Abstract
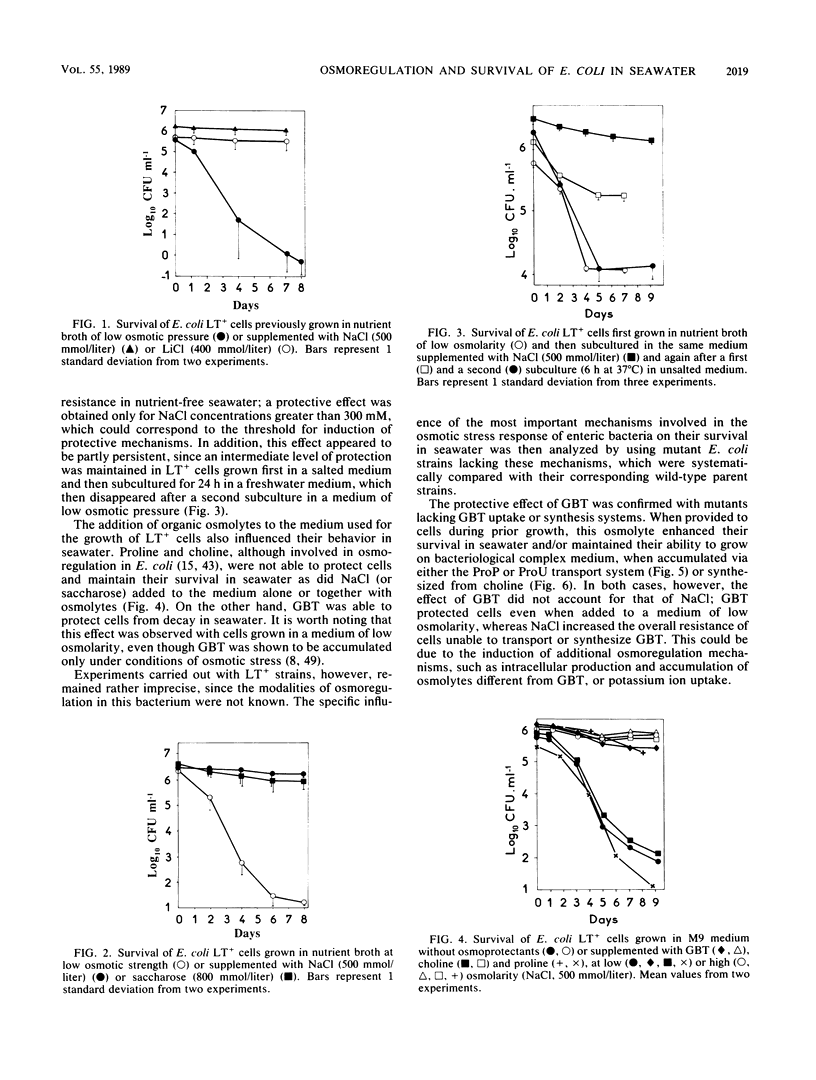
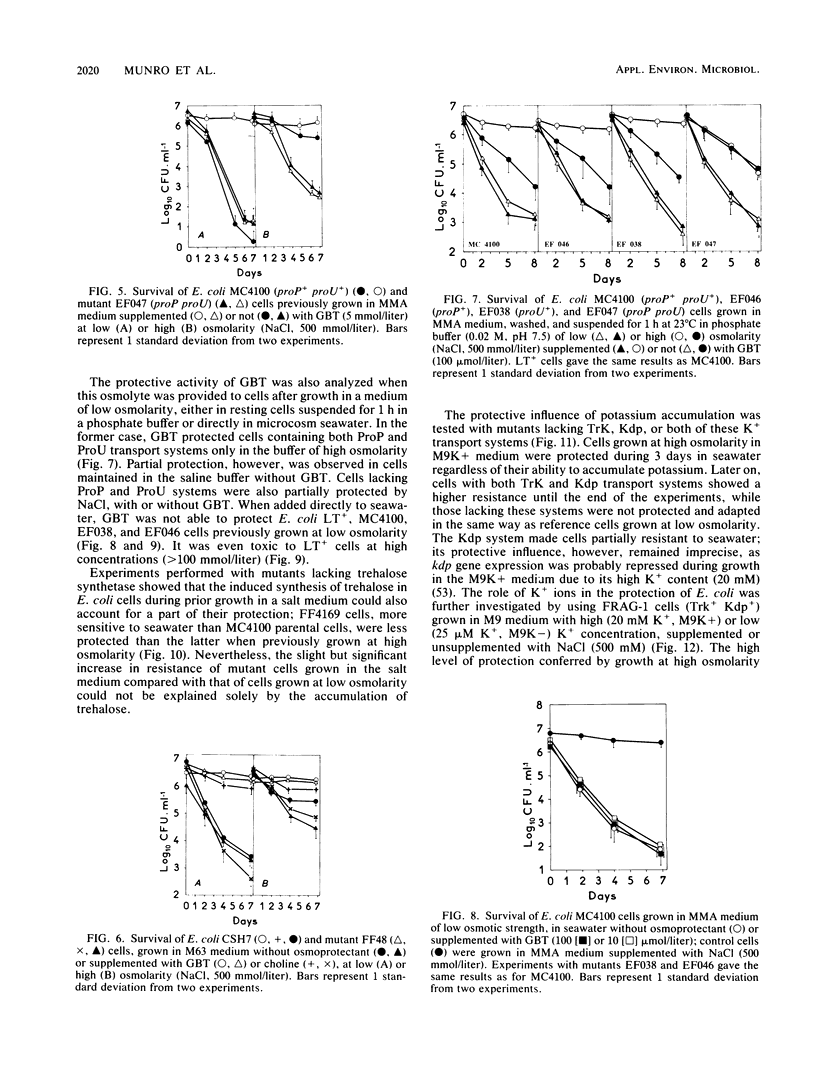
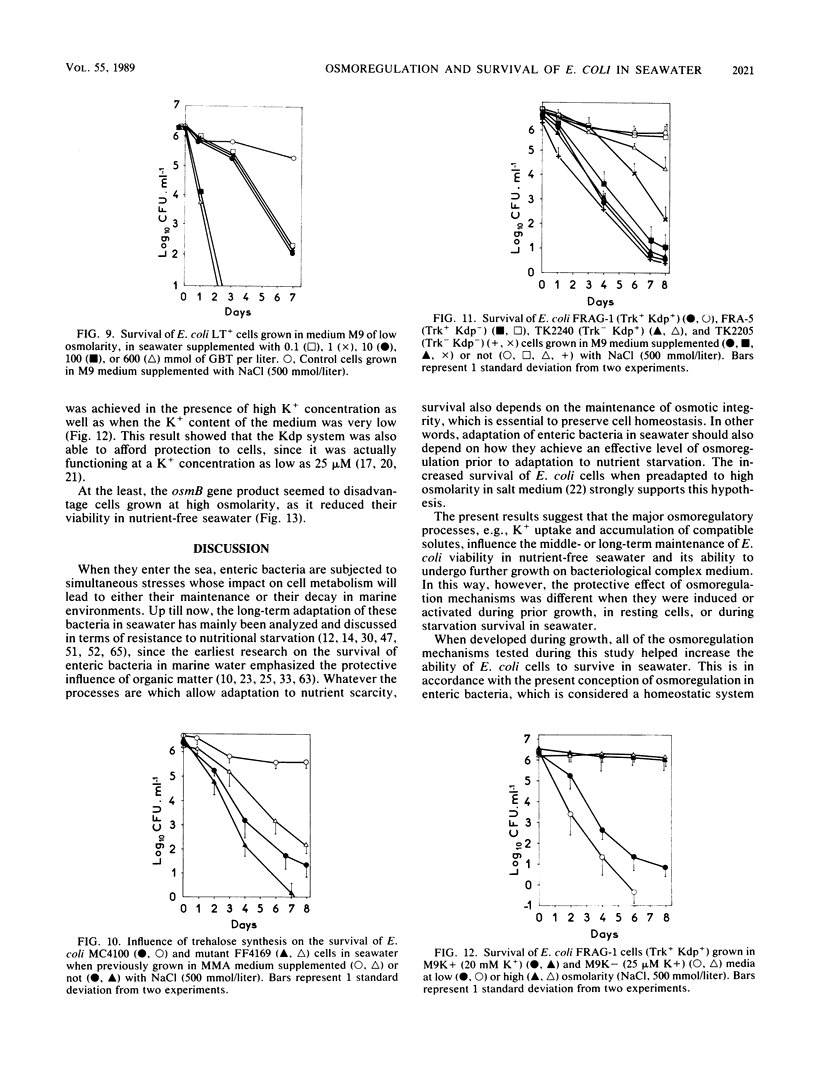
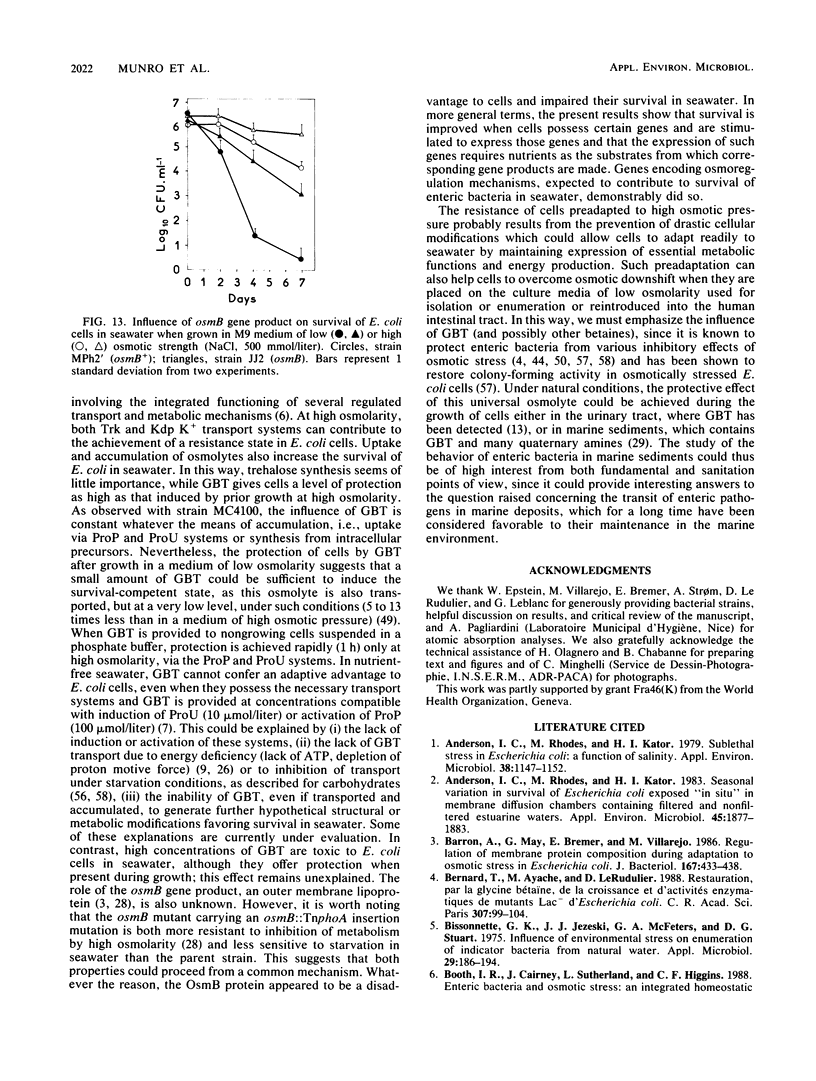
The adaptation of enteric bacteria in seawater has previously been described in terms of nutrient starvation. In the present paper, we bring experimental arguments suggesting that survival of these microorganisms could also depend on their ability to overcome the effects of osmotic stress. We analyzed the influence of osmoregulatory mechanisms (potassium transport, transport and accumulation of organic osmolytes) on the survival of Escherichia coli in seawater microcosms by using mutants lacking components of the osmotic stress response. Long-term protection was afforded to cells by growth in a medium whose osmotic pressure was increased by either NaCl, LiCl, or saccharose. Achievement of the protection state depended at least partly on osmoregulatory mechanisms, but differed when these were activated or induced during prior growth or in resting cells suspended in phosphate buffer or in seawater. When achieved during growth, K+ transport, glycine-betaine (GBT) synthesis or transport, and trehalose synthesis helped increase the ability to survive in seawater. Protection by GBT was also obtained with resting cells in a phosphate buffer at high osmotic pressure. However, when added only to the seawater, GBT did not change the survival ability of cells no matter what their osmoregulation potential. These results showed that the survival of E. coli cells in seawater depends, at least partly, on whether they possess certain genes which enable them to regulate osmotic pressure and whether they can be stimulated to express those genes before or after their release into the environment. This expression requires nutrients as the substrates from which the corresponding gene products are made.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson I. C., Rhodes M. W., Kator H. I. Seasonal variation in survival of Escherichia coli exposed in situ in membrane diffusion chambers containing filtered and nonfiltered estuarine water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1877–1883. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1877-1883.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson I. C., Rhodes M., Kator H. Sublethal stress in Escherichia coli: a function of salinity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1147–1152. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1147-1152.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron A., May G., Bremer E., Villarejo M. Regulation of envelope protein composition during adaptation to osmotic stress in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):433–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.433-438.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard T., Ayache M., Le Rudulier D. Restauration, par la glycine bétaïne, de la croissance et d'activités enzymatiques de mutants Lac- d'Escherichia coli. C R Acad Sci III. 1988;307(3):99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLUCCI A. F., PRAMER D. Factors affecting the survival of bacteria in sea water. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Nov;7:388–392. doi: 10.1128/am.7.6.388-392.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Osmoregulation of gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium: proU encodes an osmotically induced betaine transport system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1224–1232. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1224-1232.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Salmonella typhimurium proP gene encodes a transport system for the osmoprotectant betaine. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1218–1223. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1218-1223.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Higgins C. F., Booth I. R. Proline uptake through the major transport system of Salmonella typhimurium is coupled to sodium ions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.22-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai T. J. Characteristics of Escherichia coli grown in bay water as compared with rich medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1316–1323. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1316-1323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. T., Kunin C. M. Isolation of glycine betaine and proline betaine from human urine. Assessment of their role as osmoprotective agents for bacteria and the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):731–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI112878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Proline over-production results in enhanced osmotolerance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00422771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe L. L., Penrose W. R. "Bactericidal" property of seawater: death or debilitation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):829–833. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.829-833.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Davies M. Potassium-dependant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.836-843.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Kim B. S. Potassium transport loci in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):639–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.639-644.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Schultz S. G. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VI. K exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jan;49(3):469–481. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., McLeod J. S. Effect of sediments on the survival of Escherichia coli in marine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):114–120. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.114-120.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever H. M., Styrvold O. B., Kaasen I., Strøm A. R. Biochemical and genetic characterization of osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2841–2849. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2841-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Sutherland L., Cairney J., Booth I. R. The osmotically regulated proU locus of Salmonella typhimurium encodes a periplasmic betaine-binding protein. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):305–310. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E. Survival of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in estuarine waters and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):578–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.578-584.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Gutierrez C., Villarejo M. R. Sequence of an osmotically inducible lipoprotein gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):511–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.511-520.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. A., Wu S. Stress: a factor to be considered in heterotrophic microorganism enumeration from aquatic environments. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):429–431. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.429-431.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaLiberte P., Grimes D. J. Survival of Escherichia coli in lake bottom sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):623–628. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.623-628.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Osmotic control of kdp operon expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):464–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfald B., Strøm A. R. Choline-glycine betaine pathway confers a high level of osmotic tolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):849–855. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.849-855.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. I., Sydnes L. K., Landfald B., Strøm A. R. Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli by accumulation of organic osmolytes: betaines, glutamic acid, and trehalose. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Feb;147(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00492896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Bouillard L. Glycine betaine, an osmotic effector in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):152–159. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.152-159.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Strom A. R., Dandekar A. M., Smith L. T., Valentine R. C. Molecular biology of osmoregulation. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1064–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4653.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard E. J., Sieburth J. M. Survival of natural sewage populations of enteric bacteria in diffusion and batch chambers in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):950–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.950-959.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Faatz E., Villarejo M., Bremer E. Binding protein dependent transport of glycine betaine and its osmotic regulation in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00430432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J. Glycine betaine reverses the effects of osmotic stress on DNA replication and cellular division in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol. 1988 Jan;149(3):232–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Robin A., Monnier-Champeix P. Turgor-controlled K+ fluxes and their pathways in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):613–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro P. M., Gauthier M. J., Laumond F. M. Changes in Escherichia coli cells starved in seawater or grown in seawater-wastewater mixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1476–1481. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1476-1481.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perroud B., Le Rudulier D. Glycine betaine transport in Escherichia coli: osmotic modulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):393–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.393-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve C. A., Amy P. S., Matin A. Role of protein synthesis in the survival of carbon-starved Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1041–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1041-1046.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve C. A., Bockman A. T., Matin A. Role of protein degradation in the survival of carbon-starved Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.758-763.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Grimes D. J., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonrecoverable stage of Salmonella enteritidis in aquatic systems. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):334–338. doi: 10.1139/m84-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. G., Leckie M. P., Dietzler D. N. Osmotic stress drastically inhibits active transport of carbohydrates by Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. G., Leckie M. P., Dietzler D. N. Restoration of colony-forming activity in osmotically stressed Escherichia coli by betaine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3142–3146. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3142-3146.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. G., Porter S. E., Leckie M. P., Porter B. E., Dietzler D. N. Restoration of cell volume and the reversal of carbohydrate transport and growth inhibition of osmotically upshocked Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90625-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., McFeters G. A., Schillinger J. E. Membrane filter technique for the quantification of stressed fecal coliforms in the aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jul;34(1):42–46. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.1.42-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styrvold O. B., Falkenberg P., Landfald B., Eshoo M. W., Bjørnsen T., Strøm A. R. Selection, mapping, and characterization of osmoregulatory mutants of Escherichia coli blocked in the choline-glycine betaine pathway. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):856–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.856-863.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VACCARO R. F., BRIGGS M. P., CAREY C. L., KETCHUM B. H. Viability of Escherichia coli in sea water. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Oct;40(10):1257–1266. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.10.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaske S. K., Dockins W. S., McFeters G. A. Cell envelope damage in Escherichia coli caused by short-term stress in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):386–390. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.386-390.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


