Abstract
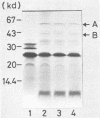
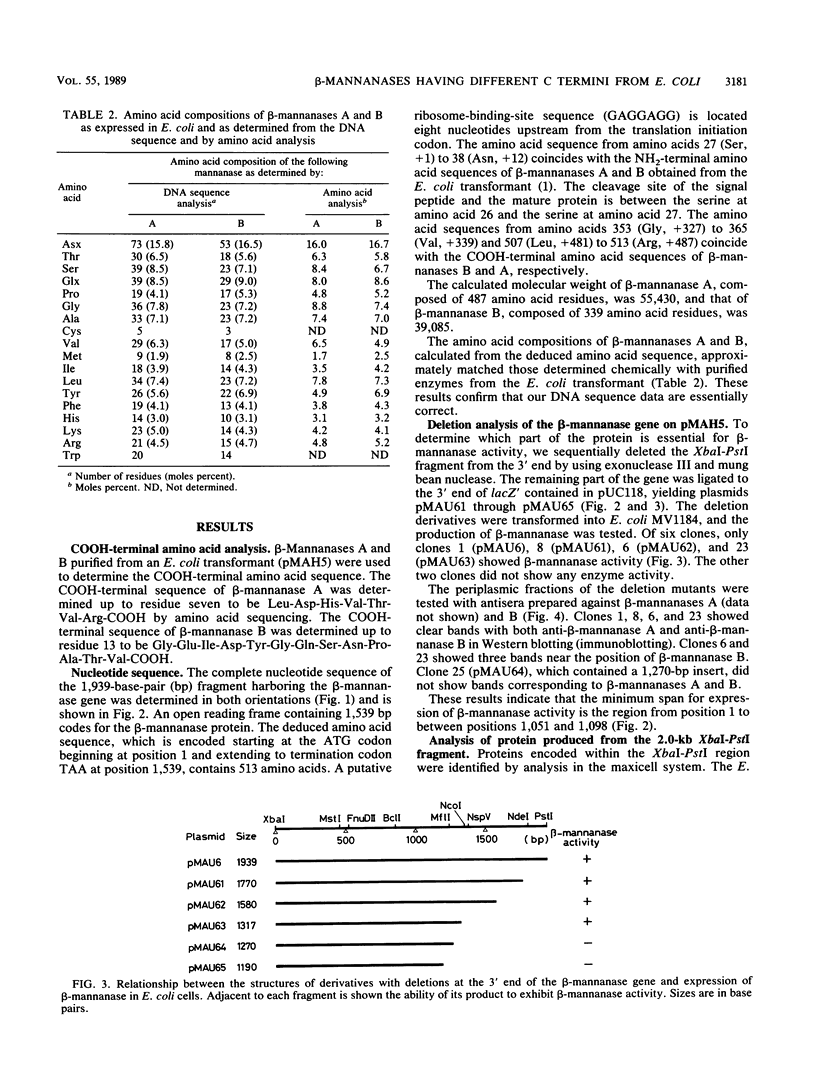
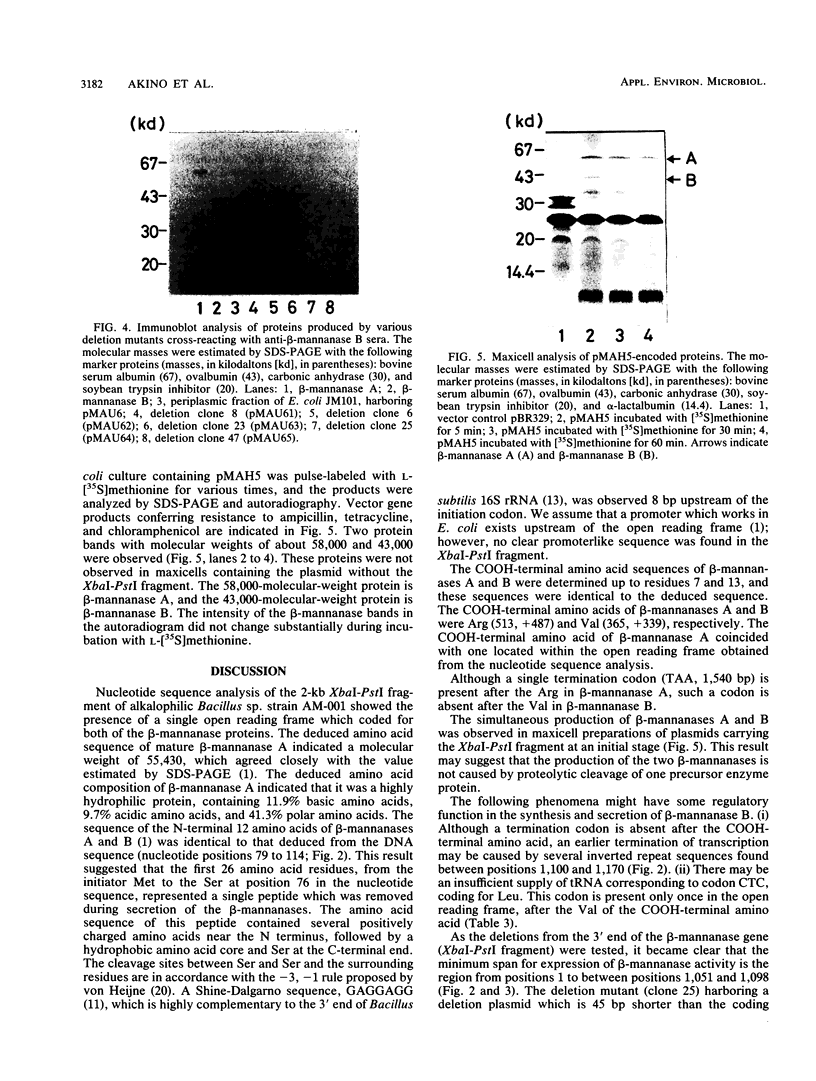
The nucleotide sequence was determined for the alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain AM-001 beta-mannanase gene which produced two beta-mannanases (A and B) in Escherichia coli transformants. The putative beta-mannanase gene was 1,539 base pairs long and encoded a mature beta-mannanase protein of 487 amino acids and a signal peptide of 26 amino acids. The COOH-terminal amino acid of beta-mannanase A is an arginine residue located at amino acid 513 of the deduced amino acid sequence, and that of beta-mannanase B is a valine residue located at amino acid 365. Deletion derivatives having 1,098 base pairs from the ATG start codon maintained the beta-mannanase activity of the encoded polypeptide. However, clones harboring DNA fragments (1,051 base pairs) shorter than the gene which encoded beta-mannanase B (1,095 base pairs) did not exhibit the beta-mannanase activity. The simultaneous production of both beta-mannanases A and B in an E. coli transformant was demonstrated by the maxicell procedure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. VI. Plasmid pBR329, a new derivative of pBR328 lacking the 482-base-pair inverted duplication. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Yokosawa H., Kumazaki T., Nakamura I. Immobilized anhydrotrypsin as a specific affinity adsorbent for tryptic peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:378–383. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequences of transcription and translation initiation regions in Bacillus phage phi 29 early genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Sato M., Toba M., Masahashi W., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ alpha-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene. 1987;61(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]