Abstract
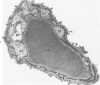
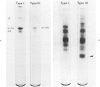
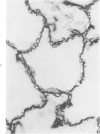
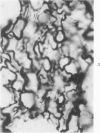
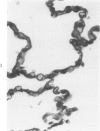
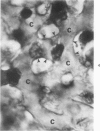
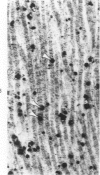
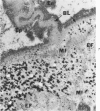
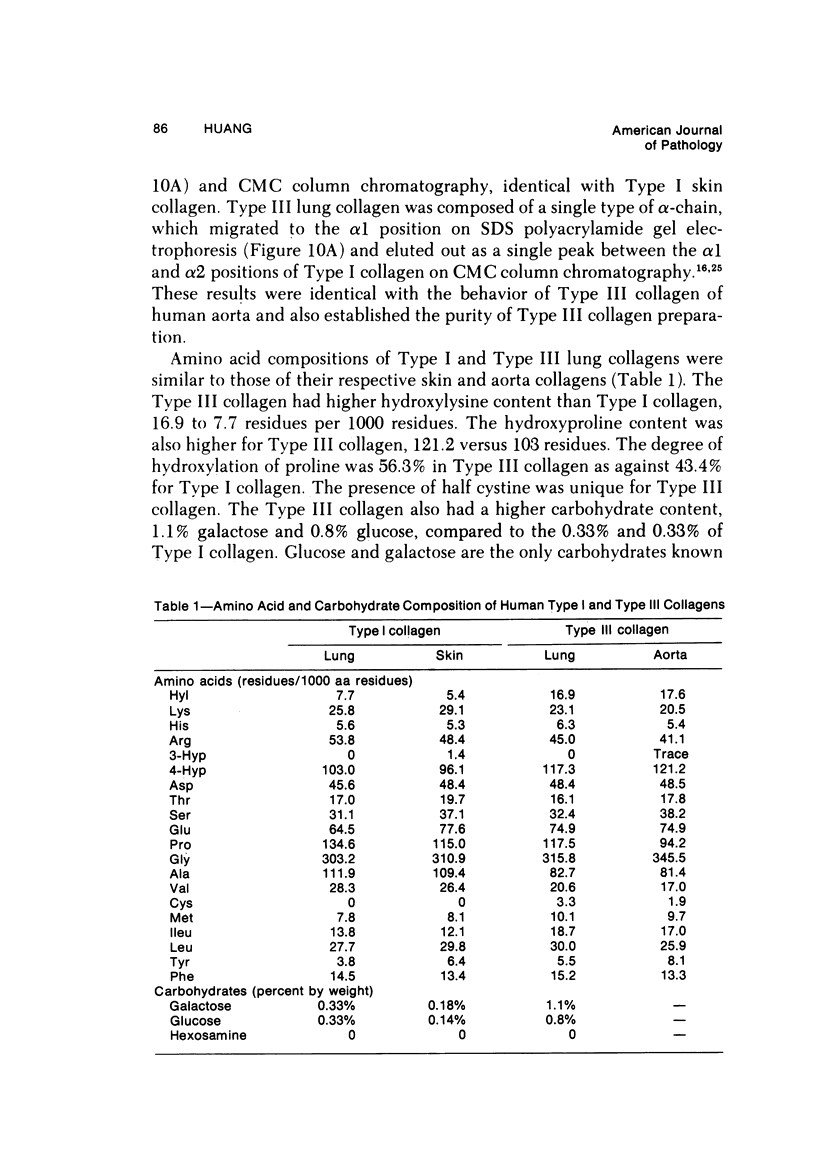
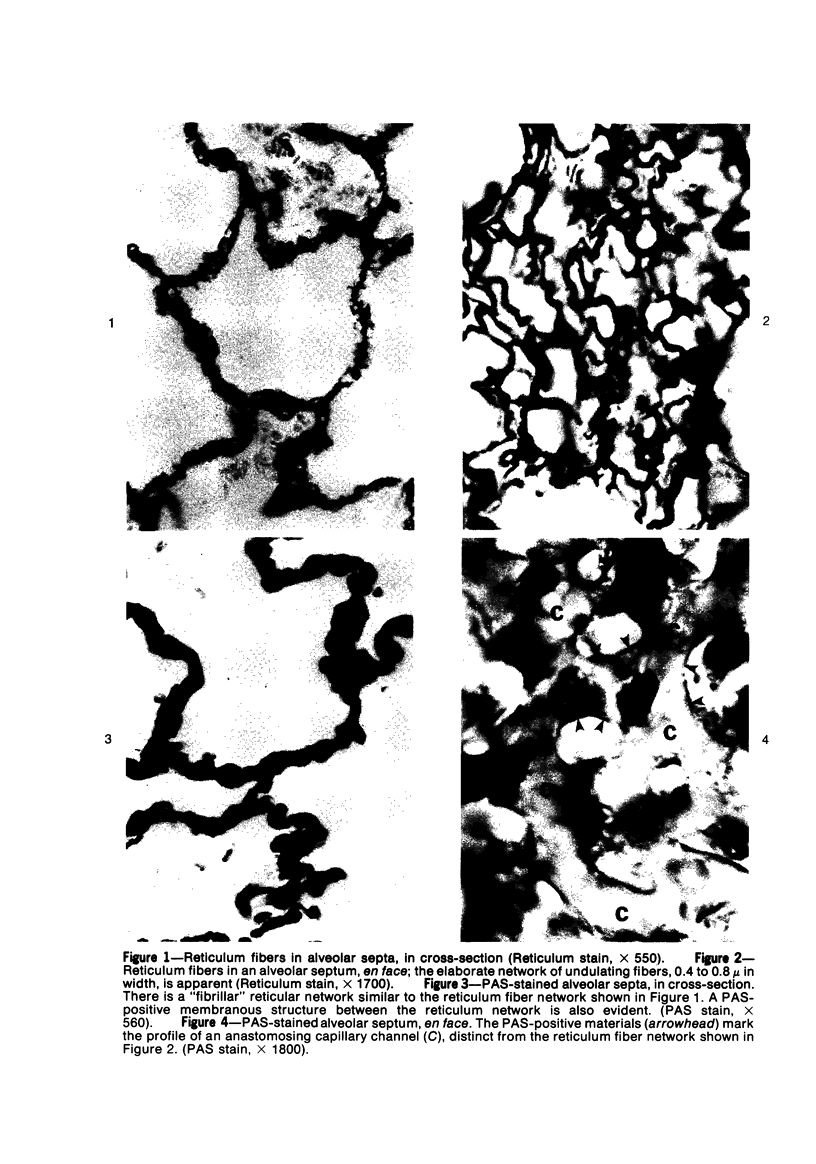
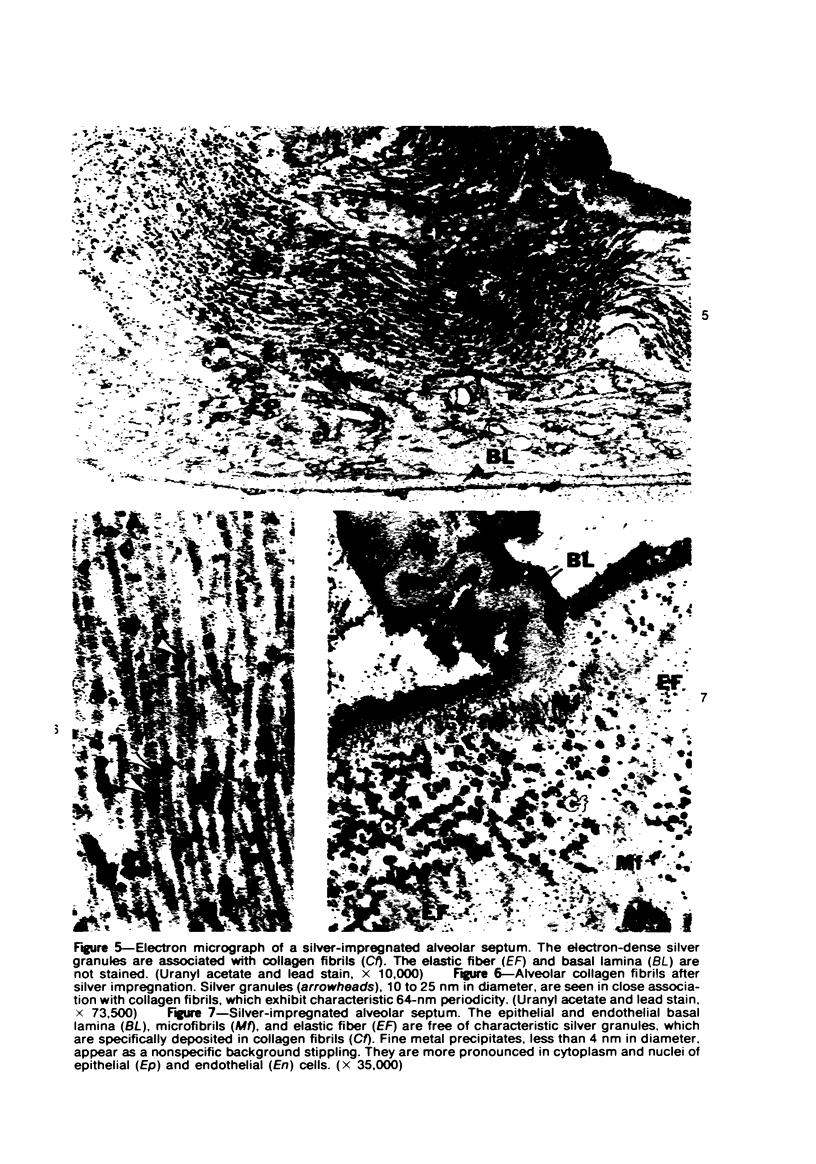
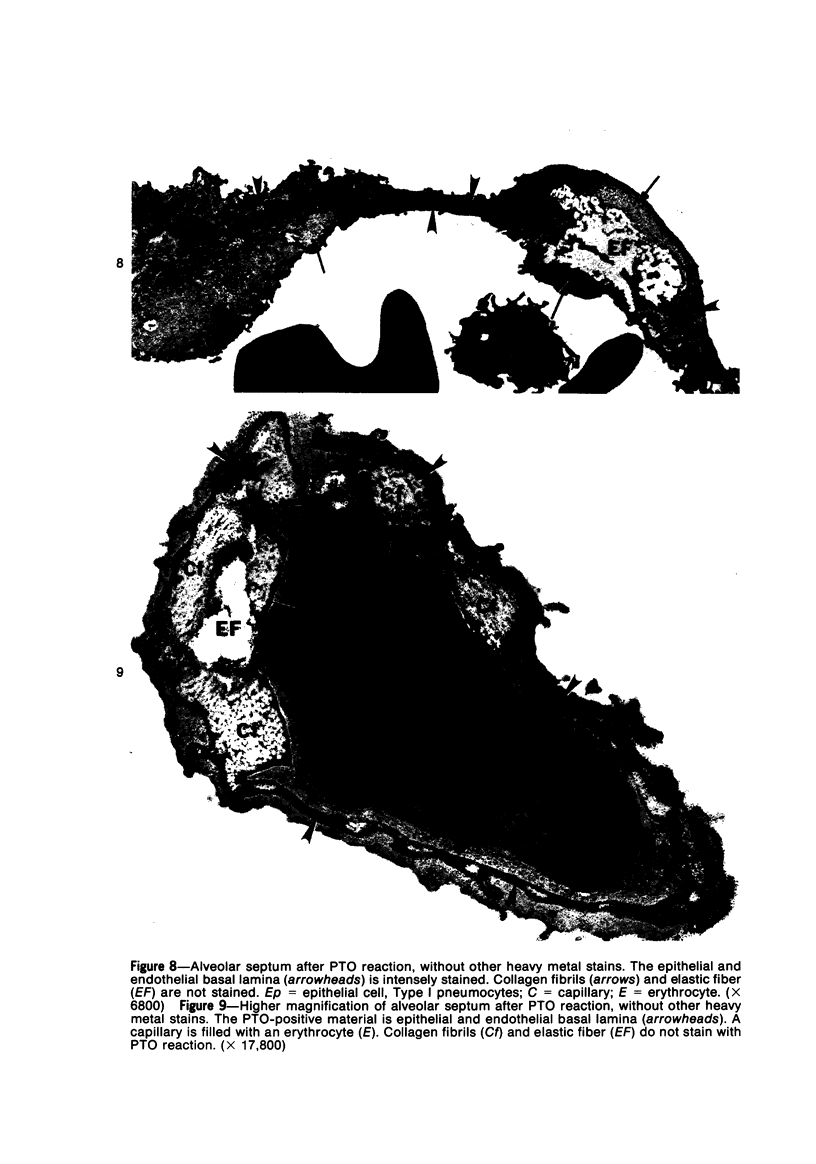
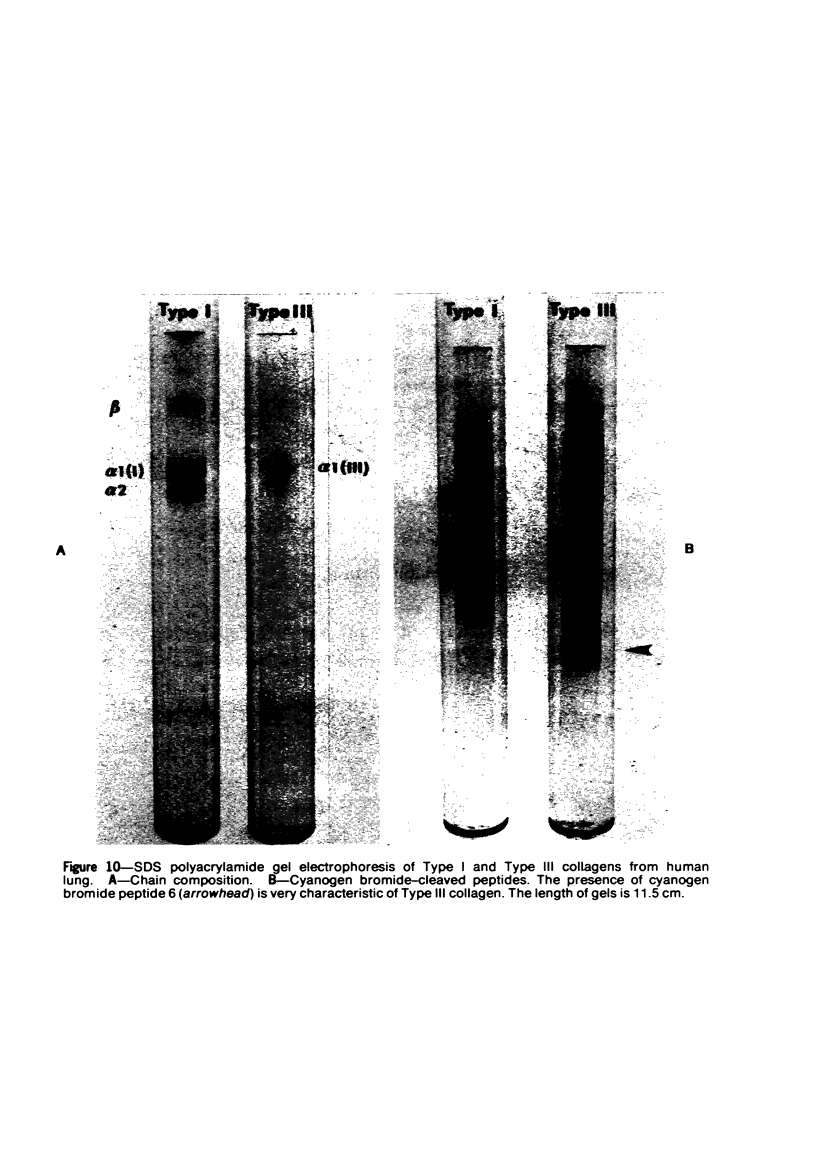
Light and electron microscopic studies have established that the normal human alveolar argyrophilic (reticulum) fiber is collagen fiber. The silver impregnation method is highly sensitive and specific for histologic demonstration of the elaborate collagen fiber network of alveolar septa. The argyrophilic alveolar collagen fiber does not stain with the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) or periodic acid-thiocarbohydrazide-osmium tetroxide (PTO) reaction. The materials positive for the PAS and PTO reactions in alveolar septa are epithelial and endothelial basal laminas, which are nonargyrophilic. Chemically, lung collagen fibers are composed of Type I and Type III collagens, which differ in amino acid composition, chain composition, and carbohydrate content. The chemical heterogeneity of lung collagen may have important biologic implications in the maintenance of normal structure and in the repair of lung injury.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chung E., Keele E. M., Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(3) chain of human collagen. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3459–3464. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Miller E. J. Collagen polymorphism: characterization of molecules with the chain composition (alpha 1 (3)03 in human tissues. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G. Lung collagen: definition, diversity and development. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2248–2255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr (Alpha1(3))3 human skin collagen. Release by pepsin digestion and preponderance in fetal life. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3225–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr, Munderloh N. H. Isolation and characterization of CNBr peptides of human (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagen and tissue distribution of (alpha 1 (I) )2 alpha 2 and (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagens. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9304–9312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESE W., GIESEKING R. Die submikroskopische Struktur des fibrillären Grundgerüstes der Alveolarwand. Beitr Pathol Anat. 1957;117(1):17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLEGG R. E., EIDINGER D., LEBLOND C. P. Some carbohydrate components of reticular fibers. Science. 1953 Nov 20;118(3073):614–616. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3073.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J. Connective tissue fine structure and some methods for its analysis. J Gerontol. 1950 Oct;5(1-4):343–360. doi: 10.1093/geronj/5.4.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt R., Berman E. R. A rapid procedure for the estimation of amino sugars on a micro scale. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Bradley K., Crystal R. G. Lung collagen heterogeneity. Synthesis of type I and type III collagen by rabbit and human lung cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):102–111. doi: 10.1172/JCI108250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Crystal R. G. The connective tissue of lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Nov;112(5):657–711. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. W., Lagunoff D., Benditt E. P. Nonaggregative adherence of platelets to basal lamina in vitro. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):156–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVING E. A., TOMLIN S. G. Collagen, reticulum and their argyrophilic properties. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Feb 18;142(906):113–125. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R., Andrews F. A. Lung scleroproteins in age and emphysema. Chest. 1970 Mar;57(3):239–244. doi: 10.1378/chest.57.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAHL V. E. Microscopic anatomy of the lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Jul;80(1 Pt 2):24–44. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.1P2.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Assimacopoulos A., Irle C., Zwahlen A., Gabbiani G. "Contractile interstitial cells" in pulmonary alveolar septa: a possible regulator of ventilation-perfusion ratio? Ultrastructural, immunofluorescence, and in vitro studies. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):375–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Denduchis B. Structural components of epithelial and endothelial basement membranes. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4613–4621. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Isolation and characterization of the collagen from glomerular basement membrane. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3103–3112. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Winzler R. J. The chemistry of glomerular basement membrane and its relation to collagen. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):702–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Dowell A. R. Connective tissue of the lung. Introduction. Arch Intern Med. 1971 May;127(5):845–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P., BERTALANFFY F. D. Reticulin membranes as the framework of alveolar lung tissue in the albino rat. Can Med Assoc J. 1951 Sep;65(3):263–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LHOTKA J. F., DAVENPORT H. A. Staining similarity of Foot's and HIO4-Schiff technics. Stain Technol. 1950 Jul;25(3):129–131. doi: 10.3109/10520295009110974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Glagov S., Mathews M. B. Cyclic stretching stimulates synthesis of matrix components by arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):475–477. doi: 10.1126/science.128820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory F. B., Parker F. Reticulum. Am J Pathol. 1927 Sep;3(5):515–526.21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Epstein E. H., Jr, Piez K. A. Identification of three genetically distinct collagens by cyanogen bromide cleavage of insoluble human skin and cartilage collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE J. A., HOCOTT J. B. Studies on the collagen and elastin content of the human lung. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:8–14. doi: 10.1172/JCI104030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Shafer J. Lung connective tissue measurements. I. Amino acid analysis procedures for determination of canine lung connective tissue. Arch Intern Med. 1971 May;127(5):891–895. doi: 10.1001/archinte.127.5.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remberger K., Gay S., Fietzek P. P. Immunohistochemische Untersuchungen zur Kollagencharakterisierung in Lebercirrhosen. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1975 Aug 12;367(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00430710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLIDDERS W., FRASER D. S., LENDRUM A. C. Silver impregnation of reticulin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(2):478–481. doi: 10.1002/path.1700750233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman A. M., Hanker J. S., Wasserkrug H., Dmochowski H., Katzoff L. Histochemical demonstration of some oxidized macromolecules with thiocarbohydrazide (tch) or thiosemicarbazide (TSC) and osmium tetroxide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Nov-Dec;13(8):629–639. doi: 10.1177/13.8.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Characterization and quantitative determination of the hydroxylysine-linked carbohydrate units of several collagens. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):602–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Characterization and quantitative determination of the hydroxylysine-linked carbohydrate units of several collagens. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):602–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L. Human aorta collagens: evidence for three distinct species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNES M. S., STEELE H. D., ROBERTSON E. M., BENCOSME S. A. CORRELATIVE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE BASEMENT MEMBRANE OF THE HUMAN ECTOCERVIX. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 May 15;92:163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(65)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]