Abstract
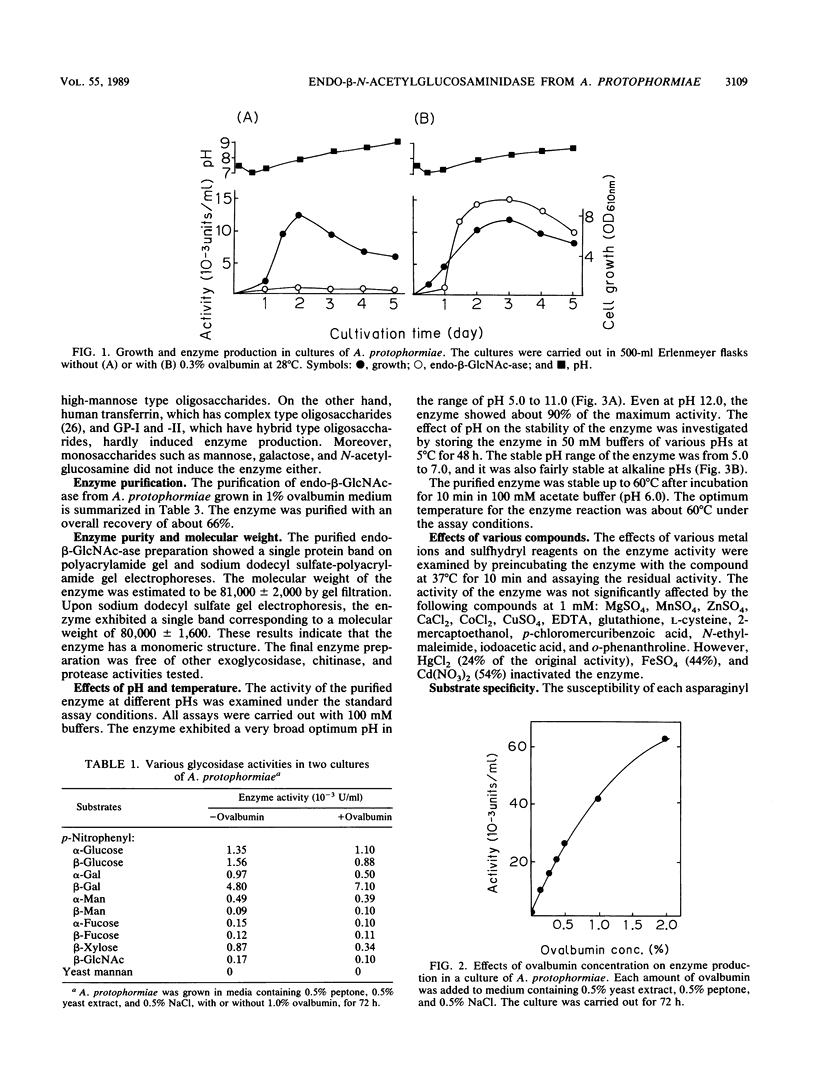
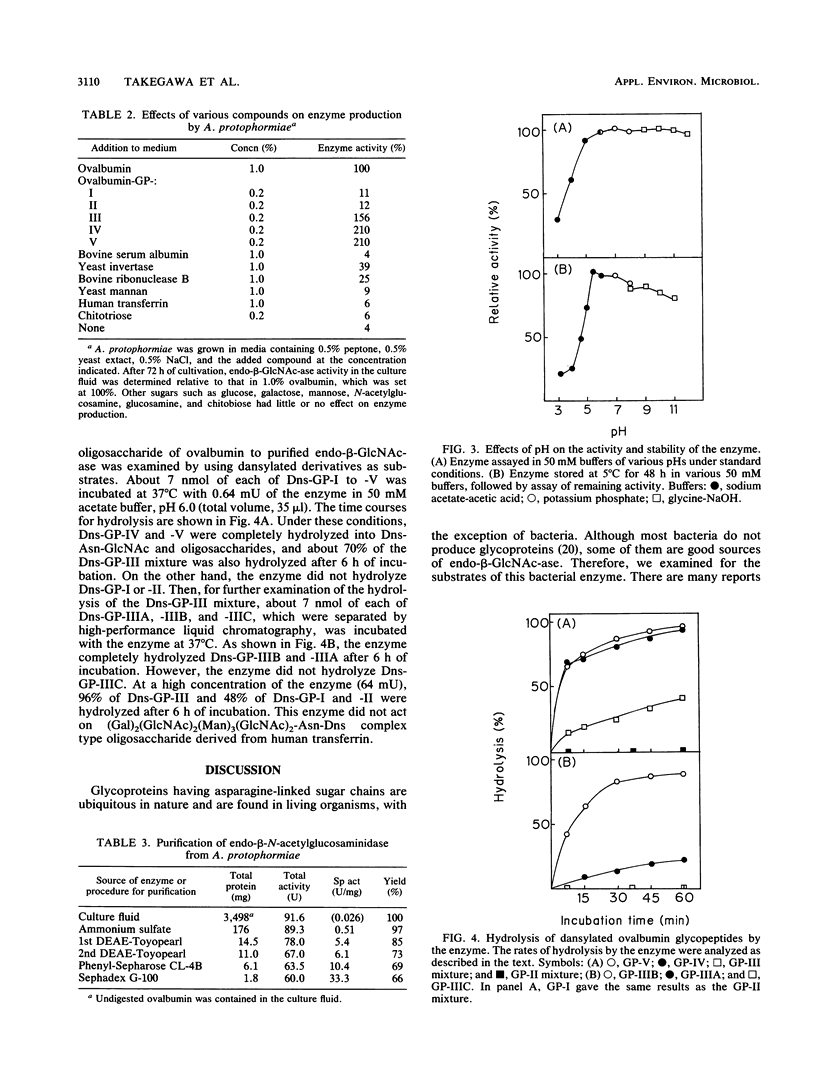
Arthrobacter protophormiae produced a high level of extracellular endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase when cells were grown in a medium containing ovalbumin. The enzyme was induced by the glycopeptide fraction of ovalbumin prepared by pronase digestion. Production of the enzyme was also induced by glycoproteins such as yeast invertase and bovine ribonuclease B but not by monosaccharides such as mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, and galactose. The enzyme was purified to homogeneity as demonstrated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and has an apparent molecular weight of about 80,000. The enzyme showed a broad optimum pH in the range of pH 5.0 to 11.0. The enzyme hydrolyzed all heterogeneous ovalbumin glycopeptides, although the hydrolysis rates for hybrid type glycopeptides were very low. The substrate specificity of A. protophormiae endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase was very similar to that of Endo-CII from Clostridium perfringens. Therefore, the enzyme induction by A. protophormiae seems to have a close relation to the substrate specificity of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER L. R., REYNOLDS D. M. The chitinase system of a strain of Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):522–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Cohen R. E., Zhang W. J., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate chains on yeast carboxypeptidase Y are phosphorylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Muramatsu T., Kobata A. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases acting on carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins: purification and properties of the two enzymes with different specificities from Clostridium perfringens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwase H., Li S. C., Li Y. T. Fractionation of Dns-glycopeptides by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1983 Sep 2;267(1):238–241. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwase H., Morinaga T., Li Y. T., Li S. C. Analysis of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity by high-pressure liquid chromatography on a silica-based chemically bonded octadecyl column. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide N., Muramatsu T. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase acting on carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4897–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauspe R., Scheer A. Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 dye-binding technique for determination of autolytic protein breakdown in Euglena gracilis and comparison to other methods of autolysis measurement. Anal Biochem. 1986 Mar;153(2):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Cohen R. E., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate structure of yeast invertase. Demonstration of a form with only core oligosaccharides and a form with completed polysaccharide chains. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12209–12218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C. J., Yamashita K., Kobata A. Structural study of the carbohydrate moiety of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease B. J Biochem. 1980 Jul;88(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. W., Jeffries T. W., Macmillan J. D. Production and ecological significance of yeast cell wall-degrading enzymes from oerskovia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):594–605. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.594-605.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F., Strominger J. L. Purification and characterization of a prokaryotic glucoprotein from the cell envelope of Halobacterium salinarium. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2005–2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minobe S., Nakajima H., Itoh N., Funakoshi I., Yamashina I. Structure of a major oligosaccharide of Taka-amylase A. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1851–1854. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Kozutsumi Y., Funakoshi I., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I., Mutsaers J. H., Van Halbeek H., Vliegenthart J. F. Structures of oligosaccharides on beta-galactosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):171–179. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Bayard B., Fournet B., Strecker G., Bouquelet S., Montreuil J. Studies on glycoconjugates. LXIV. Complete structure of two carbohydrate units of human serotransferrin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):296–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana Y., Yamashita K., Kobata A. Substrate specificity of mammalian endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase: study with the enzyme of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Ito S., Kobata A. Structures of the carbohydrate moiety of ovalbumin glycopeptide III and the difference in specificity of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases CII and H. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6687–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Ogata-Arakawa M., Koide N., Muramatsu T., Iwashita S., Inoue Y., Kobata A. Structural studies of two ovalbumin glycopeptides in relation to the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase specificity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8569–8575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegawa K., Kawasaki N., Iwahara S., Yamamoto K., Tochikura T., Mikami B., Morita Y. Primary structure of an N-linked sugar chain derived from glucoamylase of Rhizopus niveus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 27;990(1):98–100. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Tachibana Y., Kobata A. The structures of the galactose-containing sugar chains of ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3862–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


