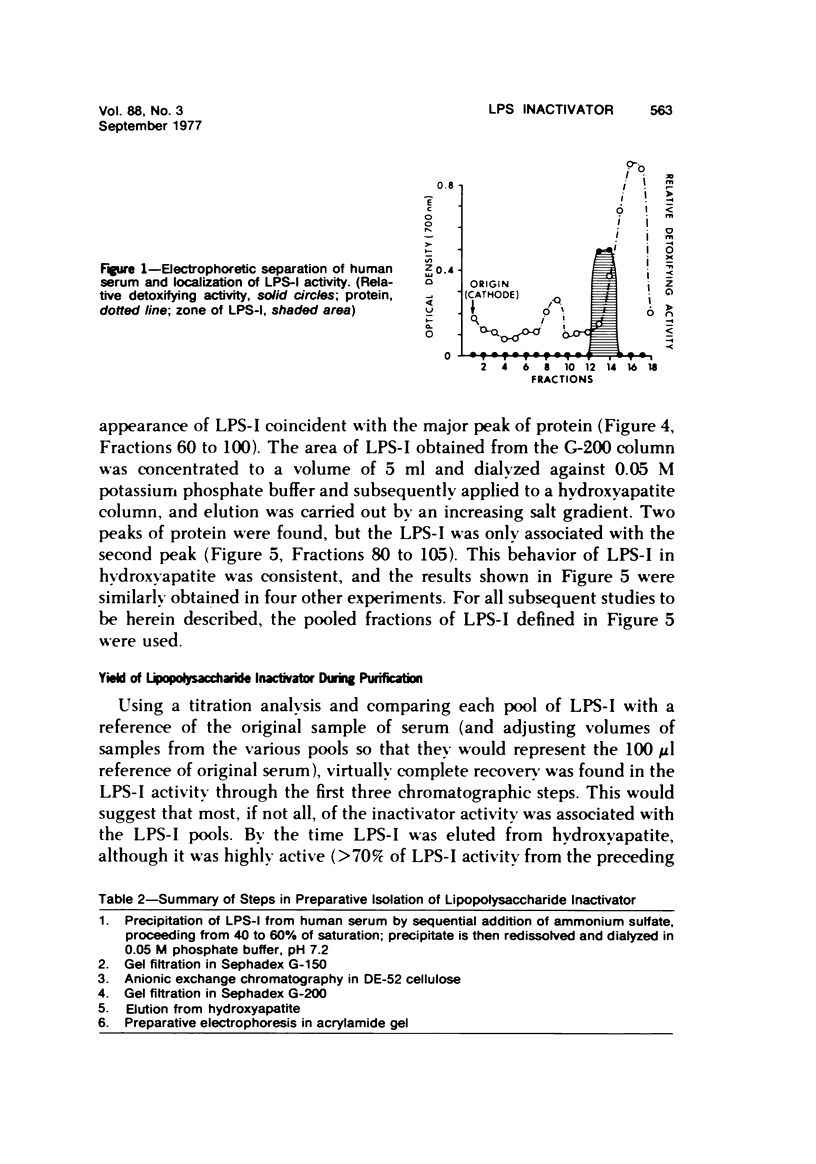
Abstract
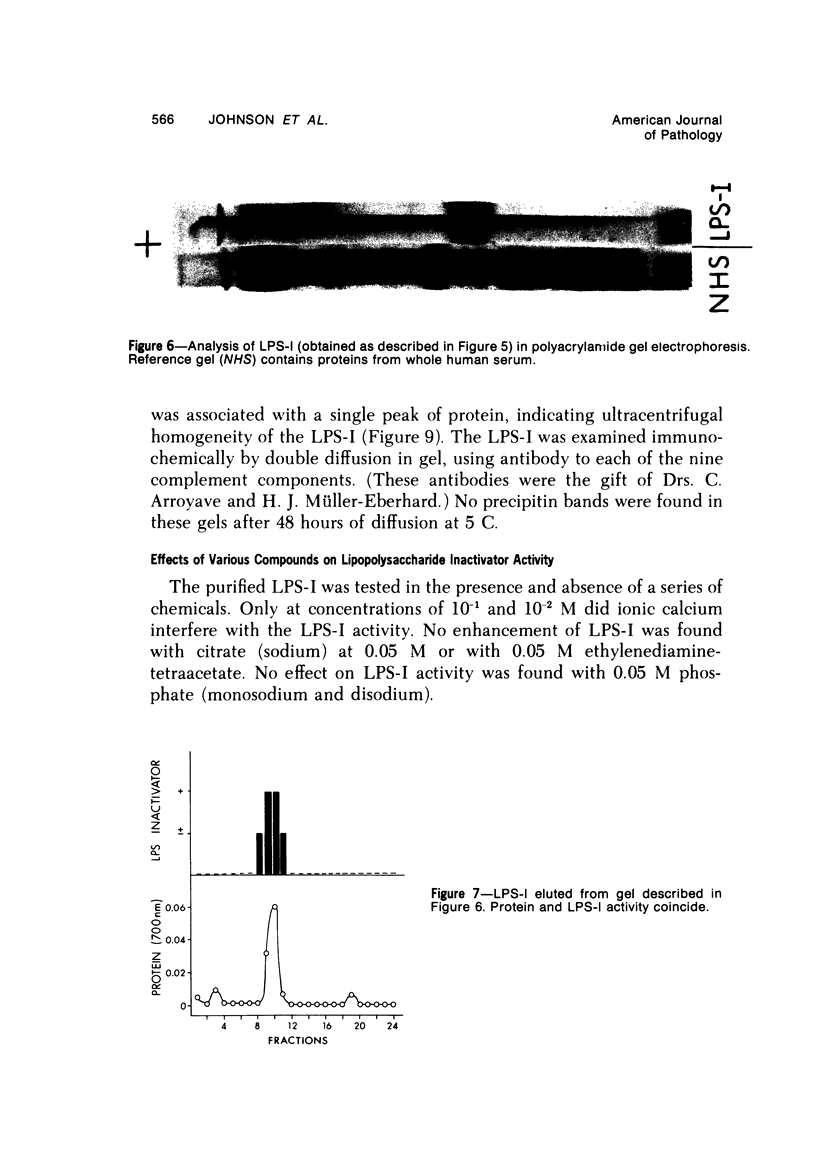
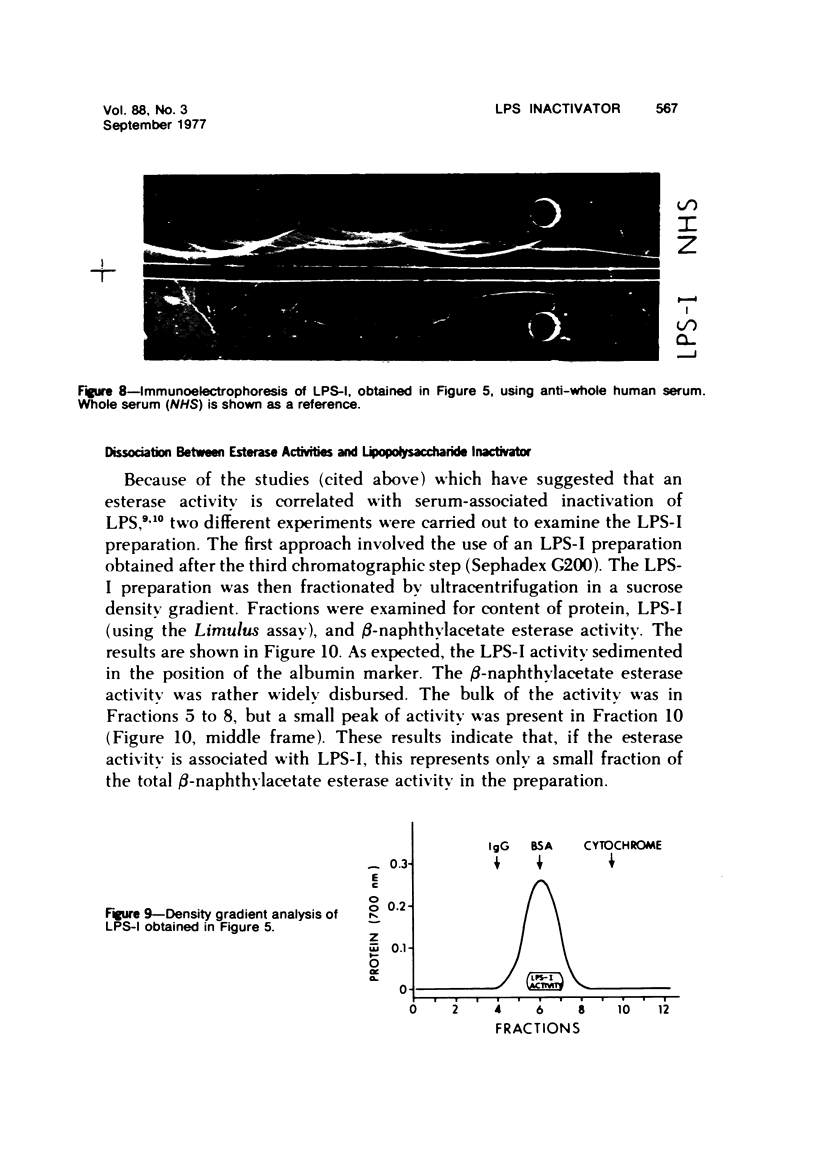
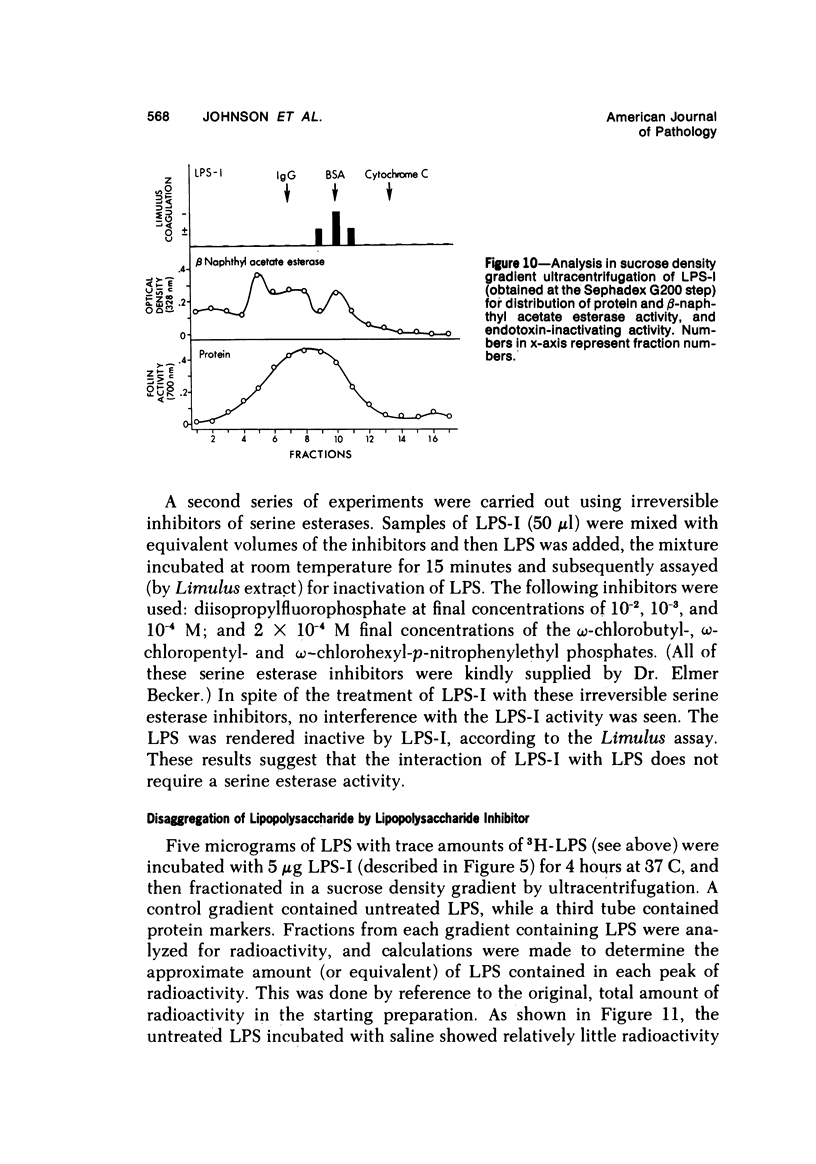
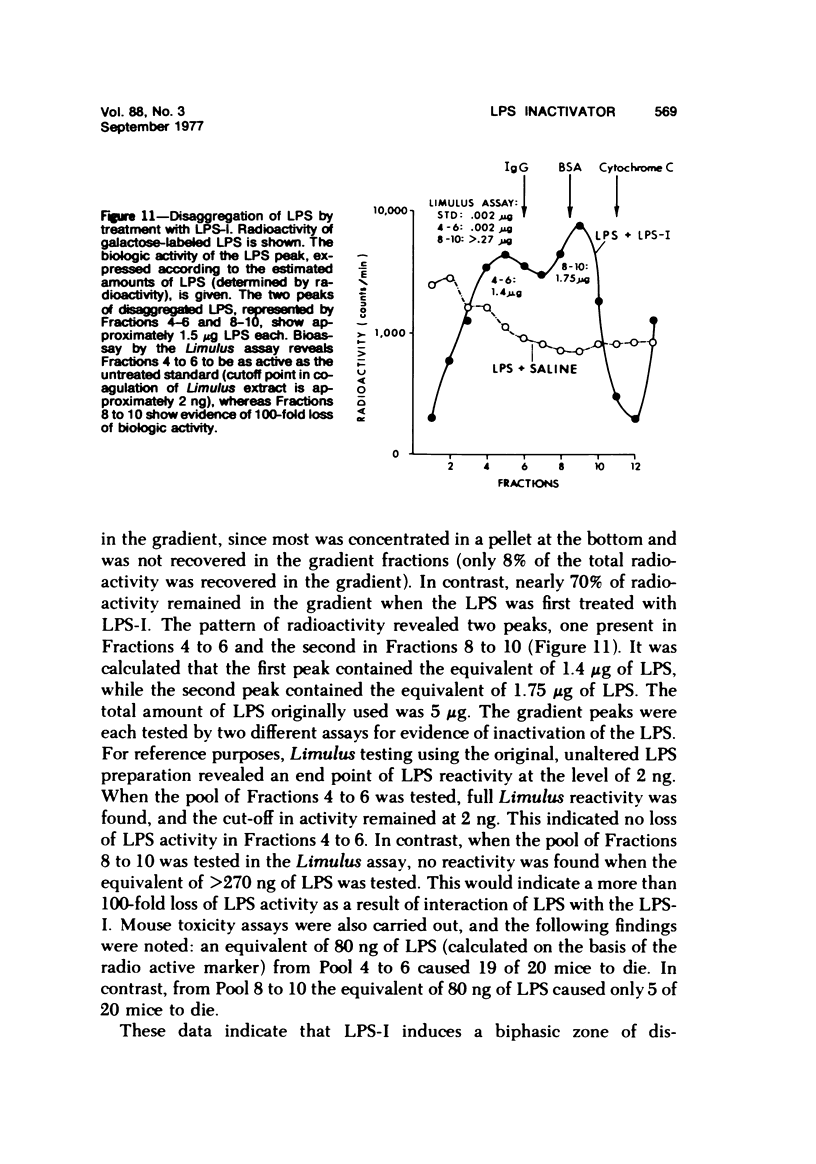
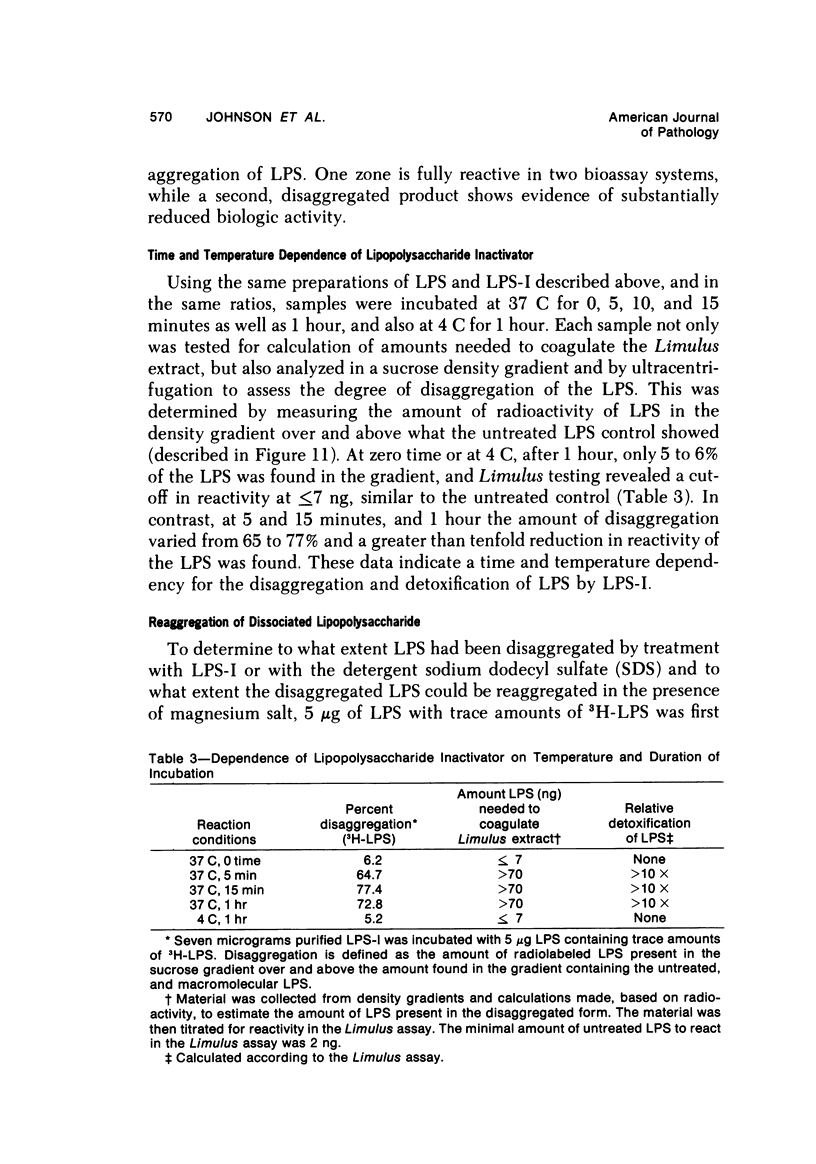
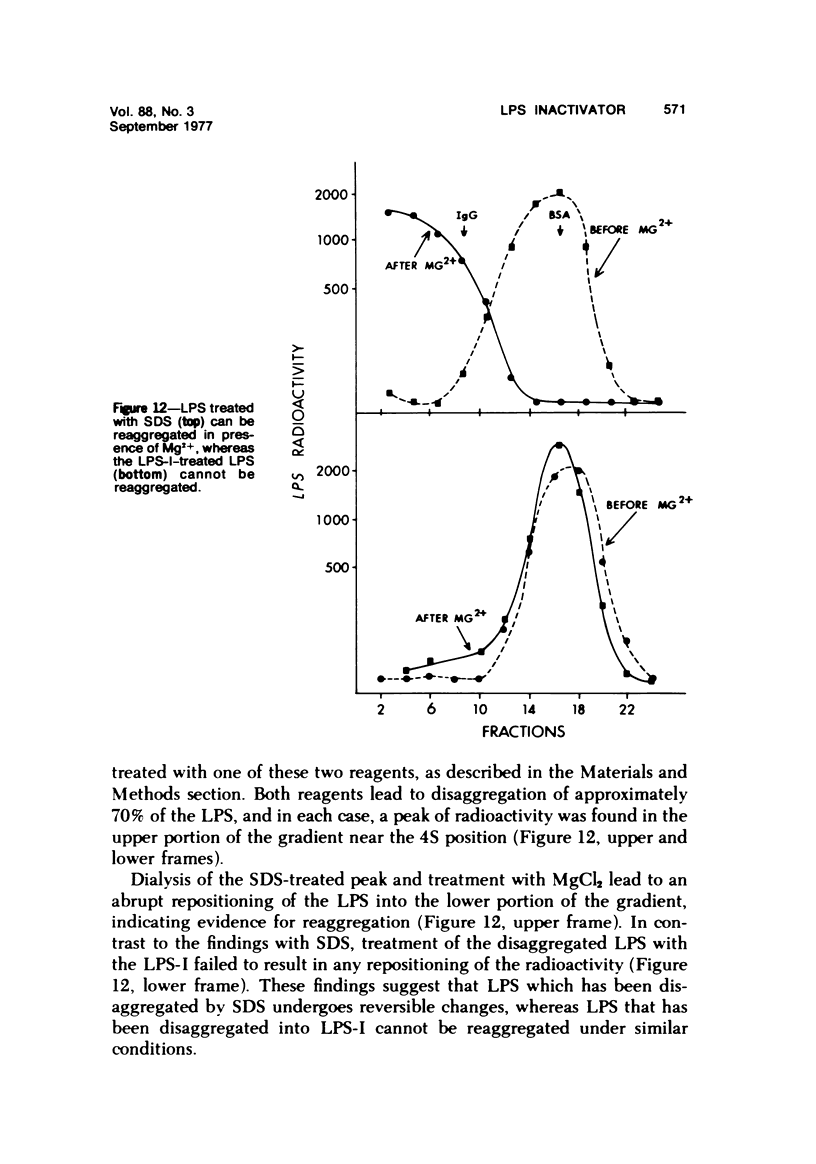
By a series of chromatographic procedures involving precipitation by salt, gel filtration, anionic exchange, and hydroxyapatite elution, a protein--termed the lipopolysaccharide inactivator (LPS-I)--has been isolated from normal human serum. As a result of treatment of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by LPS-I, the treated LPS loses its toxicity for mice and reactivity in the Limulus assay and appears to be irreversibly disaggregated. The inactivation of the LPS by the purified LPS-I is temperature and time dependent and is not blocked by the addition of irreversible inhibitors of serine esterases. The LPS inactivator migrates as an alpha-globulin in whole serum and has a sedimentation velocity of approximately 4.5S. Characteristics of the inactivated LPS are briefly described using internally labeled LPS.
Full text
PDF



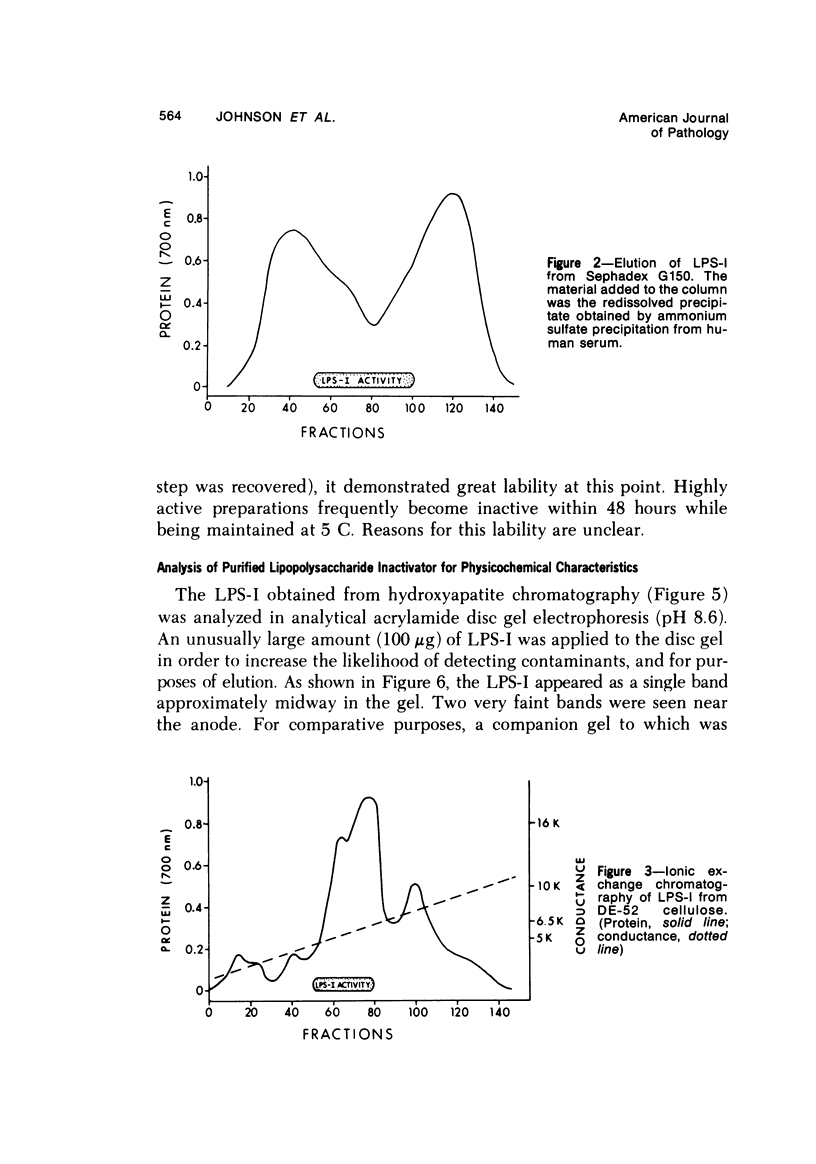
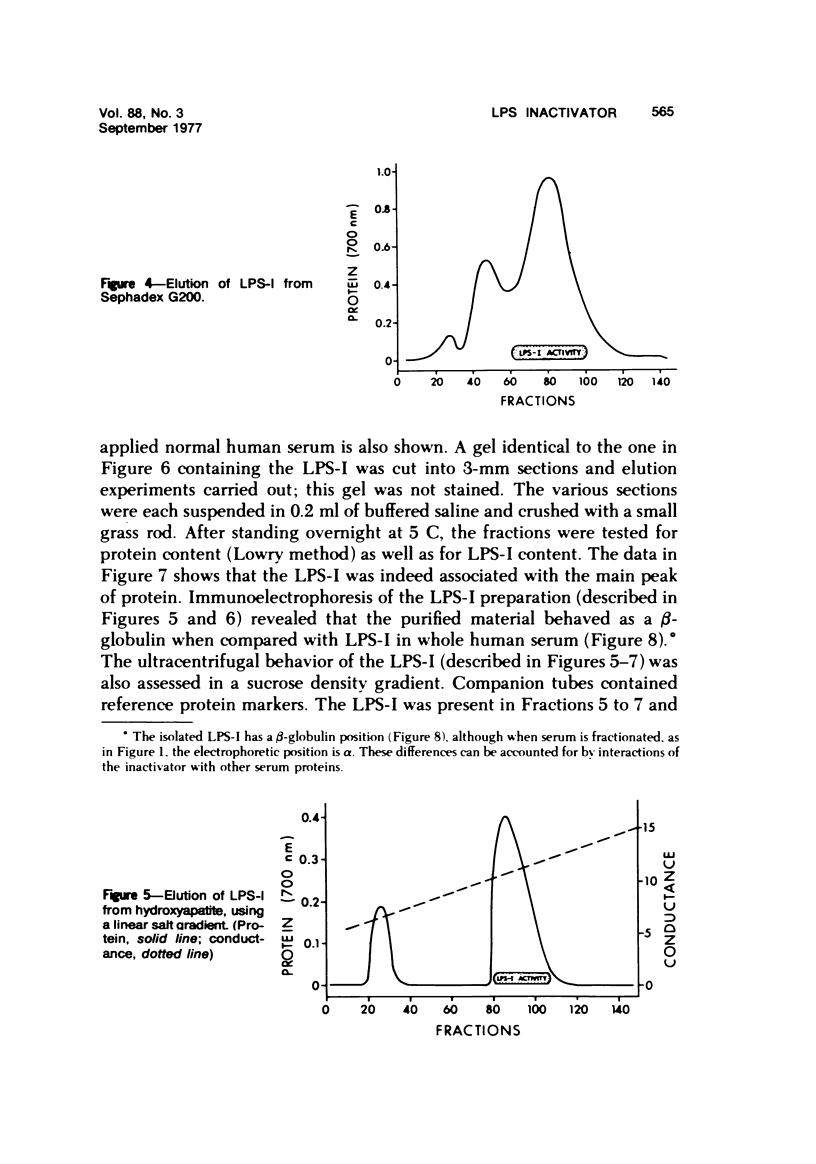



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braude A. I., Douglas H., Davis C. E. Treatment and prevention of intravascular coagulation with antiserum to endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):157–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. The requirement for serum complement in the detoxification of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., TRAPANI R. J., SHEAR M. J. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. IV. Alteration in the immunological properties of typhoid endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:731–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OROSZLAN S. I., MORA P. T. DISSOCIATION AND RECONSTITUTION OF AN ENDOTOXIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:345–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., HORECKER B. L. Biosynthesis of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. I. Enzymatic incorporation of galactose in a mutant strain of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1831–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDBACH J. A., JOHNSON A. G. Changes in serologic reactivity of endotoxin induced by fraction IV-1 (Cohn) of normal human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:651–655. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A., Anacker R. L., Haskins W. T., Johnson A. G., Milner K. C., Ribi E. Physical aspects of reversible inactivation of endotoxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):629–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A., Johnson A. G. Alteration and restoration of endotoxin activity after complexing with plasma proteins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):892–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.892-898.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKARNES R. C., ROSEN F. S., SHEAR M. J., LANDY M. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. II. Interaction of endotoxin with serum and plasma. J Exp Med. 1958 Nov 1;108(5):685–699. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUCH J. E., JOHNSON A. G. The alteration of bacterial endotoxins by human and rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1959 Mar;82(3):252–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Becker E. L. The alteration of endotoxin by postheparin plasma and purified fractions. II. Relationship of the endotoxin detoxifying activity of euglobulin from postheparin plasma to lipoprotein lipase. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):482–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. Host defense against bacterial endotoxemia: mechanism in normal animals. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):300–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. The inactivation of endotoxin after interaction with certain proteins of normal serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):644–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G., Ward P. A. Two distinct chemotactic factor inactivators in human serum. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):843–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Hill J. H. Detection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS): an improved method for isolation of the Limulus extract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]