Abstract
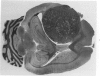
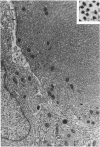
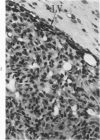
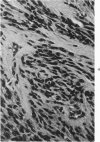
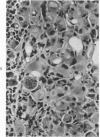
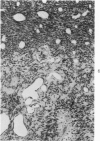
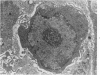
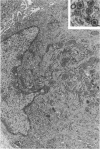
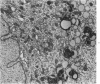
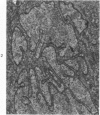
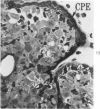
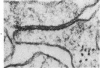
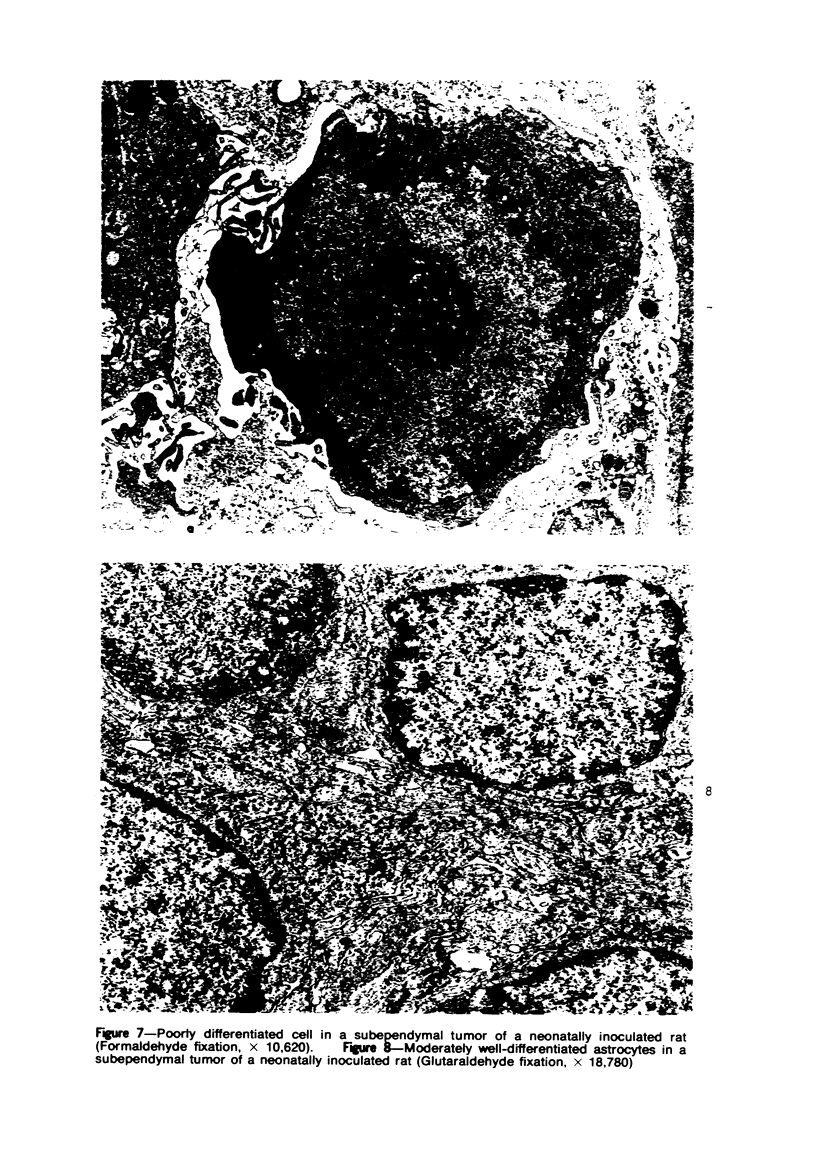
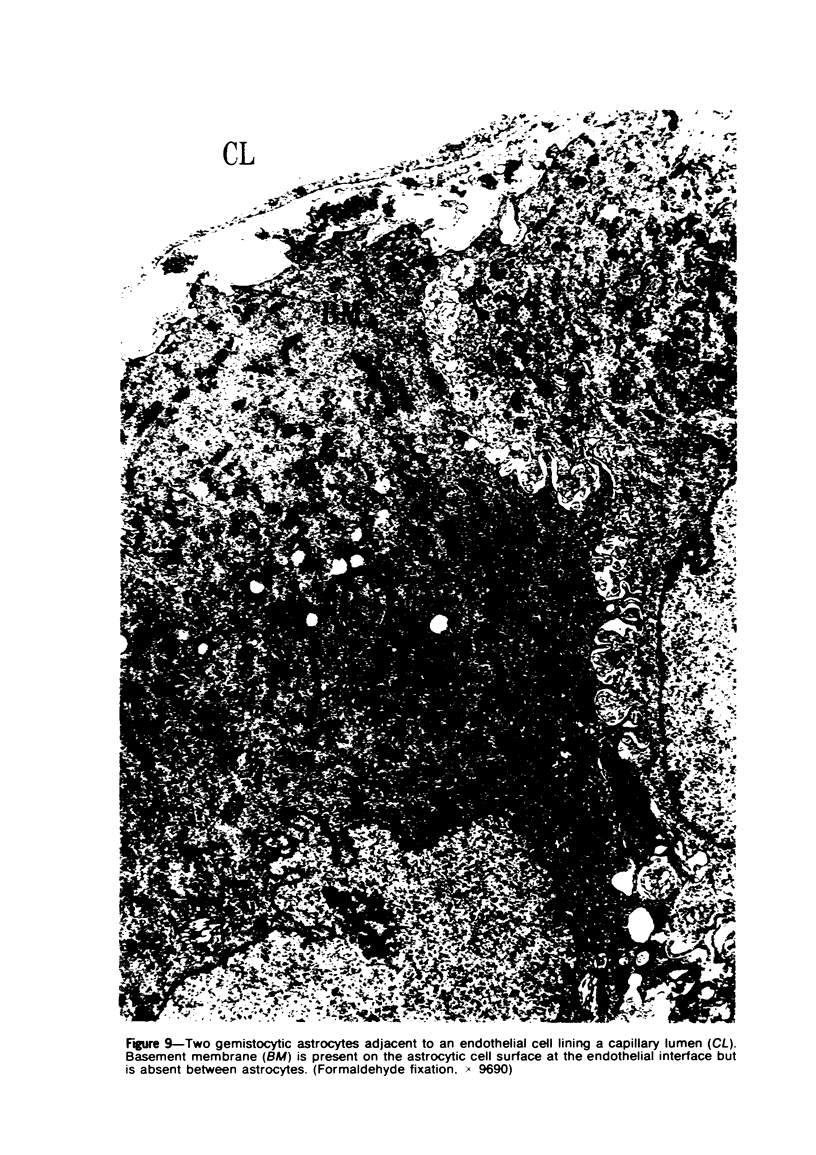
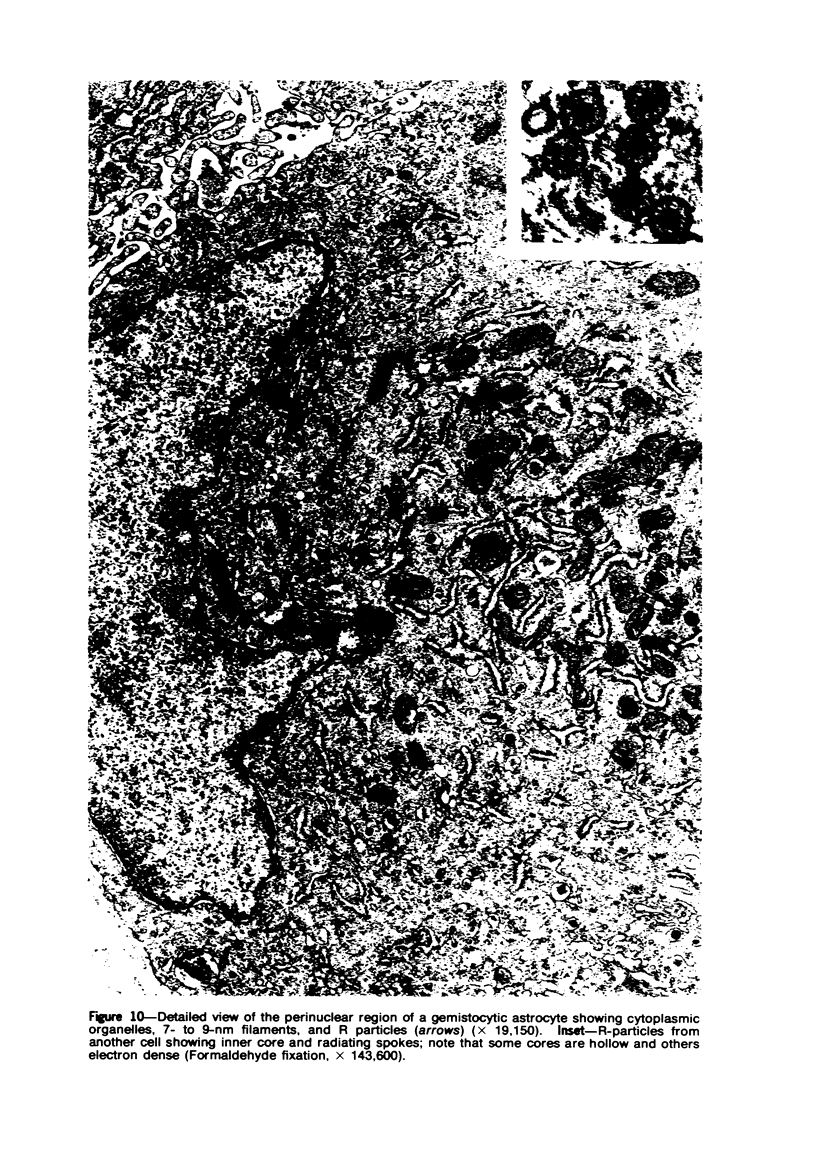
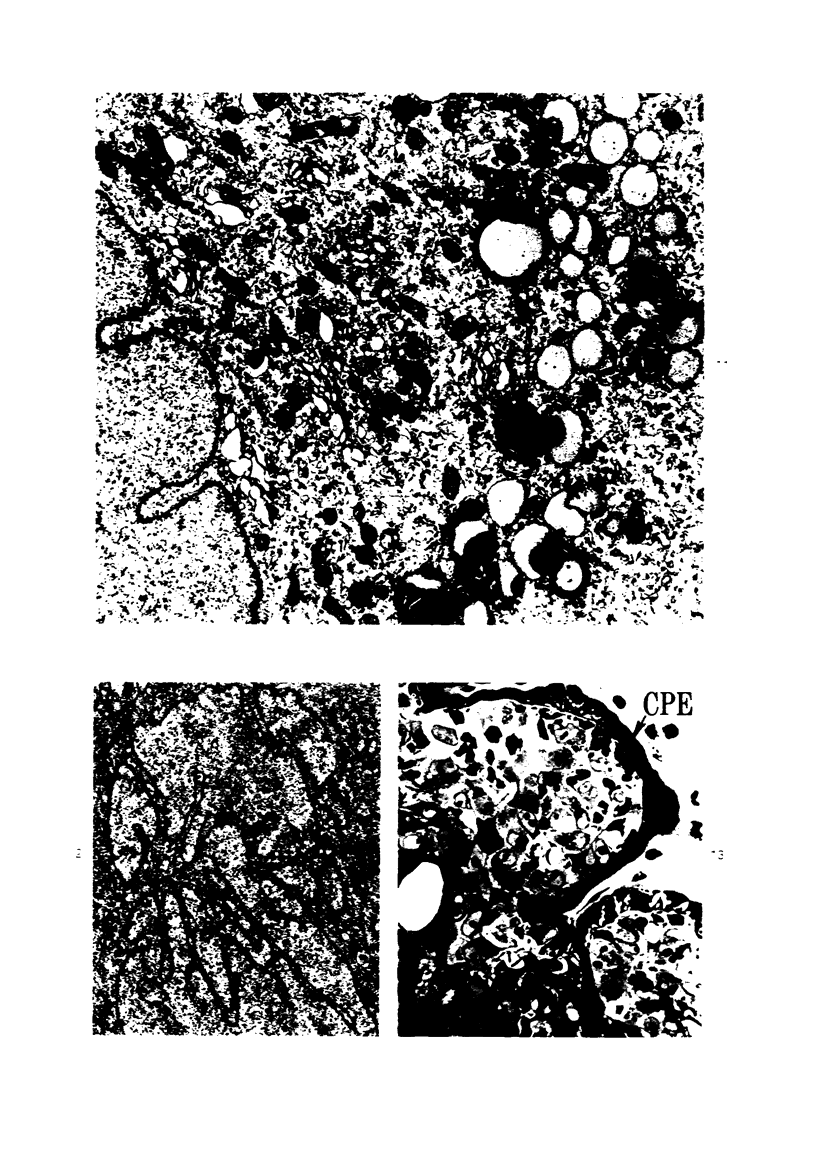
Groups of F-344 rats were inoculated with the Bratislava-77 strain of avian sarcoma virus (B-77 ASV) within 24 hours of birth, at 9 days of age, or between 97 and 119 days of age. Intracranial tumors developed in each age group. Multiple tumors with mixed histologic patterns developed in rats inoculated at 1 or 9 days of age. Solitary tumors with a uniform histologic pattern developed in rats inoculated as adults. On the basis of light and electron microscopic study, the majority of tumors in each age group were classified as astrocytomas and divided into either poorly differentiated, gemistocytic, pilocytic, or polymorphic varieties. The polymorphic astrocytomas were most common among neonatally inoculated rats, while the pilocytic astrocytomas were most common among rats inoculated as adults. Ultrastructural characteristics of astrocytes, including gap junctions and 7- to 9-nm filaments, were present in the majority of tumors in each age groups. Astrocytomas induced in adult rats were remarkable for the presence of extensive basement membrane alone the astrocytic cell surfaces. Intracytoplasmic virus-like particles (R particles) were common in the tumor cells. These virus-like particles are morphologically distinct from C-type B-77 ASV, and no morphologic evidence of C-type virus replication was observed in any of the tumors.
Full text
PDF
















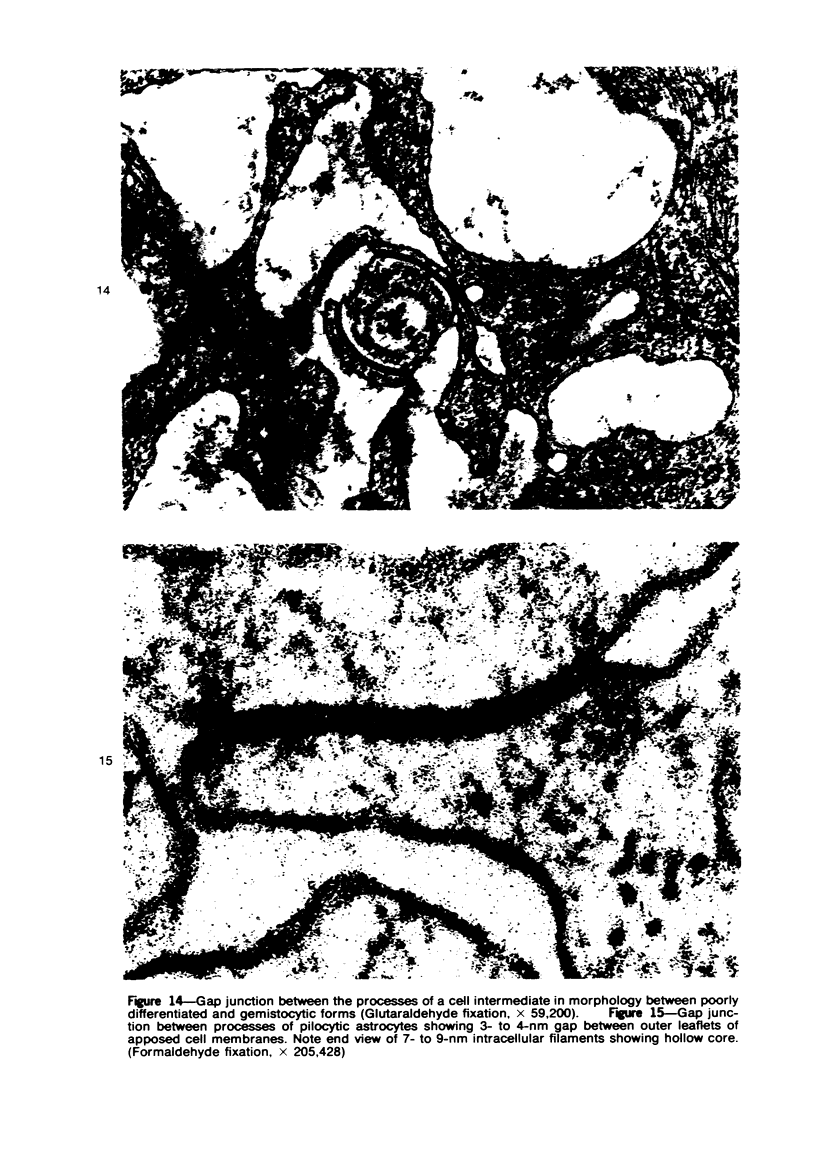
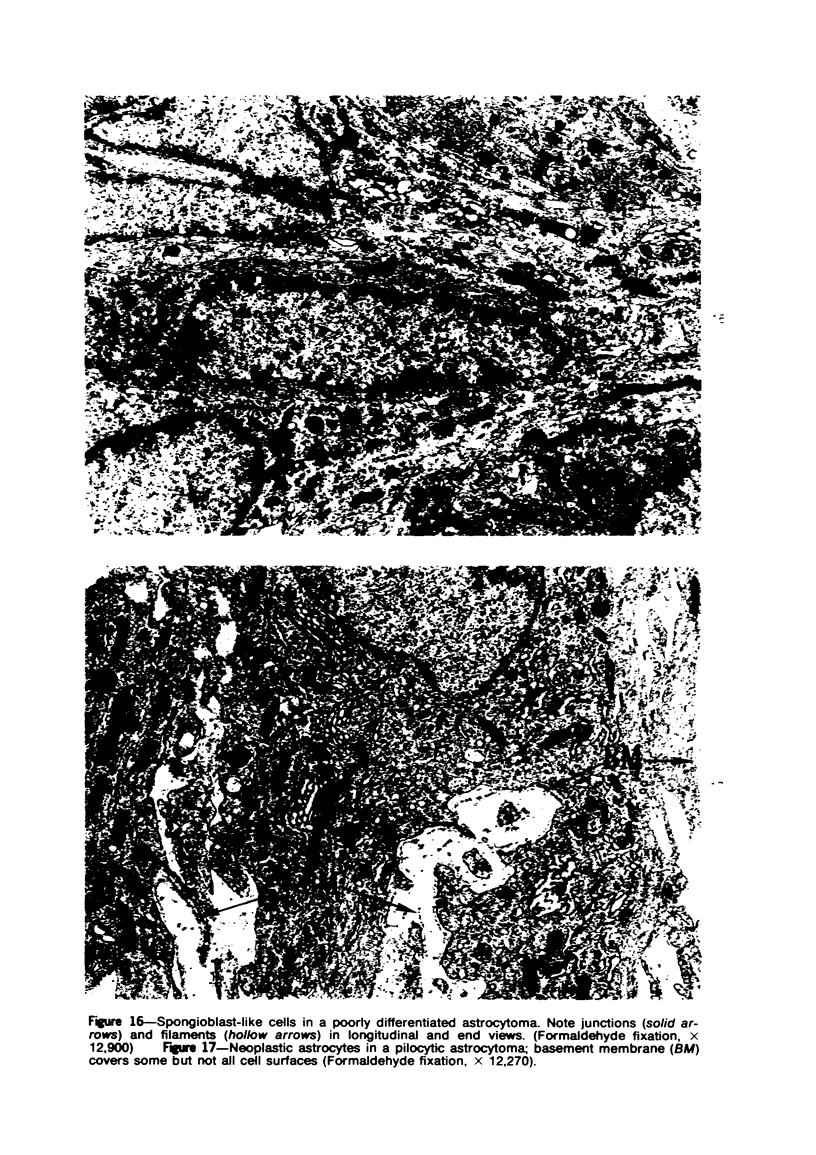
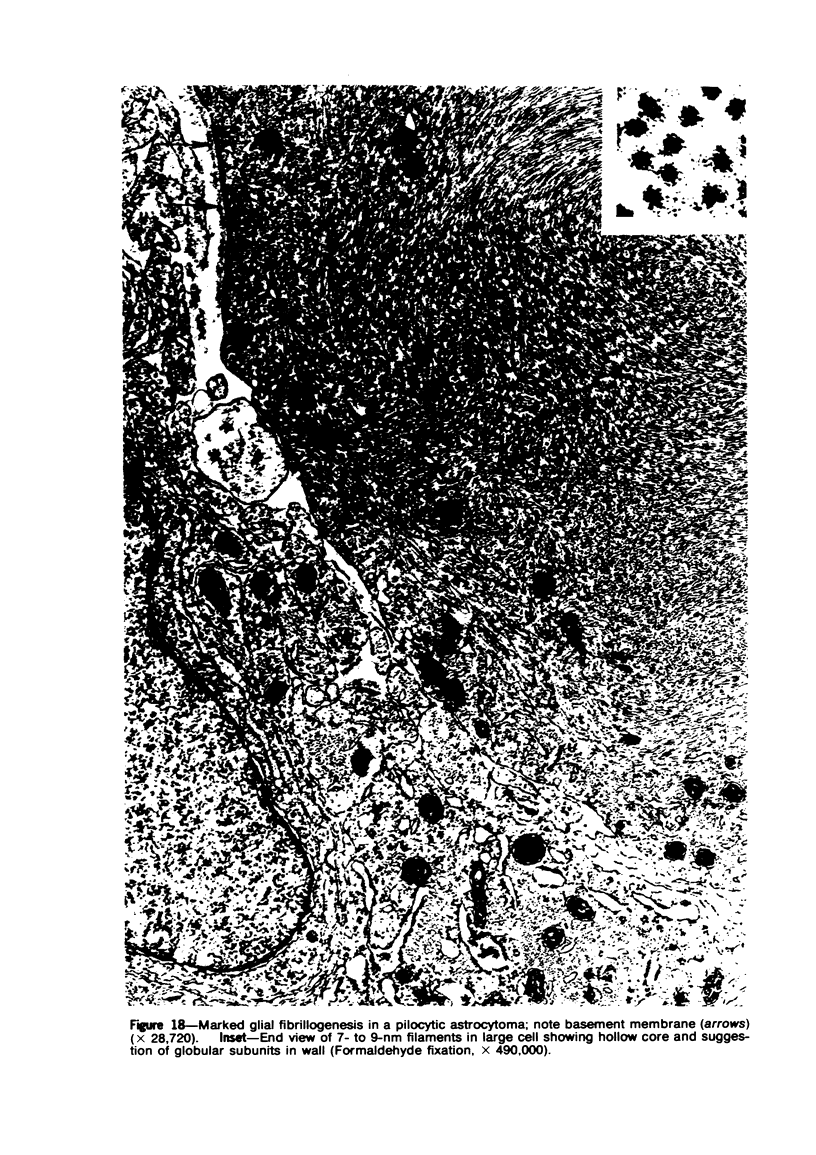
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakemore W. F. The ultrastructure of the subependymal plate in the rat. J Anat. 1969 May;104(Pt 3):423–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucciarelli E., Rabotti G. F., Dalton A. J. Ultrastructure of gliomas induced in hamsters with Rous sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Jun;38(6):865–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucciarelli E., Rabotti G. F., Dalton A. J. Ultrastructure of meningeal tumors induced in dogs with Rous sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Mar;38(3):359–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Bigner D. D., Self D. J. Morphologic observations of brain tumors in PD4 hamsters induced by four strains of avian sarcoma virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1973;26(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00685520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caley D. W., Maxwell D. S. An electron microscopic study of the neuroglia during postnatal development of the rat cerebrum. J Comp Neurol. 1968 May;133(1):45–70. doi: 10.1002/cne.901330104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson F. L., Martin J. H., Lynn J. A. Formalin fixation for electron microscopy: a re-evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;59(3):365–373. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Burger P. C., Bigner D. D. R-type virus-like particles in avian sarcoma virus-induced rat central nervous system tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1479–1482. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland D. D., Vogel F. S., Bigner D. D. The induction of intractranial neoplasms by the inoculation of avian sarcoma virus in perinatal and adult rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1975 Jul;34(4):340–358. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197507000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. M., Di Stefano H. S. Virus particles associated with "nonproducer" Rous sarcoma cells. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G., BARR Y. M. VIRUS PARTICLES IN CULTURED LYMPHOBLASTS FROM BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):702–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. E., Schardein J. L., Kurtz S. M. Spontaneous tumors of the nervous system in albino rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jan;52(1):265–273. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.1.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A. A., Hendrick E. B., Conen P. E. Case reports. Intracerebral schwannoma. Report of a case. J Neurosurg. 1966 Feb;24(2):552–557. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.2.0552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haguenau F., Rabotti G. F., Lyon G., Moraillon A. Gliomas induced by rous sarcoma virus in the dog--an ultrastructural study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Mar;46(3):539–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haguenau F., Rabotti G. F., Lyon G., Moraillon A. Tumeurs cèrèbrales expèrimentales d'ètiologie virale chez le chien. Leur similitude histologique avec les tumeurs humaines dèmontrèe par une ètude ultrastructurale de 44 mèningiomes, 19 spongioblastomes et un èpendymome. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1972 May;126(5):347–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. S., Sinex F. M. On the relationship of brain filaments to microtubules. J Neurochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):321–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb07594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumanishi T., Ikuta F., Yamamoto T. Brain tumors induced by Rous sarcoma virus, Schmidt-Ruppin strain. 3. Morphology of brain tumors induced in adult mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jan;50(1):95–109. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantos P. L. An electron microscope study of reacting astrocytes in gliomas induced by n-ethyl-n-nitrosourea in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;30(2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00685441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mac Kenzie W. F., Garner F. M. Comparison of neoplasms in six sources of rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 May;50(5):1243–1257. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawdesley-Thomas L. E., Newman A. J. Some observations on spontaneously occurring tumours of the central nervous system of Sprague-Dawley derived rats. J Pathol. 1974 Feb;112(2):107–116. doi: 10.1002/path.1711120206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Leblond C. P. Identification of microglia in light and electron microscopy. J Comp Neurol. 1969 Jan;135(1):57–80. doi: 10.1002/cne.901350104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Mawdesley-Thomas L. E. Spontaneous tumours of the central nervous system of laboratory rats. J Comp Pathol. 1974 Jan;84(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(74)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson J. A., Privat A., Ling E. A., Leblond C. P. Investigation of glial cells in semithin sections. 3. Transformation of subependymal cells into glial cells, as shown by radioautography after 3 H-thymidine injection into the lateral ventricle of the brain of young rats. J Comp Neurol. 1973 May 1;149(1):83–102. doi: 10.1002/cne.901490106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privat A., Leblond C. P. The subependymal layer and neighboring region in the brain of the young rat. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Nov;146(3):277–302. doi: 10.1002/cne.901460302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L., Rubinstein L. J. Electron microscopic observations on a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1965 Nov 18;5(2):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00686519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. C., Herman M. M., Rubinstein L. J. Electron microscopic observations on human glioblastomas and astrocytomas maintained in organ culture systems. Am J Pathol. 1973 Dec;73(3):589–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. C., Rubinstein L. J., Herman M. M., Bignami A. Ethylnitrosourea-induced astrocytomas. Morphologic observations on rat tumors maintained in tissue and organ culture systems. Lab Invest. 1974 Dec;31(6):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenberg J. A., Koestner A., Wechsler W. The induction of tumors of the nervous system with intravenous methylnitrosourea. Lab Invest. 1972 Jan;26(1):74–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani E., Ikeda K., Yamagata S., Nishiura M., Higashi N. Specialized junctional complexes in human meningioma. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;28(4):305–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00685285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani E., Nishiura M., Higashi N. Freeze-fracture studies of gap junctions of normal and neoplastic astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Oct 11;26(2):127–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00697748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. E., Pease D. C. Electron microscopic studies of wallerian degeneration in rat optic nerves. II. Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and adventitial cells. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Oct;140(2):207–226. doi: 10.1002/cne.901400205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick N. A., Bigner D. D., Kvedar J. P. The fine structure of canine gliomas and intracranial sarcomas induced by the Schmidt-Ruppin strain of the Rous sarcoma virus. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jul;30(3):354–367. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197107000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick N. A., Bigner D. D. Some structural aspects of dog brain tumors induced with the Schmidt-Ruppin strain of the Rous sarcoma virus. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1972;17:59–73. doi: 10.1159/000393668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfong R. F., Bigner D. D., Self D. J., Wechsler W. Brain tumor types induced by the Schmidt-Ruppin strain of Rous sarcoma virus in inbred Fischer rats. Acta Neuropathol. 1973;25(3):196–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00685199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZURHEIN G., CHOU S. M. PARTICLES RESEMBLING PAPOVA VIRUSES IN HUMAN CEREBRAL DEMYELINATING DISEASE. Science. 1965 Jun 11;148(3676):1477–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3676.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]