Abstract
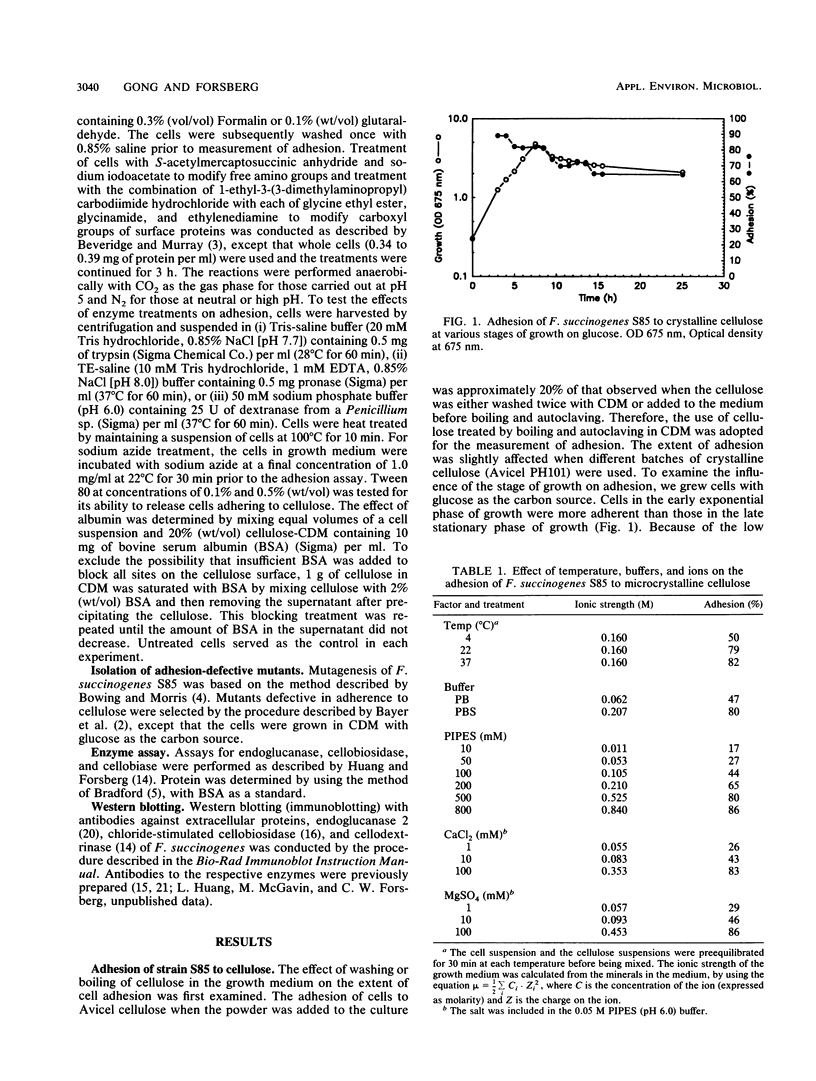
Fibrobacter succinogenes subsp. succinogenes S85, formerly Bacteroides succinogenes, adheres to crystalline cellulose present in the culture medium. When the cells are suspended in buffer, adhesion is enhanced by increasing the ionic strength. Heat, glutaraldehyde, trypsin, and pronase treatments markedly reduce the extent of adhesion. Treatment with dextrinase, modification of amino and carboxyl groups with Formalin or other chemical agents, and inclusion of either albumin (1%) or Tween 80 (0.5%) do not decrease the degree of adhesion. Adherence-defective mutants isolated by their inability to bind to cellulose exhibited different growth characteristics. Class 1 mutants grew on glucose, cellobiose, amorphous cellulose, and crystalline cellulose. Class 3 mutants grew on glucose and cellobiose but not on amorphous or crystalline cellulose. No substantial changes were detected in the endoglucanase, cellobiosidase, and cellobiase activities of the wild type and the mutants. These data suggest that adhesion to crystalline cellulose is specific and that it involves surface proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andro T., Chambost J. P., Kotoujansky A., Cattaneo J., Bertheau Y., Barras F., Van Gijsegem F., Coleno A. Mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi defective in secretion of pectinase and cellulase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1199-1203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Kenig R., Lamed R. Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):818–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.818-827.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowring S. N., Morris J. G. Mutagenesis of Clostridium acetobutylicum. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;58(6):577–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Beveridge T. J., Hellstrom A. Cellulase and Xylanase Release from Bacteroides succinogenes and Its Importance in the Rumen Environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):886–896. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.886-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Lam K. Use of adenosine 5'-triphosphate as an indicator of the microbiota biomass in rumen contents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):528–537. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.528-537.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Forsberg C. W. Isolation of a Cellodextrinase from Bacteroides succinogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1034–1041. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1034-1041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Forsberg C. W. Purification and Comparison of the Periplasmic and Extracellular Forms of the Cellodextrinase from Bacteroides succinogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1488–1493. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1488-1493.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Forsberg C. W., Thomas D. Y. Purification and characterization of a chloride-stimulated cellobiosidase from Bacteroides succinogenes S85. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2923–2932. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2923-2932.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo H., Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Electron microscopic study of the methylcellulose-mediated detachment of cellulolytic rumen bacteria from cellulose fibers. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Mar;33(3):267–272. doi: 10.1139/m87-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Naimark J., Morgenstern E., Bayer E. A. Specialized cell surface structures in cellulolytic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3792–3800. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3792-3800.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin M., Forsberg C. W. Catalytic and substrate-binding domains of endoglucanase 2 from Bacteroides succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3310–3315. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3310-3315.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin M., Forsberg C. W. Isolation and characterization of endoglucanases 1 and 2 from Bacteroides succinogenes S85. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2914–2922. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2914-2922.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



