Abstract
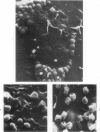
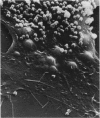
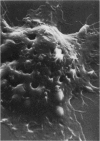
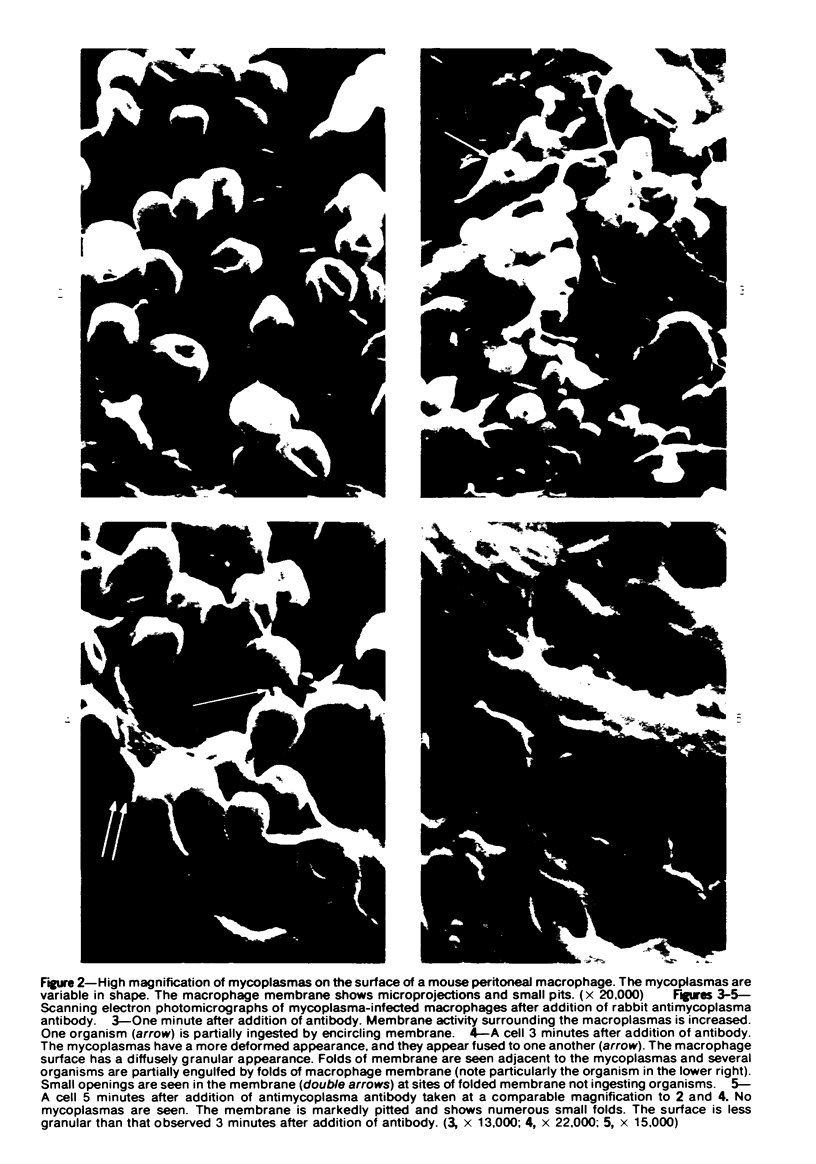
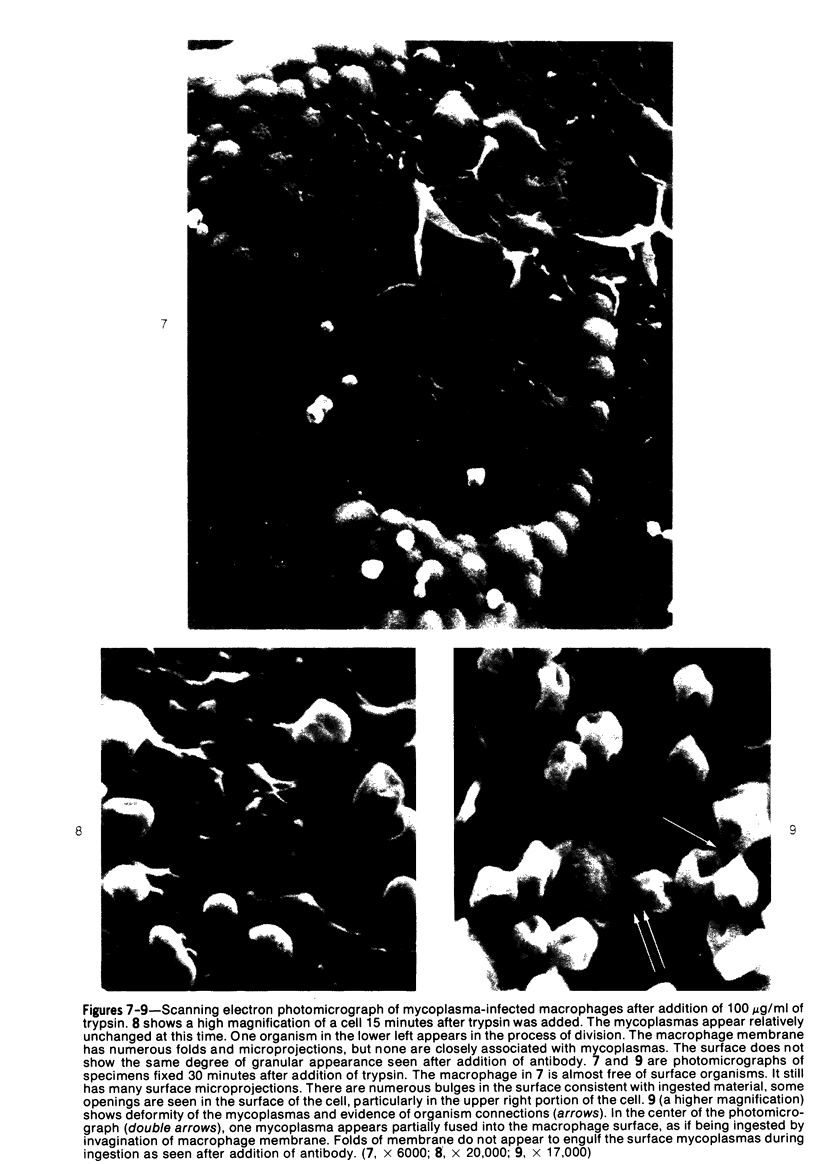
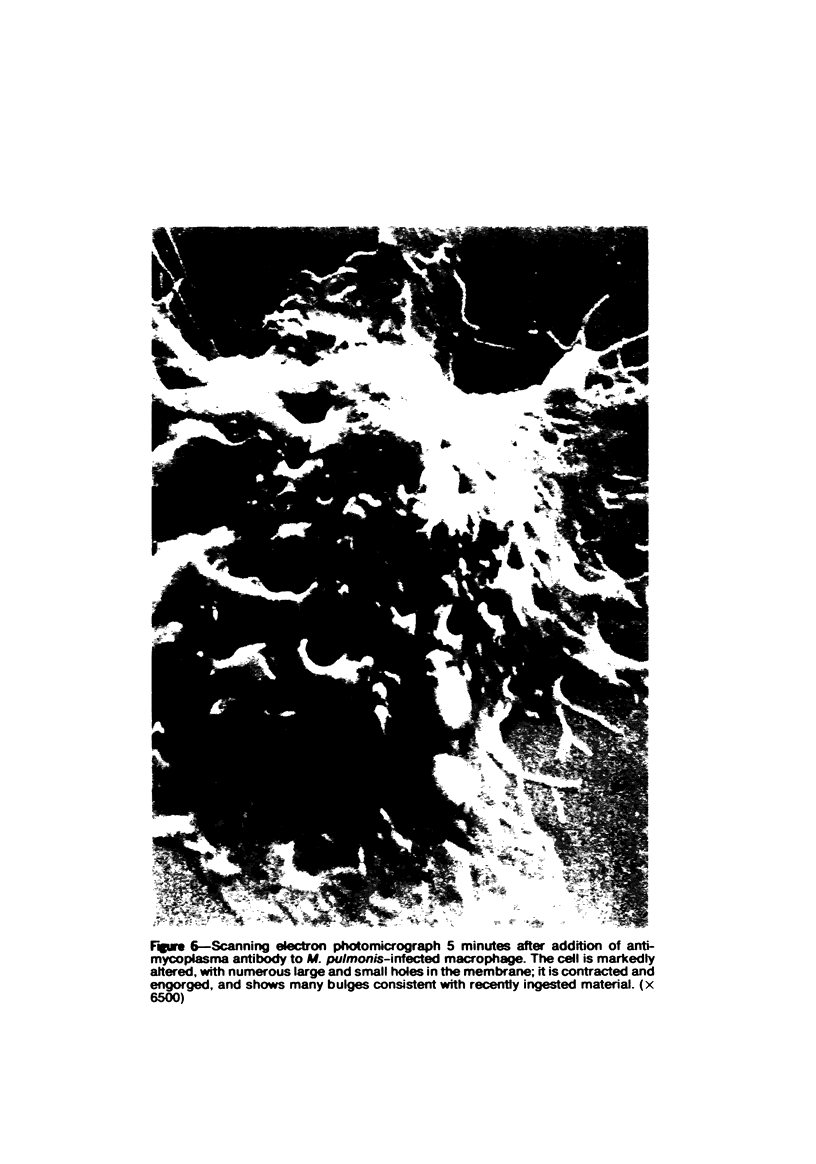
Mycoplasmas adhere closely to the central region of the surface of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. They do not appear connected to each other or the macrophage membrane, and they induce no change in the surface of the cell. After addition of antimycoplasma antibody, mycoplasmas show interconnections and the cell shows an increase occurrence of ruffled membrane and folding over the mycoplasmas. Large and small lacunae appear in the membrane at sites other than those taking in organisms, and the cell develops a diffusely granular appearance. These changes are associated with an increase in pinocytosis of horseradish peroxidase that is 85% above controls. Five minutes after addition of antibody, the macrophage appears contracted and engorged and has persistent membrane changes consisting of pits, openings, and membrane folds. Trypsin causes slow ingestion of surface mycoplasmas without the obvious membrane folding over organisms but with evidence of a predominantly invaginating process of phagocytosis. The macrophage surface has numerous microprojections, but is does not have the granular appearance seen after addition of antibody. Trypsin and Mycoplasma pulmonis antigen do not enhance macrophage pinocytic rates. (Am J Pathol 87:347-358, 1977).
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohn Z. A., Parks E. The regulation of pinocytosis in mouse macrophages. IV. The immunological induction of pinocytic vesicles, secondary lysosomes, and hydrolytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction in vitro of Mycoplasma pulmonis with mouse peritoneal macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):231–259. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Yeh S., Hirsch J. G. Studies on attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis of Mycoplasma pulmonis by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):464–470. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polliack A., Gordon S. Scanning electron microscopy of murine macrophages. Surface characteristics during maturation, activation, and phagocytosis. Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;33(5):469–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H. Interactions of actin, myosin, and a new actin-binding protein of rabbit pulmonary macrophages. II. Role in cytoplasmic movement and phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):602–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]