Abstract
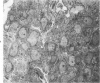
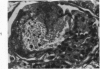
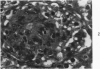
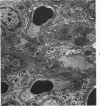
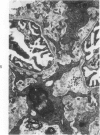
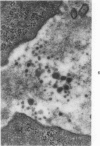
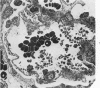
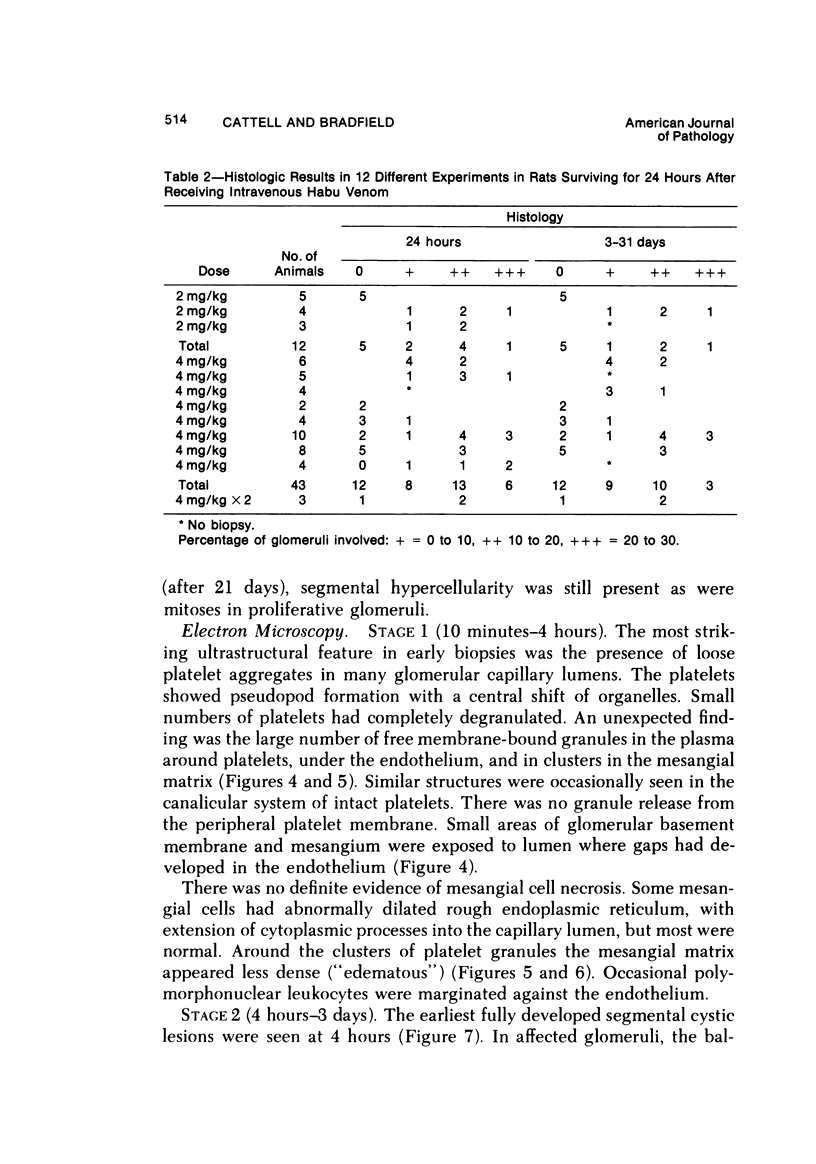
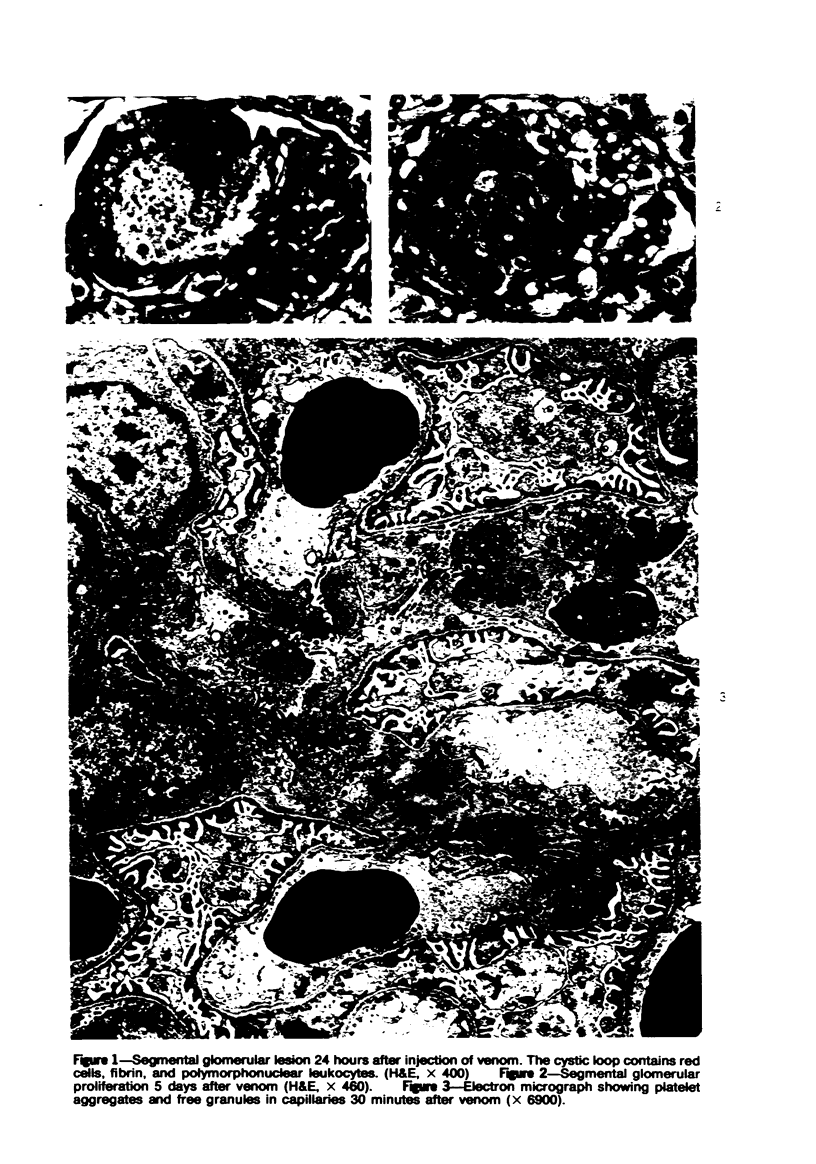
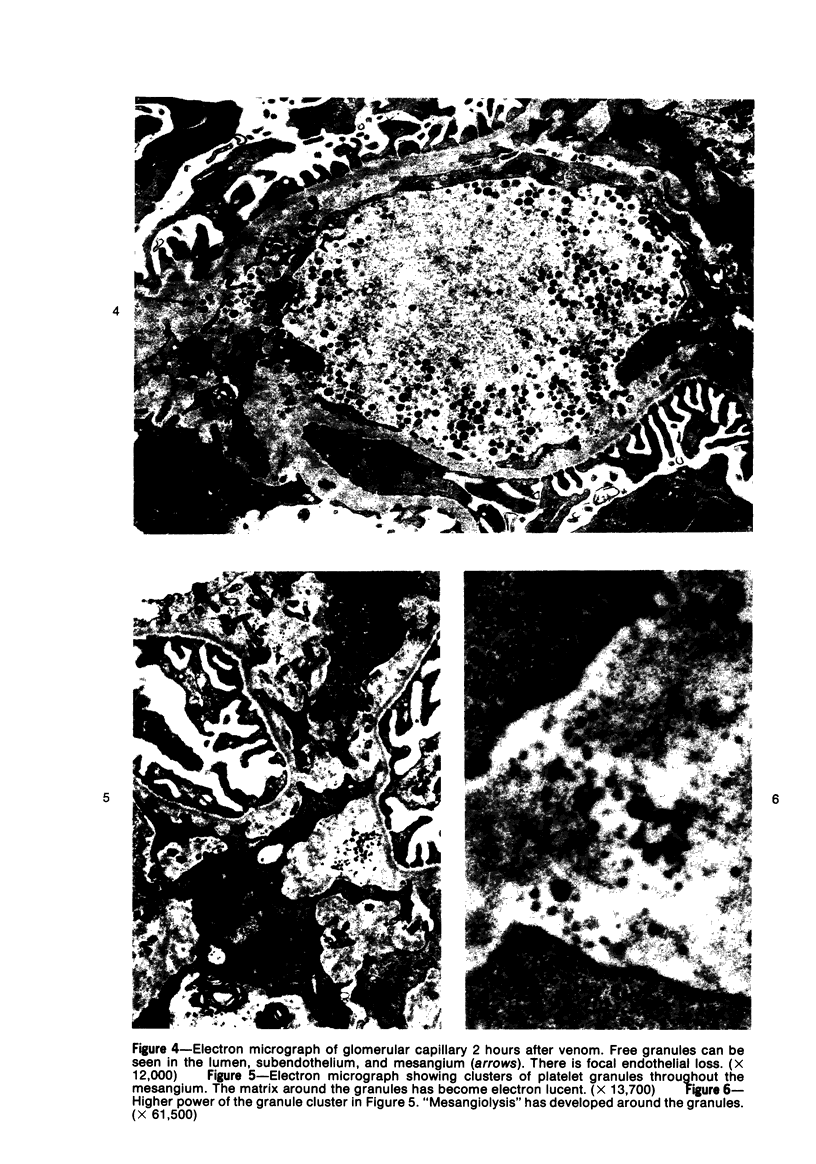
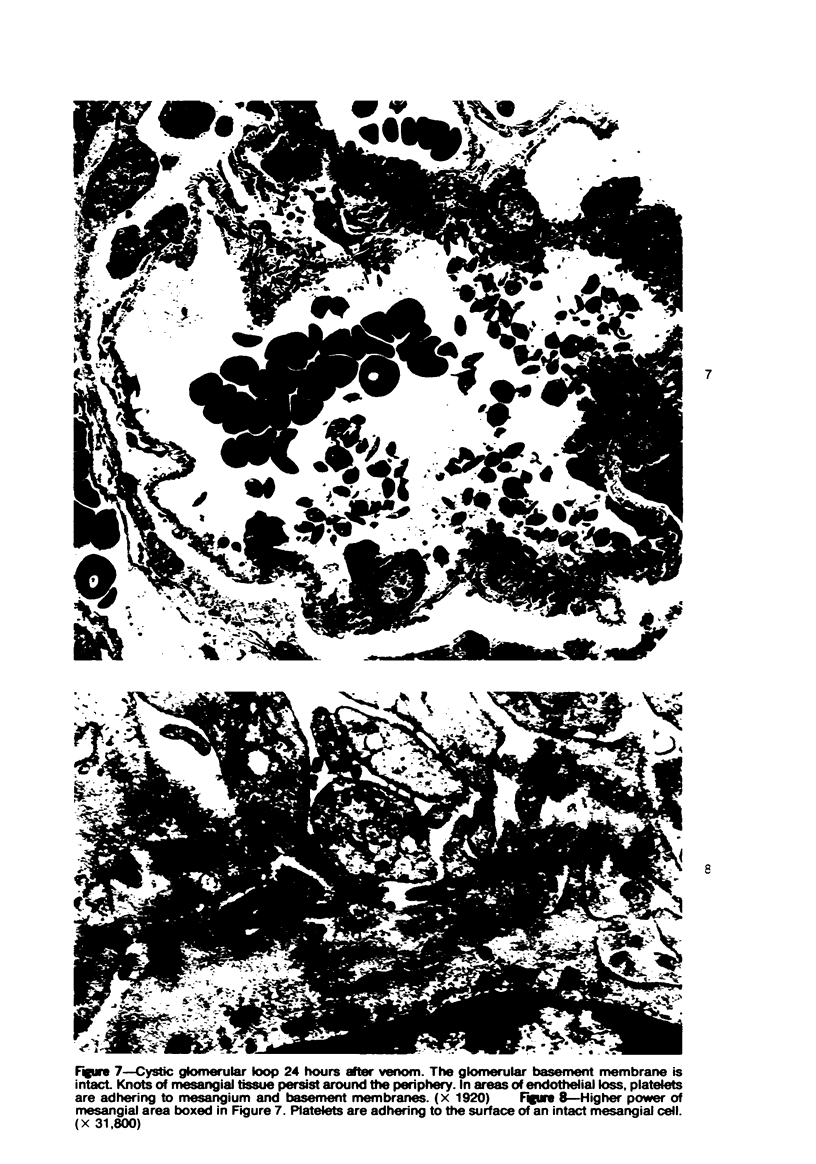
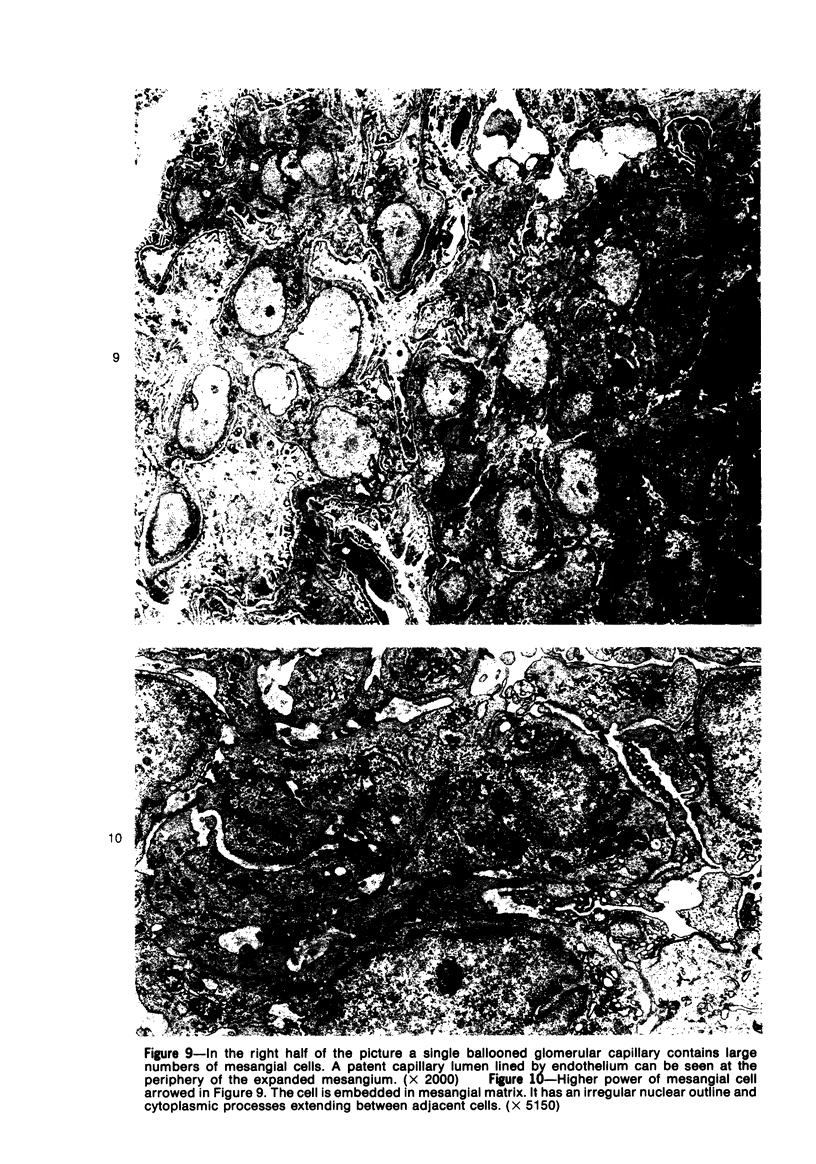
A new model of focal mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis in the rat has been produced by intravenous habu snake venom. Glomerulonephritis developed in 70% of rats surviving the first 6 hours after venom administration. The earliest ultrastructural change (10 minutes after venom) was the presence of loose platelet aggregates and free granules in the capillary lumen and mesangium. This was followed by dissolution of the matrix and endothelial damage. Between 4 and 24 hours, a characteristic focal and segmental ballooned lesion of glomerular capillaries developed. In these lesions, from 3 days onwards a segmental mesangial proliferation occurred, which persisted until sacrifice at 21 days.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busch C., Wasteson A., Westermark B. Release of a cell growth promoting factor from human platelets. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):493–500. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. F., Friesen M., Linton A. L., Lindsay R. M. The platelet as a mediator of tissue damage in immune complex glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1976 Jul;6(1):287–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. G., Lüscher E. F. Actions of some coagulant snake venoms on blood platelets. Nature. 1965 Aug 14;207(998):730–732. doi: 10.1038/207730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAERTNER C., GOLDBLUM N., GITTER S., DE VRIES A. The action of various snake venoms and their chromatographic fractions on animal cells in culture. J Immunol. 1962 Apr;8:526–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kosuge T., Okonogi T., Hattori Z., Sawai Y. A histopathological study on arterial lesions caused by Habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Aug;37(4):323–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSHUA H., DJALDETTI M., OZCAN E., BESSLER H., ROSEN M., DE VRIES A. MECHANISM OF THROMBOCYTOPENIA IN THE DOG AND THE GUINEA PIG FOLLOWING ECHIS COLORATA VENOM INOCULATION. Hemostase. 1964 Dec;4:333–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Porras J. M. Biochemistry of snake venoms. Clin Toxicol. 1970 Sep;3(3):389–431. doi: 10.3109/15563657008990116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen L., Glynn M. F., Hovig T., Murphy E. A., Buchanan M. R., Mustard J. F. Renal lesions and rise in blood pressure caused by adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in rabbits. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):347–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Shigematsu H., Okabayashi A. Cellular aspects of rabbit Masugi nephritis. III. Mesangial changes. Lab Invest. 1976 Apr;34(4):363–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenhaupt R., Nathan P. Platelet accumulation observed by electron microscopy in the early phase of renal allotransplant rejection. Nature. 1968 Nov 23;220(5169):822–825. doi: 10.1038/220822b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrazo A., Suzuki Y., Churg J. Radiation nephritis: acute changes following high dose of radiation. Am J Pathol. 1969 Mar;54(3):507–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Moroz C., De Vries A., Csavossy I., Cruse V. The action of hemorrhagin and phospholipase derived from Vipera palestinae venom on the microcirculation. Lab Invest. 1970 May;22(5):387–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Kainer R. A., Tu A. T. Pathogenesis of hemorrhage induced by rattlesnake venom. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):401–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford R. B., Ross R. Platelet factors stimulate fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells quiescent in plasma serum to proliferate. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):196–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAGUCHI H., KAWAMURA S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE MESANGIOLYSIS. THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF THE "HABU SNAKE" VENOM ON THE RENAL GLOMERULUS. Keio J Med. 1963 Jun;12:99–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandbank U., Jerushalmy Z., Ben-David E., De Vries A. Effect of Echis coloratus venom on brain vessels. Toxicon. 1974 May;12(3):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. E., Abdelbaki Y. Z., Tu A. T. Nephrotoxic action of rattlesnake and sea snake venoms: an electron-microscopic study. J Pathol. 1976 Feb;118(2):75–81. doi: 10.1002/path.1711180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedat Y. K., Reddy J., Edington D. A. Acute renal failure due to proliferative nephritis from snake bite poisoning. Nephron. 1974;13(6):455–463. doi: 10.1159/000180424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. A quantitative evaluation of anticoagulants in experimental nephrotoxic nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Feb;19(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., SIMON G., ROUILLER C. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF PLATELET CHANGES INITIATED IN VIVO BY THROMBIN. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Oct;11:374–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinazzer H. Coagulation studies during therapeutic application of arvin. Thromb Res. 1976 Feb;8(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Exocytosis of secretory organelles from blood platelets incubated with cationic polypeptides. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):41–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Ogawa H., Osaka A., Omori-Sato T. Action of Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom and the partially purified hemorrhagic principles on animal cells cultivated in vitro. Toxicon. 1966 Nov;4(3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(66)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]