Abstract
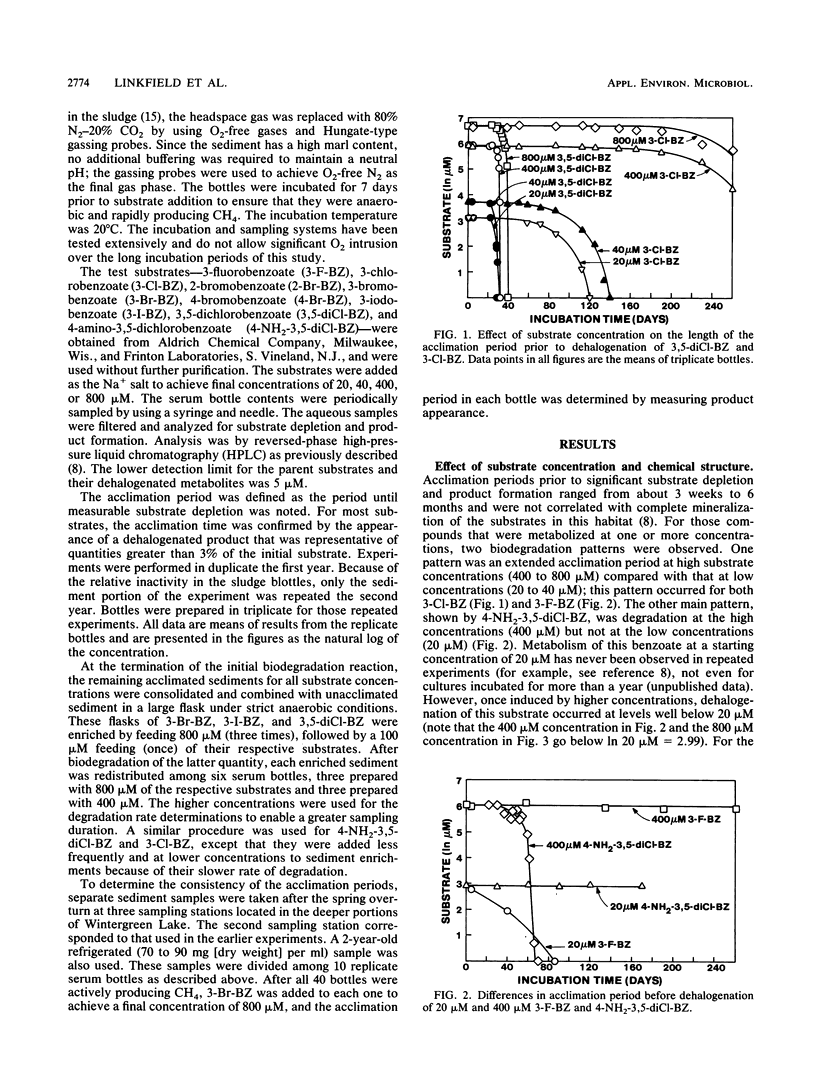
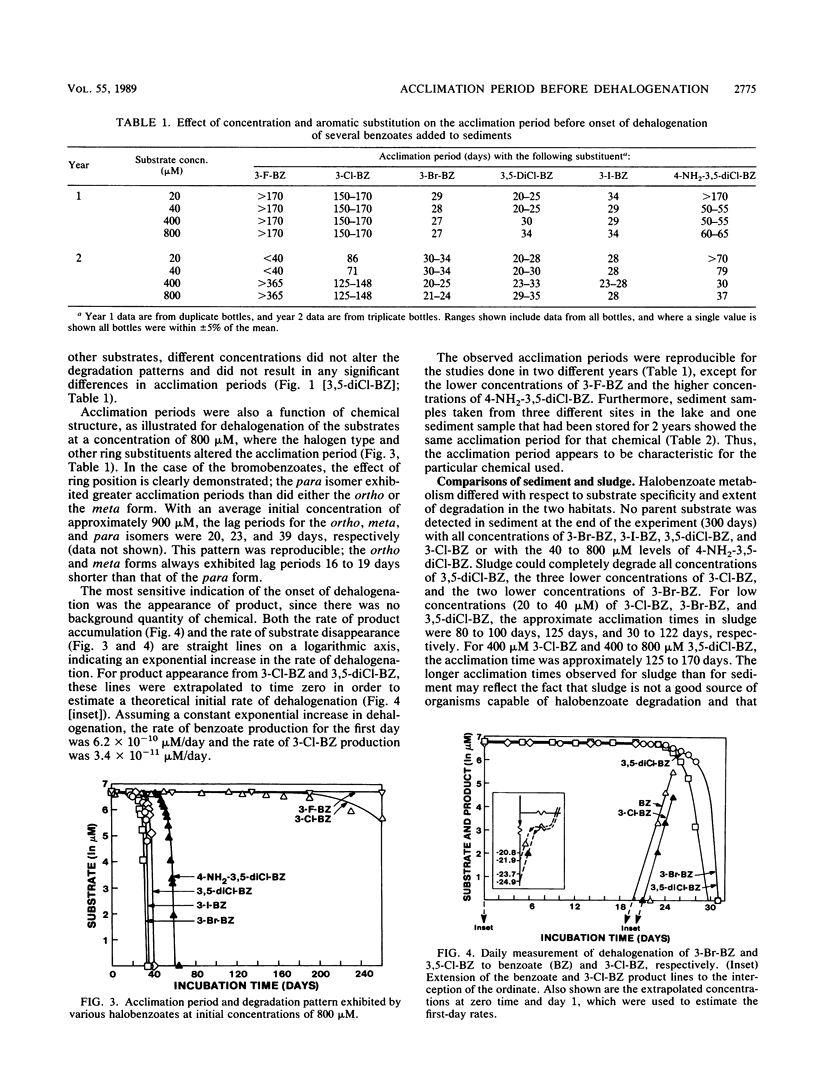
The acclimation periods prior to detectable dehalogenation of halogenated benzoates in anaerobic lake sediments ranged from 3 weeks to 6 months. These acclimation periods were reproducible over time and among sampling sites and were characteristic of the chemical tested. The lengthy acclimation period appears to represent an induction phase in which little or no aryl dehalogenation is observed, followed by an exponential increase in activity typical of an enrichment response. Continuous growth from the time of the first exposure to the chemical is inconsistent with the extremely low per-cell activities estimated for the early days of the acclimation period and the fact that the dehalogenation yields no carbon to support microbial growth. The finding of a characteristic acclimation time for each chemical argues against nutritional deficiency, inhibition, or predation as an explanation for this phase of metabolism, while the reproducibility of the findings with time and space and among replicates argues against genetic changes as the explanation. The acclimation times did correlate with the eventual dehalogenation rates. This may reflect the general energy limitations in the anaerobic communities and suggests that those chemicals with faster dehalogenation rates provide more energy for the induction and growth phases of the active population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. Biodegradation: problems of molecular recalcitrance and microbial fallibility. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1965;7:35–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boethling R. S., Alexander M. Effect of concentration of organic chemicals on their biodegradation by natural microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1211–1216. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1211-1216.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Transformations of 1- and 2-carbon halogenated aliphatic organic compounds under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1286–1294. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1286-1294.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Growth yield increase linked to reductive dechlorination in a defined 3-chlorobenzoate degrading methanogenic coculture. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00425073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Reductive dehalogenations of halobenzoates by anaerobic lake sediment microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1459-1465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg S. T., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmid-assisted molecular breeding: new technique for enhanced biodegradation of persistent toxic chemicals. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1133–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.7302584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Kollig H. P., Hodson R. E. Nutrient limitation and adaptation of microbial populations to chemical transformations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):598–603. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.598-603.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris D. F., Steen W. C., Baughman G. L., Barnett J. T. Second-order model to predict microbial degradation of organic compounds in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):603–609. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.603-609.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. E., Subba-Rao R. V., Alexander M. Rates of mineralization of trace concentrations of aromatic compounds in lake water and sewage samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1133–1138. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1133-1138.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Hellwig M., Knackmuss H. J. Degradation of chlorophenols by a defined mixed microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1038–1044. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1038-1044.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Pritchard P. H., Bourquin A. W. Effects of adaptation on biodegradation rates in sediment/water cores from estuarine and freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):726–734. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.726-734.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba-Rao R. V., Rubin H. E., Alexander M. Kinetics and extent of mineralization of organic chemicals at trace levels in freshwater and sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1139–1150. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1139-1150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventullo R. M., Larson R. J. Adaptation of aquatic microbial communities to quaternary ammonium compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):356–361. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.356-361.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins B. A., Jones S. H., Alexander M. Explanations for the acclimation period preceding the mineralization of organic chemicals in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):791–796. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.791-796.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


