Abstract
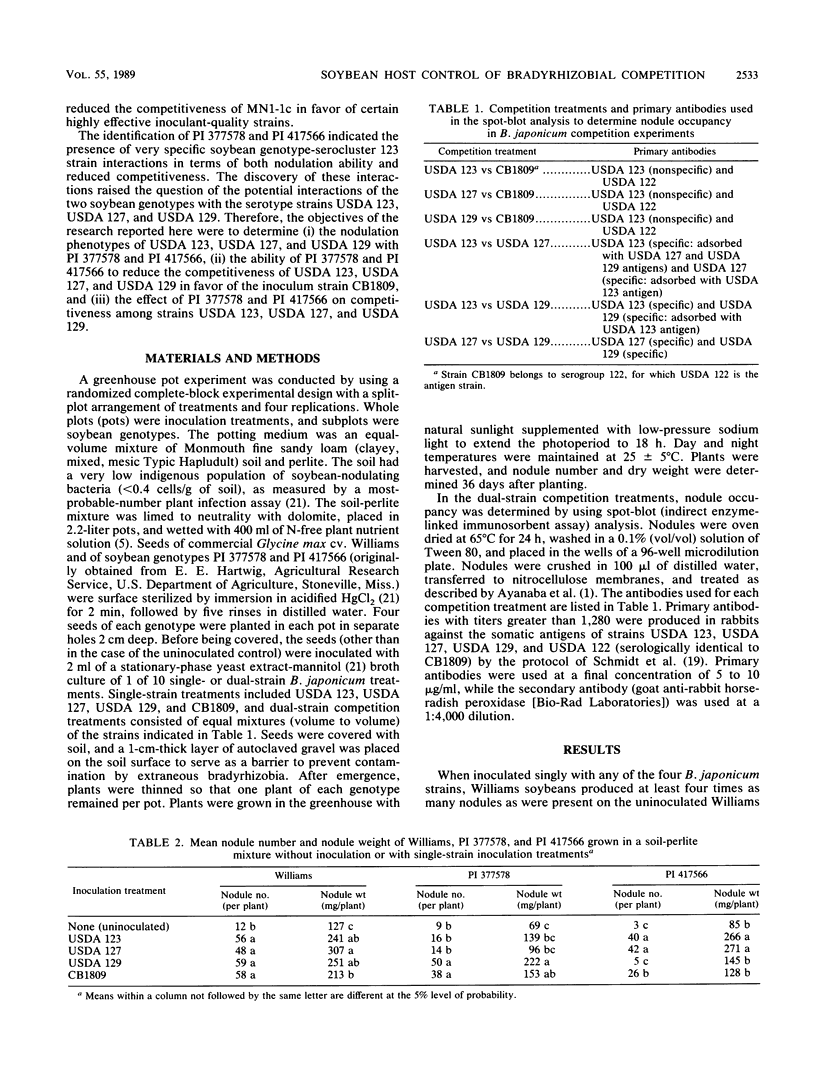
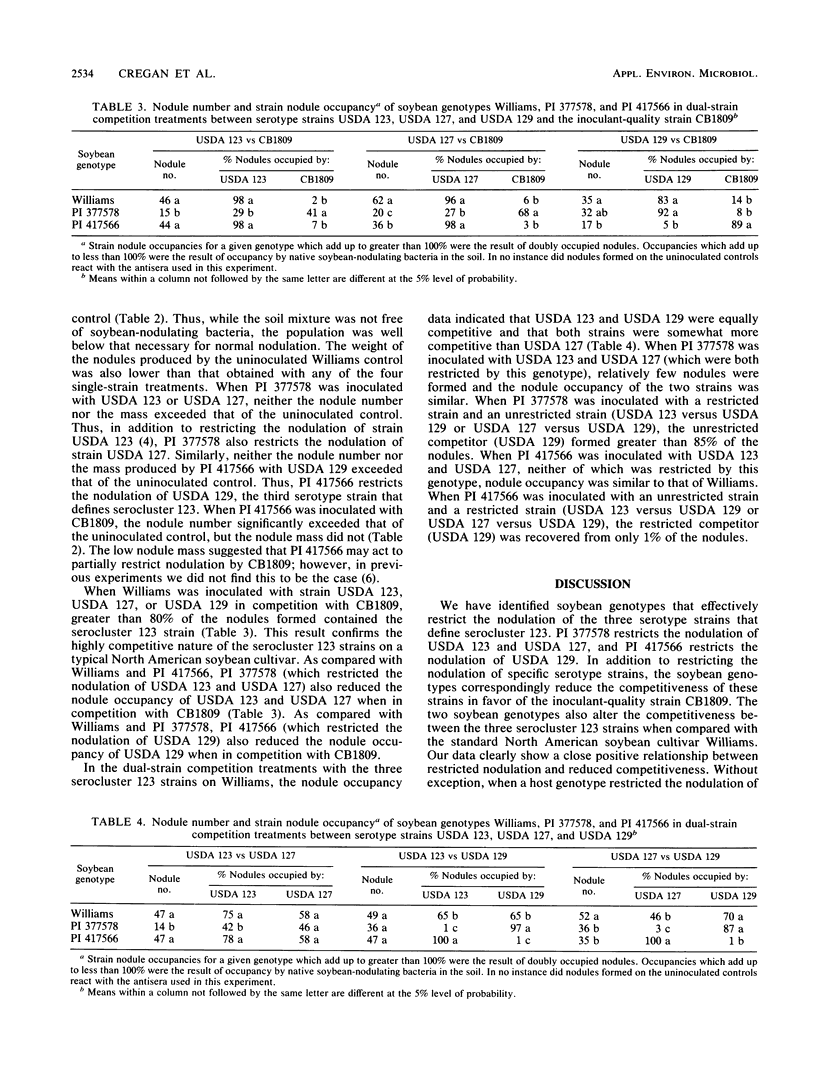
Strains in Bradyrhizobium japonicum serocluster 123 are the major indigenous competitors for nodulation in a large portion of the soybean production area of the United States. Serocluster 123 is defined by the serotype strains USDA 123, USDA 127, and USDA 129. The objective of the work reported here was to evaluate the ability of two soybean genotypes, PI 377578 and PI 417566, to restrict the nodulation and reduce the competitiveness of serotype strains USDA 123, USDA 127, and USDA 129 in favor of the highly effective strain CB1809 and to determine how these soybean genotypes alter the competitive relationships among the three serotype strains in the serocluster. The soybean genotypes PI 377578 and PI 417566 along with the commonly grown cultivar Williams were planted in soil essentially free of soybean rhizobia and inoculated with single-strain treatments of USDA 123, USDA 127, USDA 129, or CB1809 and six dual-strain competition treatments of USDA 123, USDA 127, or USDA 129 versus CB1809, USDA 123 versus USDA 127, USDA 123 versus USDA 129, and USDA 127 versus USDA 129. PI 377578 severely reduced the nodulation and competitiveness of USDA 123 and USDA 127, while PI 417566 similarly affected the nodulation and competitiveness of USDA 129. Thus, the two soybean genotypes can reduce the nodulation and competitiveness of each of the three serocluster 123 serotype strains. Our results indicate that host control of restricted nodulation and reduced competitiveness is quite specific and effectively discriminates between B. japonicum strains which are serologically related.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayanaba A., Weiland K. D., Zablotowicz R. M. Evaluation of Diverse Antisera, Conjugates, and Support Media for Detecting Bradyrhizobium japonicum by Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1132-1138.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cregan P. B., Keyser H. H. Influence of Glycine spp. on Competitiveness of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Rhizobium fredii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):803–808. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.803-808.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATE R. A., DECKER A. M. MINIMAL ANTIGENIC CONSTITUTION OF 28 STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Feb;11:1–8. doi: 10.1139/m65-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Cregan P. B. Nodulation and Competition for Nodulation of Selected Soybean Genotypes among Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serogroup 123 Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2631–2635. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2631-2635.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moawad H. A., Ellis W. R., Schmidt E. L. Rhizosphere Response as a Factor in Competition Among Three Serogroups of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum for Nodulation of Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):607–612. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.607-612.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Zidwick M. J., Abebe H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 and Diversity among Member Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1212-1215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


