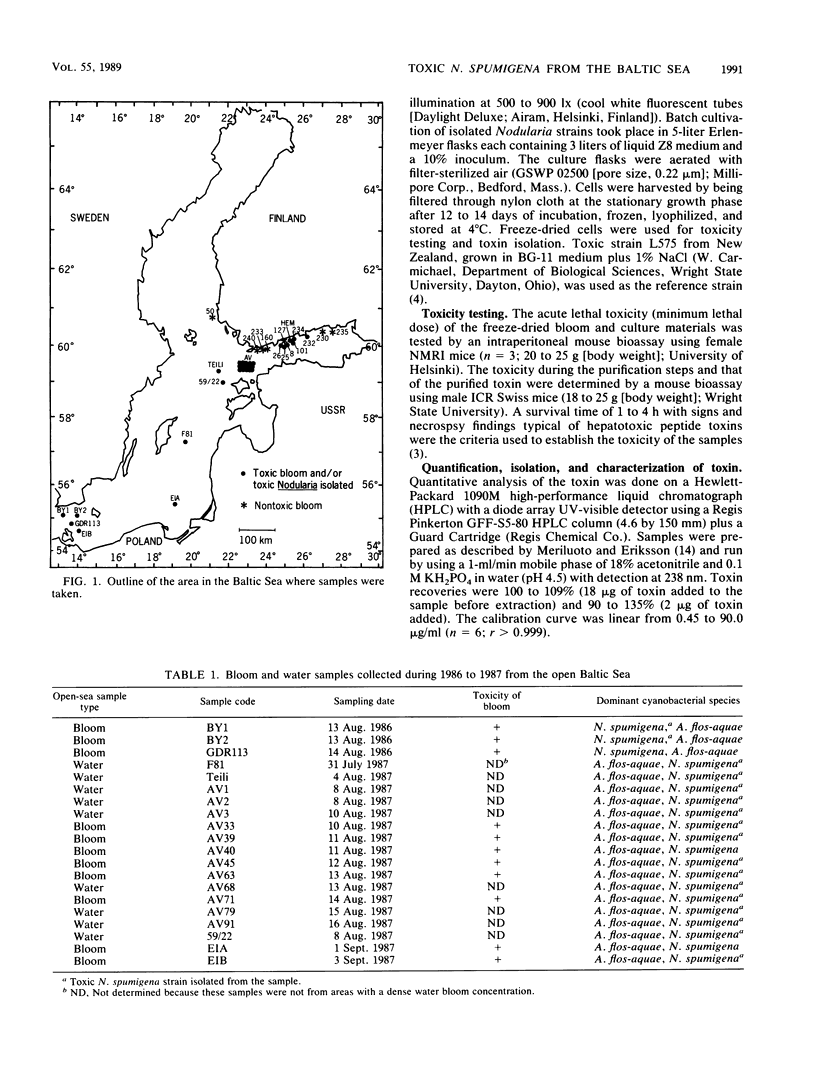
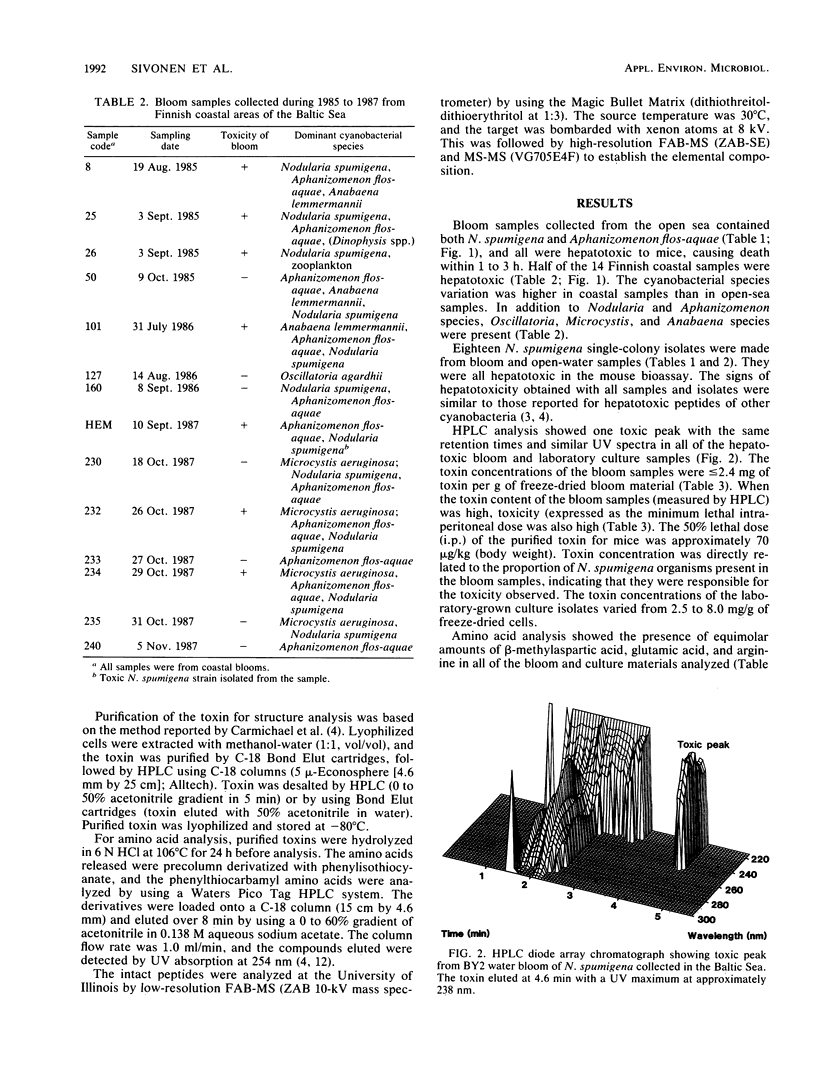
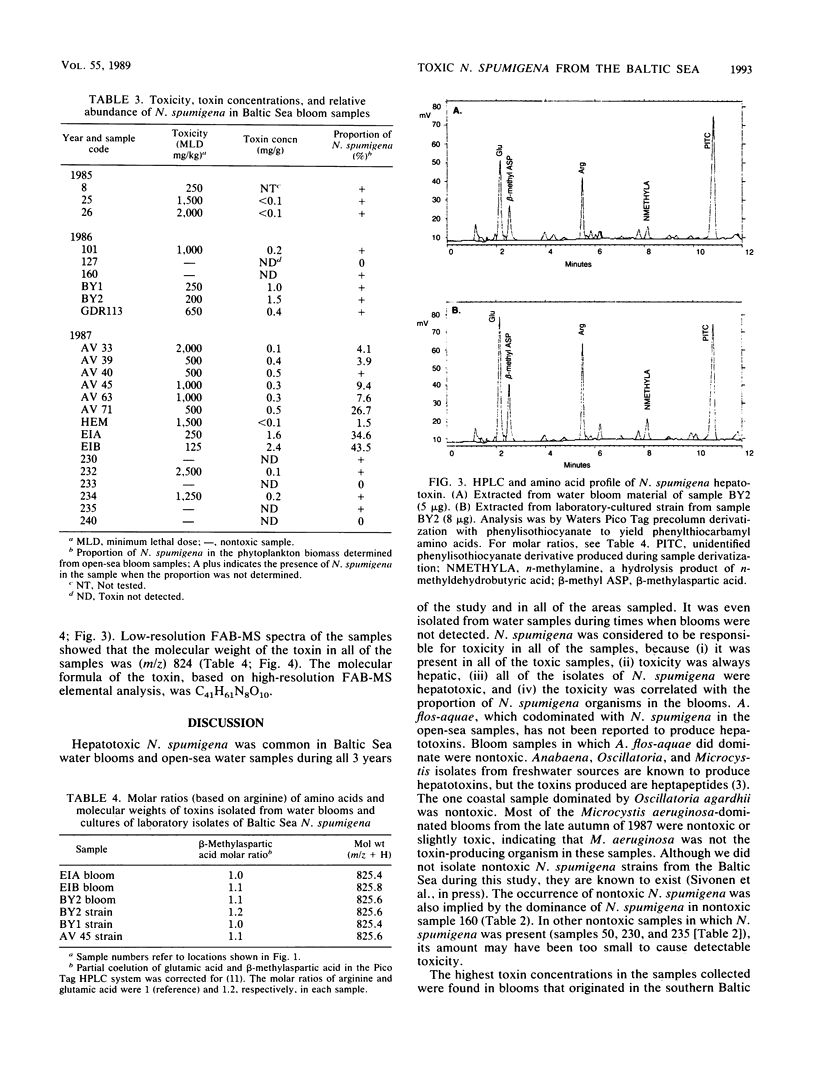
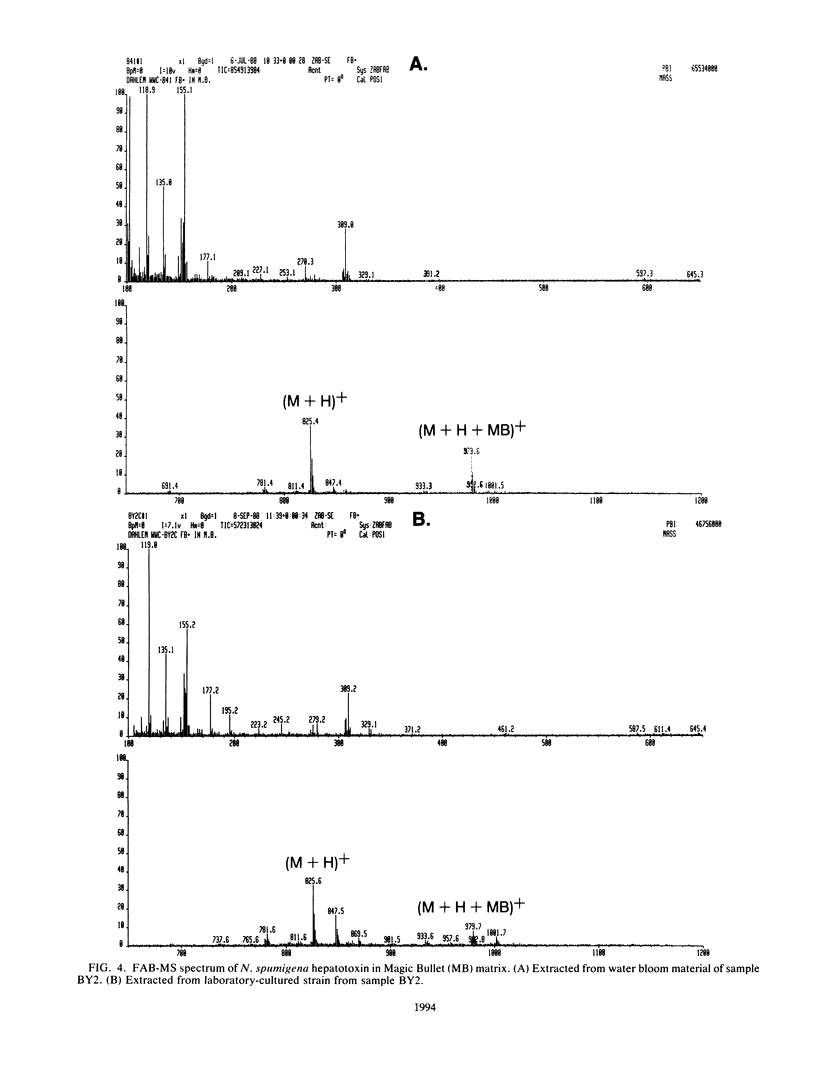
Water blooms formed by potentially toxic species of cyanobacteria are a common phenomenon in the Baltic Sea in late summer. Twenty-five cyanobacterial bloom samples were collected from open and coastal waters of the Baltic Sea during 1985 to 1987, and their toxicity was determined by mouse bioassay. All of 5 bloom samples from the southern Baltic Sea, 6 of 6 from the open northern Baltic Sea (Gulf of Finland), and 7 of 14 Finnish coastal samples were found to contain hepatotoxic cyanobacteria. Nodularia spumigena and Aphanizomenon flos-aquae occurred together in high amounts in blooms from the open-sea areas. In addition, coastal samples contained the species Anabaena lemmermannii, Microcystis aeruginosa, and Oscillatoria agardhii. Eighteen hepatotoxic N. spumigena cultures were isolated from water bloom and open-sea water samples. High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of both hepatotoxic bloom samples and Nodularia strains showed a single toxic fraction. The toxin concentrations of the blooms were less than or equal to 2.4 mg/g of freeze-dried material, and those of laboratory-grown cultures were 2.5 to 8.0 mg/g of freeze-dried cells. A single toxin was isolated from three N. spumigena-containing bloom samples and three N. spumigena laboratory isolates. Amino acid analysis and low- and high-resolution fast-atom bombardment mass spectroscopy indicated that the toxin from all of the sources was a cyclic pentapeptide (molecular weight, 824) containing glutamic acid, beta-methylaspartic acid, arginine, N-methyldehydrobutyrine, and 3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyl-4,6-decadienoic acid.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botes D. P., Kruger H., Viljoen C. C. Isolation and characterization of four toxins from the blue-green alga, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon. 1982;20(6):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael W. W., Eschedor J. T., Patterson G. M., Moore R. E. Toxicity and partial structure of a hepatotoxic peptide produced by the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena Mertens emend. L575 from New Zealand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2257–2263. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2257-2263.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J. E., Meriluoto J. A., Kujari H. P., Osterlund K., Fagerlund K., Hällbom L. Preliminary characterization of a toxin isolated from the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Toxicon. 1988;26(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. O., GORHAM P. R., ZEHNDER A. Toxicity of a unialgal culture of Microcystis aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Jun;4(3):225–236. doi: 10.1139/m58-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy T., Carmichael W. W., Sarver E. W. Toxic peptides from freshwater cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). I. Isolation, purification and characterization of peptides from Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos-aquae. Toxicon. 1986;24(9):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriluoto J. A., Eriksson J. E. Rapid analysis of peptide toxins in cyanobacteria. J Chromatogr. 1988 Apr 1;438(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnegar M. T., Jackson A. R., Falconer I. R. Toxicity of the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena Mertens. Toxicon. 1988;26(2):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Harda K., Matsuura K., Kawai H., Suzuki M. Toxins contained in Microcystis species of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1988;26(11):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


