Abstract
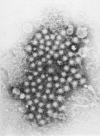
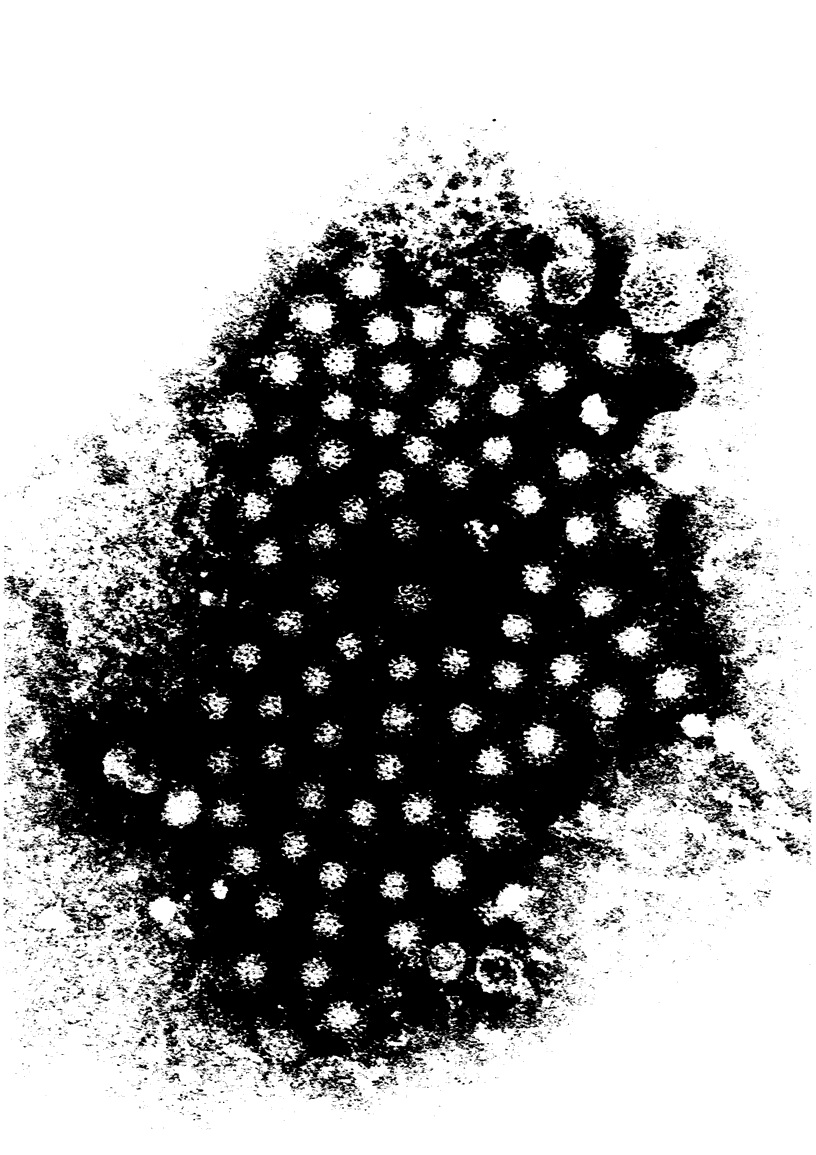
The basis for the epidemiologic and etiologic differentiation of two major forms of viral hepatitis, hepatitis A and B, was established in a series of studies undertaken between 1930 and 1970. Final recovery and visualization of the presumed etiologic agent of hepatitis A was not, however, accomplished until the technique of immune electron microscopy was applied to the examination of specimen materials collected from individuals in the early acute stages of infection. Morphologically homogeneous virus-like particles of 27 nm diameter have now been recovered from stools of patients with hepatitis A ill from a variety of sources. Antibody to these particles has been shown to develop during the course of infection with hepatitis A but not with hepatitis B and disease has been induced in nonhuman primates inoculated with purified particle containing fractions. The classification of hepatitis A virus has not been conclusively established, but it would appear to be either a parvovirus or an enterovirus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. The morphology of virus-antibody interaction. Adv Virus Res. 1969;15:307–338. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Hornbeck C. L., Cood E. H., Maynard J. E., Gravelle C. R. CsCl banding of hepatitis A-associated virus-like particles. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinhardt F., Holmes A. W., Capps R. B., Popper H. Studies on the transmission of human viral hepatitis to marmoset monkeys. I. Transmission of disease, serial passages, and description of liver lesions. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):673–688. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H. Buoyant density of the hepatitis A virus-like particle in cesium chloride. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1412–1414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1412-1414.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
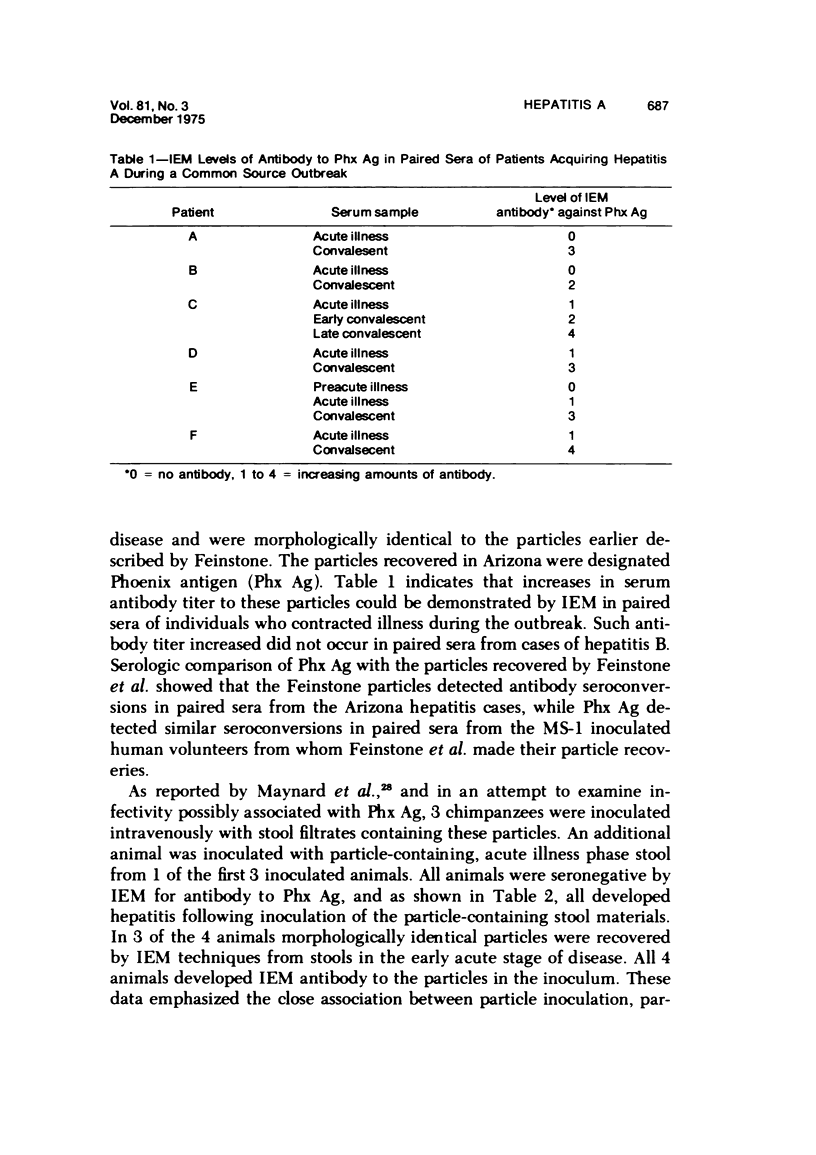
- Gravelle C. R., Hornbeck C. L., Maynard J. E., Schable C. A., Cook E. H., Bradley D. W. Hepatitis A: report of a common-source outbreak with recovery of a possible etiologic agent. II. Laboratory studies. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):167–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. W., Wolfe L., Deinhardt F., Conrad M. E. Transmission of human hepatitis to marmosets: further coded studies. J Infect Dis. 1971 Nov;124(5):520–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.5.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. W., Wolfe L., Rosenblate H., Deinhardt F. Hepatitis in marmosets: induction of disease with coded specimens from a human volunteer study. Science. 1969 Aug 22;165(3895):816–817. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3895.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1075–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1075-1081.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P., Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967 May 1;200(5):365–373. doi: 10.1001/jama.200.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leger R. T., Boyer K. M., Pattison C. P., Maynard J. E. Hepatitis A: report of a common-source outbreak with recovery of a possible etiologic agent. I. Epidemiologic studies. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):163–166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Stott A. C., Gust I. D. Letter: Pitfalls in hepatitis A? Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):1007–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascoli C. C., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Arguedas J. A., Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Recovery of hepatitis agents in the marmoset from human cases occurring in Costa Rica. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):276–282. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
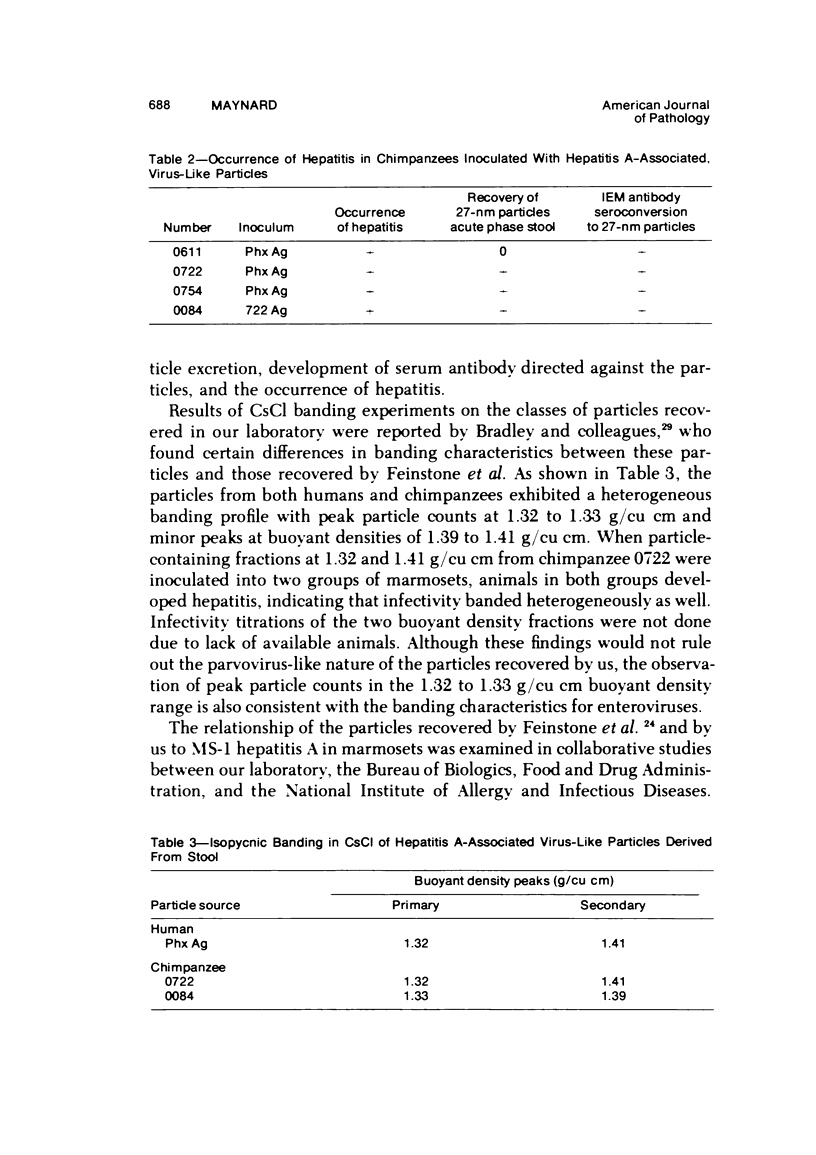
- Maynard J. E., Bradley D. W., Gravelle C. R., Ebert J. W., Krushak D. H. Preliminary studies of hepatitis A in chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):194–197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Melnick J. L. Attempted isolation of hepatitis viruses in marmosets. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):539–547. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Wolanski B. S., Miller W. J., Ittensohn O. L., McAleer W. J., Hilleman M. R. Physical, chemical and morphologic dimensions of human hepatitis A virus strain CR326 (38578). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):532–539. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]