Abstract
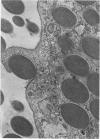
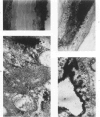
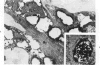
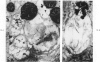
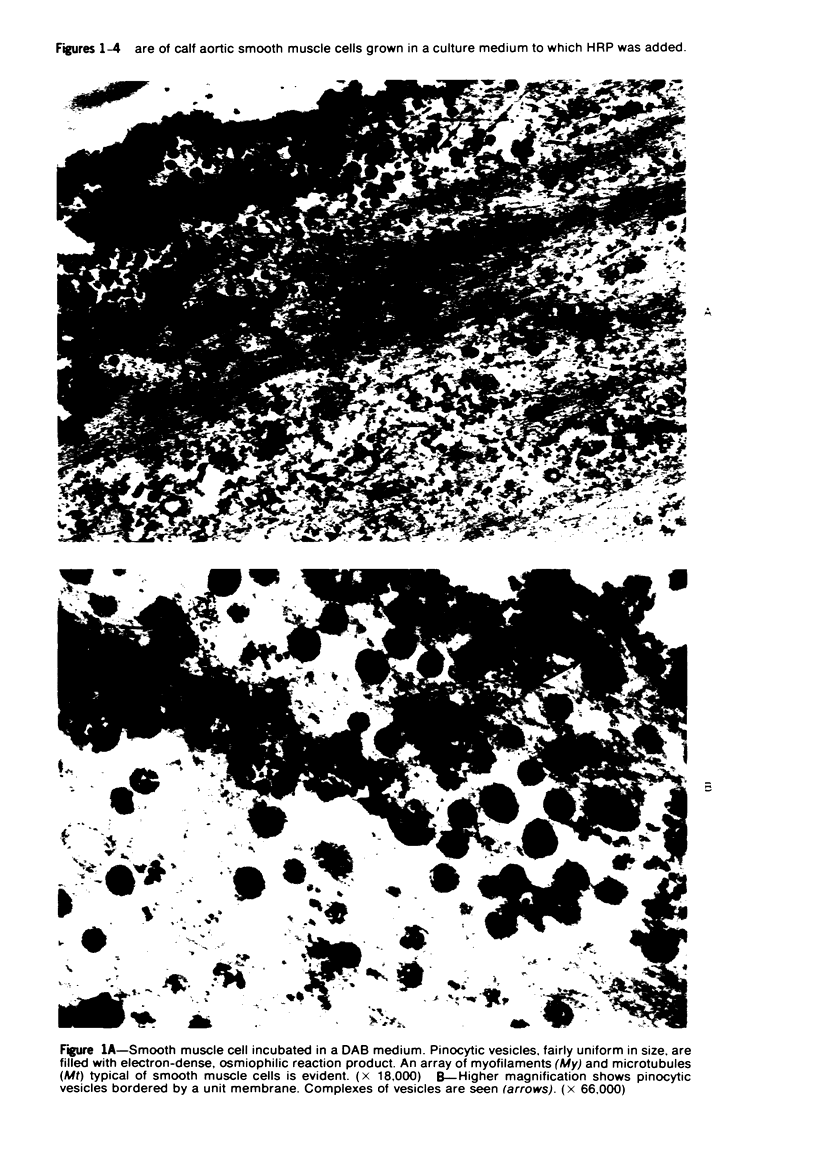
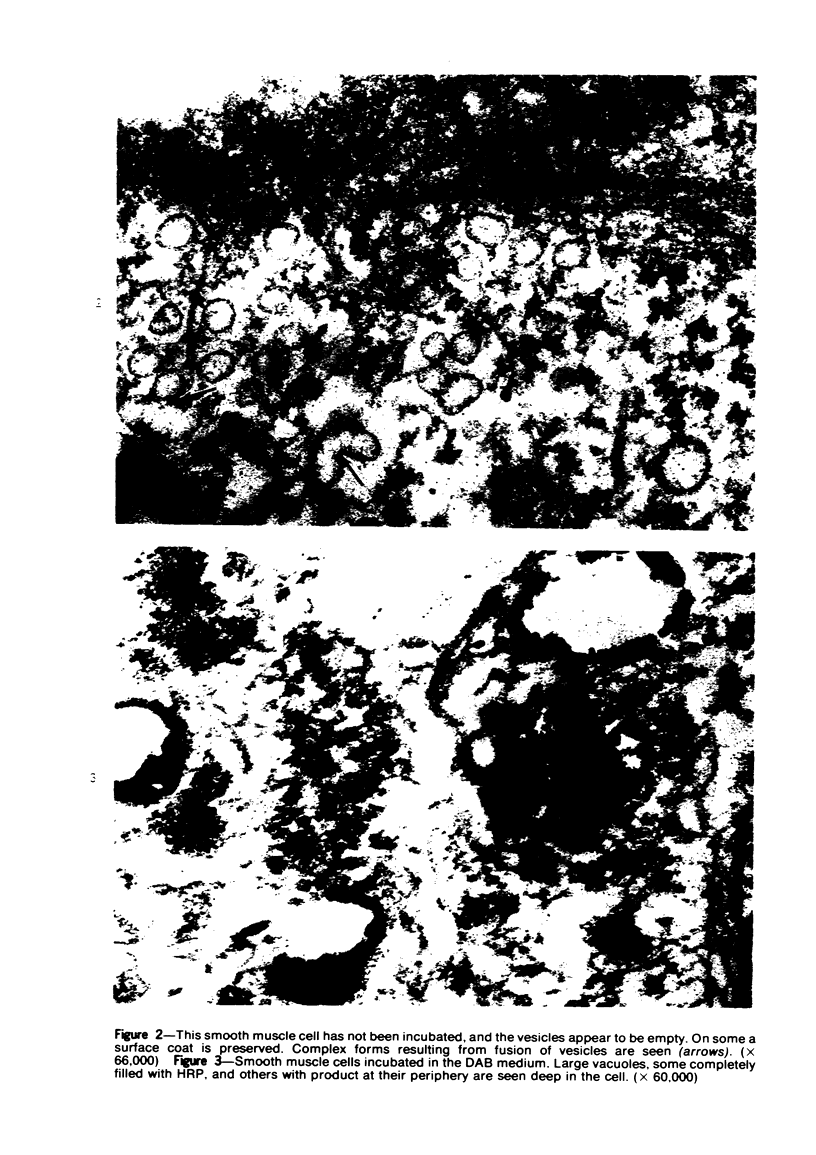
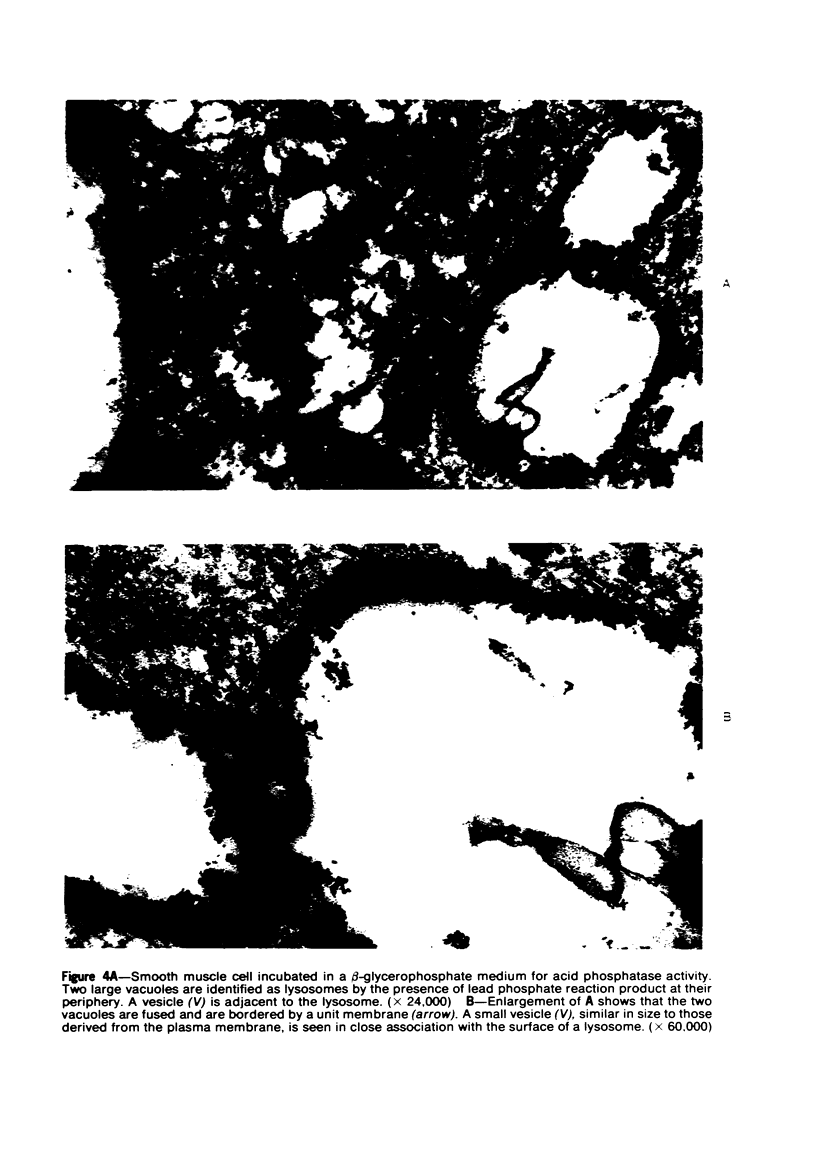
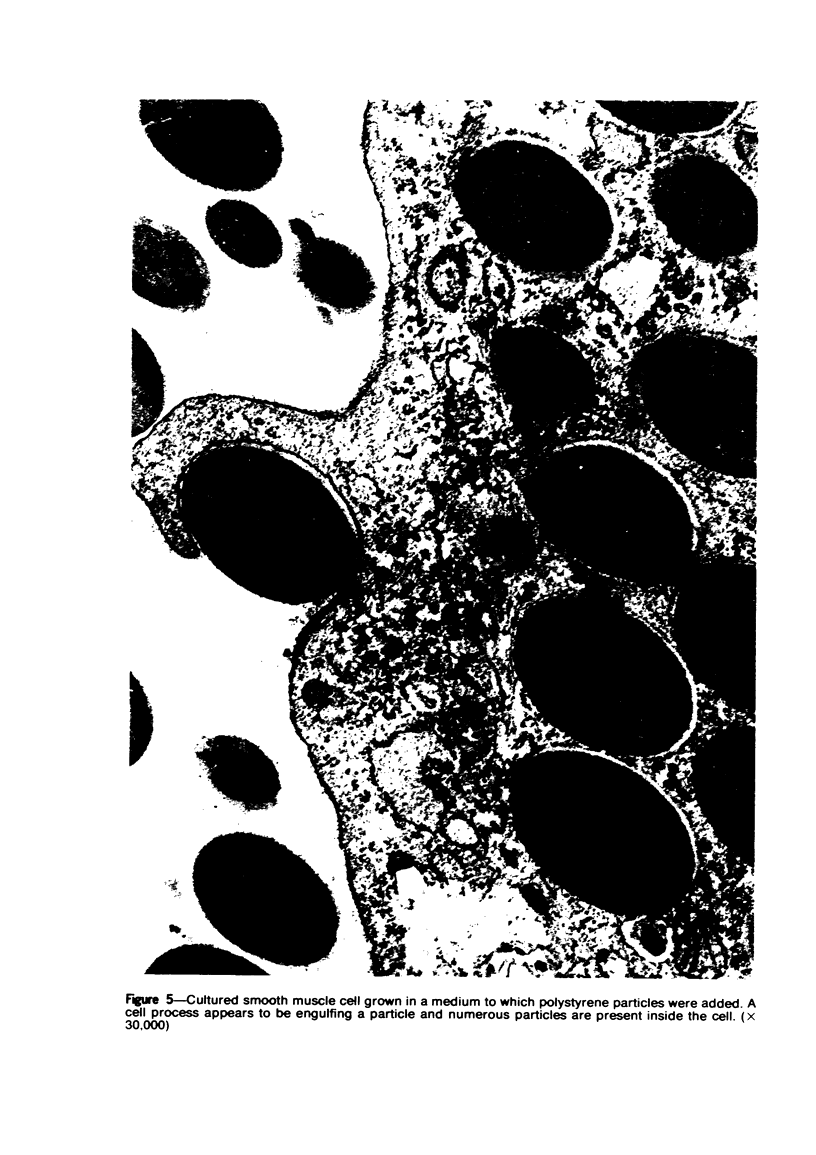
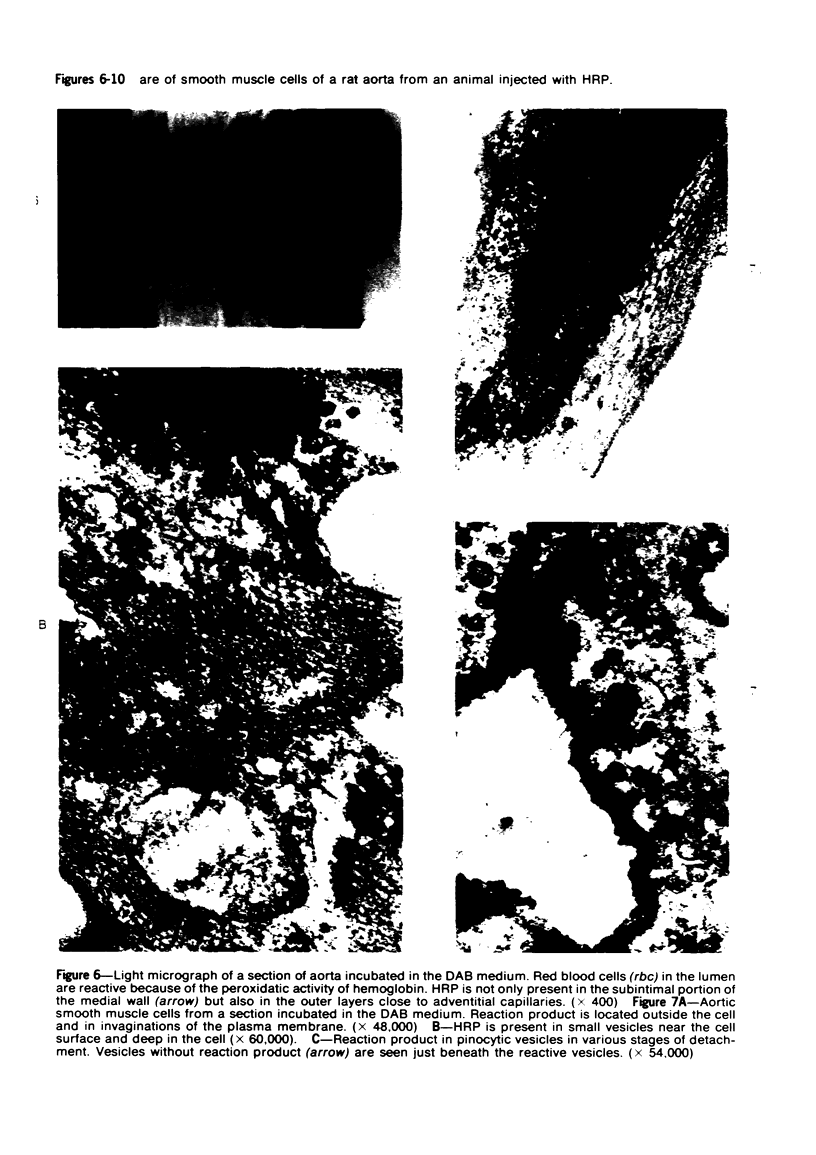
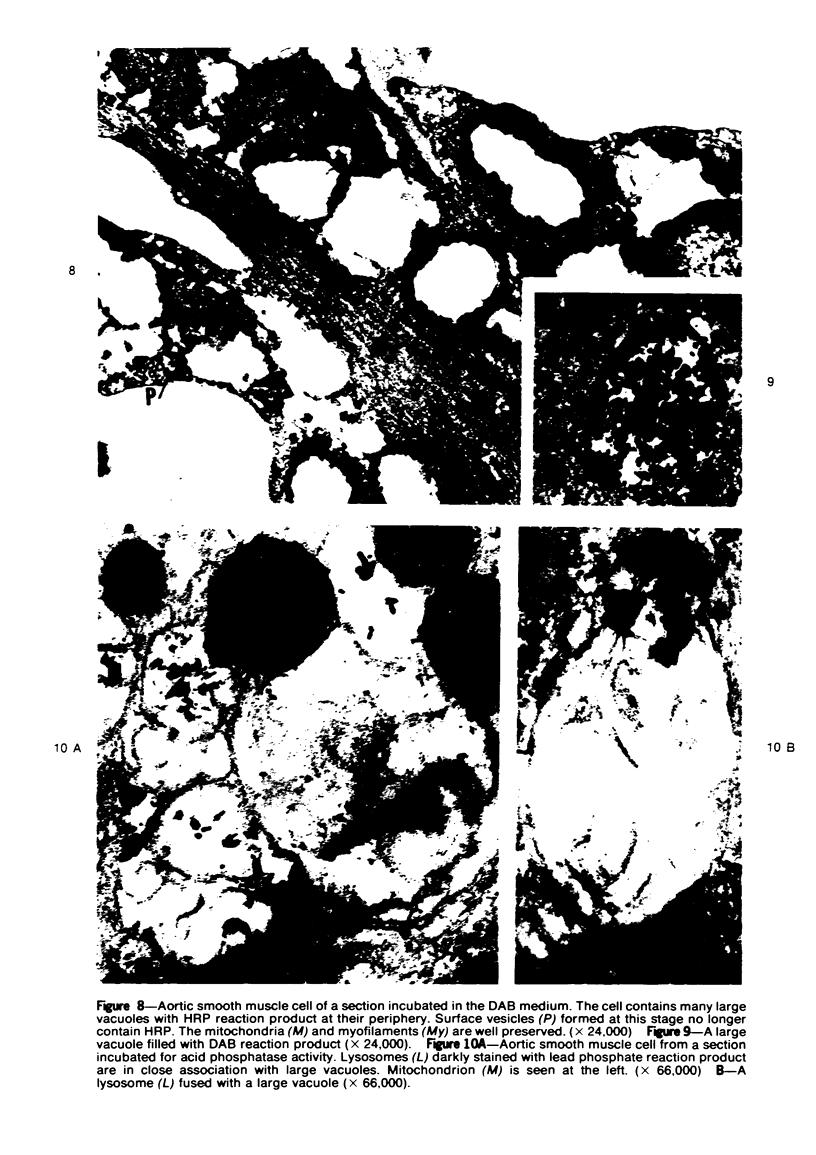
Overloading of lysosomes of smooth muscle cells with excess substrate may be a key event in the development of hypertensive and atherosclerotic vascular disease. Cellular uptake of materials and its relation to lysosomal function were studied by ultrastructural cytochemistry in aortic smooth muscle cells grown in vitro and in the intact animal. Injection of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) into hypertensive rats resulted in rapid insudation of the material into the environs of medial smooth muscle cells, entrance into surface pinocytic vesicles, and transport via vesicles into the cell interior where material was seen to accumulate within lysosomes. In vitro exposure of calf aortic cells to HRP in the medium resulted in a similar sequence of events. Pinocytic vesicles, seen both in vitro and in vivo, ranged in diameter from 650-1000 A. These dimensions are adequate to permit incorporation of intact lipoproteins of all classes, except the larger chylomicrons.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell F. P., Gallus A. S., Schwartz C. J. Focal and regional patterns of uptake and the transmural distribution of 131-I-fibrinogen in the pig aorta in vivo. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Apr;20(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfield R. E., Chacko S., Blose S. Phagocytosis by muscle cells. Lab Invest. 1975 Oct;33(4):418–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Wiener J., Spiro D. The cellular pathology of experimental hypertension. V. Increased permeability of cerebral arterial vessels. Am J Pathol. 1970 Apr;59(1):133–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Schiller B., Wolinsky H. Lipid accumulation in smooth muscle cell lysosomes im primate atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1975 Mar;78(3):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S. The cytochemical localization of myoglobin in striated muscle of man and walrus. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):398–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Lipoprotein receptors, cholesterol metabolism, and atherosclerosis. Arch Pathol. 1975 Apr;99(4):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. An electron microscope study of the aorta in young and in aging mice. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Mar;5:1–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoproteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROSSER C. L., BURNSTOCK G., KAHN J. Conduction in smooth muscle: comparative structural properties. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:545–552. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodesch F. R., Dumont J. E., Nève P. Phagocytosis of latex beads by isolated thyroid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jun;60(3):354–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Siminoescu M., Palade G. E. Permeability of muscle capillaries to small heme-peptides. Evidence for the existence of patent transendothelial channels. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):586–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y., Goodman D. S., Fidge N. H. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesteryl ester in rat liver. A combined radioautographic-electron microscopic and biochemical study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):410–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Silver J. M., Cohn Z. A. Pinocytosis in fibroblasts. Quantitative studies in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):949–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster W. S., Bishop S. P., Geer J. C. Experimental aortic intimal thickening. II. Endothelialization and permeability. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):265–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Cohn Z. A. Cholesterol metabolism in the macrophage. 3. Ingestion and intracellular fate of cholesterol and cholesterol esters. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):21–44. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Reynolds J. J. Stimulation by endocytosis of the secretion of collagenase and neutral proteinase from rabbit synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1482–1497. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky H., Goldfischer S., Schiller B., Kasak L. E. Lysosomes in aortic smooth muscle cells. Effects of hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1973 Dec;73(3):727–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C. The participation of lysosomes in the transformation of smooth muscle cells to foamy cells in the aorta of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Acta Cardiol. 1974;Suppl 20:9–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]