Abstract
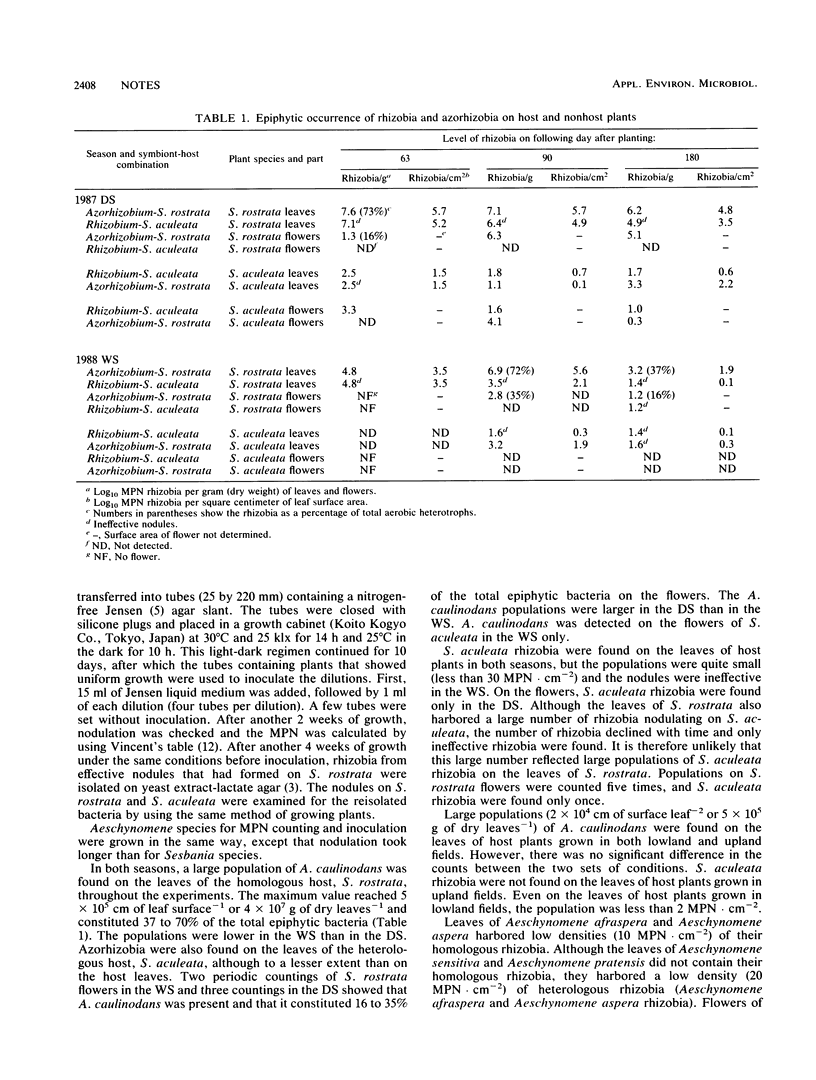
A large population of Azorhizobium caulinodans was present on Sesbania rostrata; up to 5 × 10−5 cm−2 were found on leaves and fewer were found on flowers. Although A. caulinodans was also present on the leaves of Sesbania aculeata (nonhost), the populations were much smaller than that observed on S. rostrata. The population of S. aculeata rhizobia on host leaves was less than 30 cm−2, and their presence on host flowers was sporadic. Aeschynomene afraspera and Aeschynomene aspera rhizobia, which are profusely stem nodulating, were found on the leaves of host and nonhost plants and on the flowers of host plants, but, Aeschynomene pratensis and Aeschynomene sensitiva rhizobia were not found on the leaves and flowers of host plants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dreyfus B. L., Elmerich C., Dommergues Y. R. Free-living Rhizobium strain able to grow on n(2) as the sole nitrogen source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):711–713. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.711-713.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladha J. K., Garcia M., Miyan S., Padre A. T., Watanabe I. Survival of Azorhizobium caulinodans in the Soil and Rhizosphere of Wetland Rice under Sesbania rostrata-Rice Rotation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):454–460. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.454-460.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


