Abstract
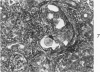
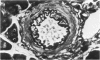
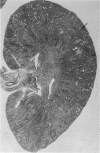
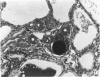
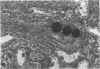
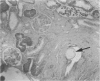
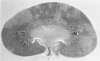
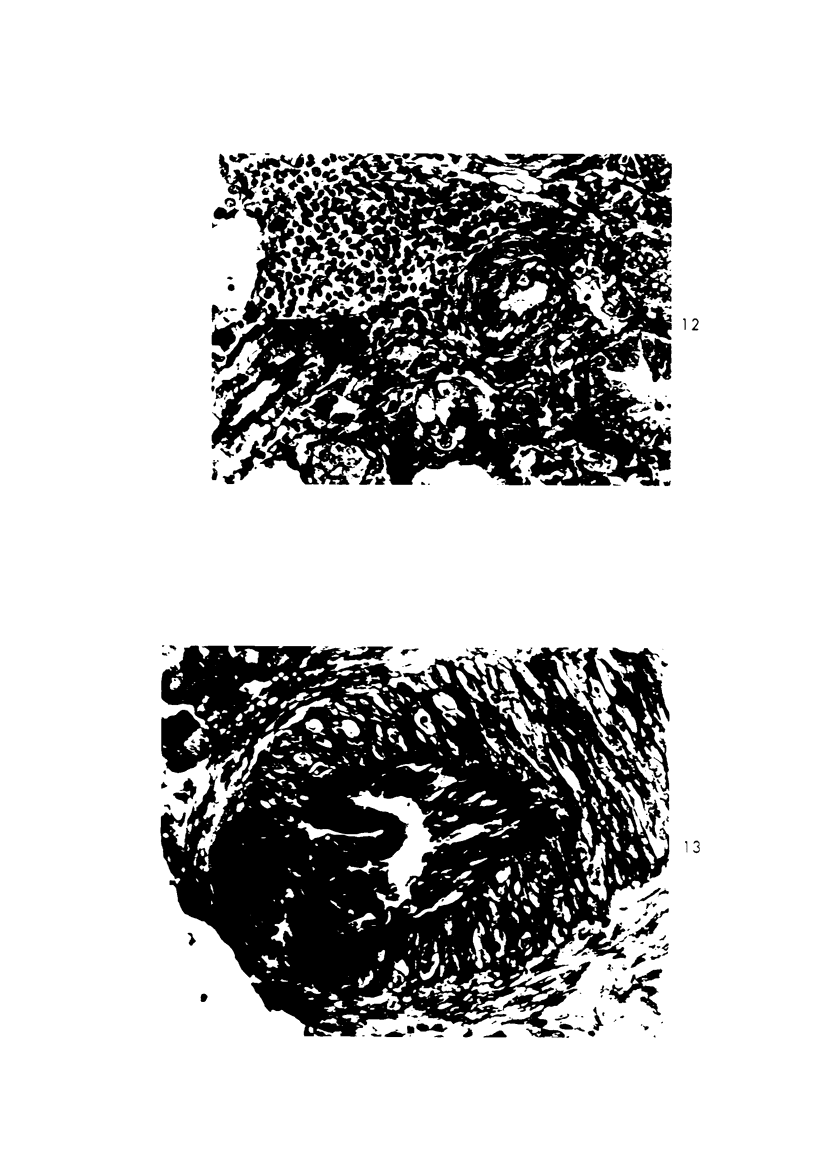
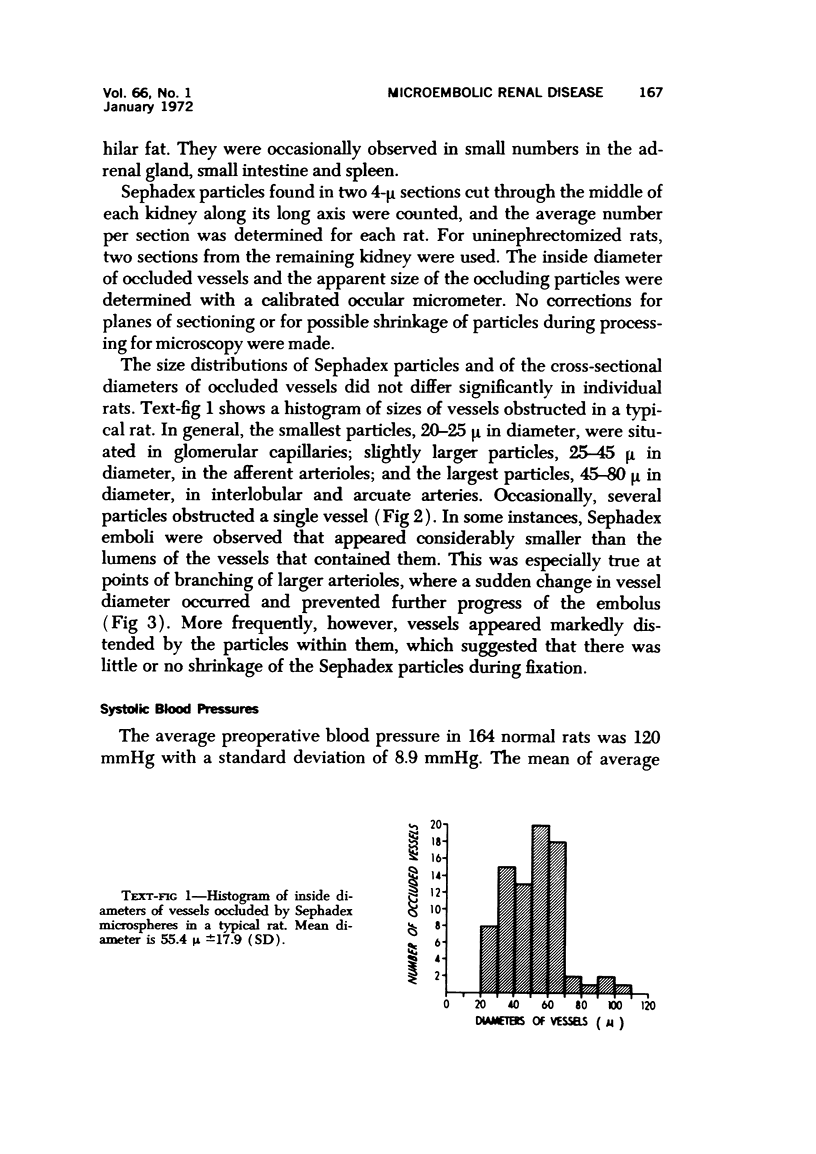
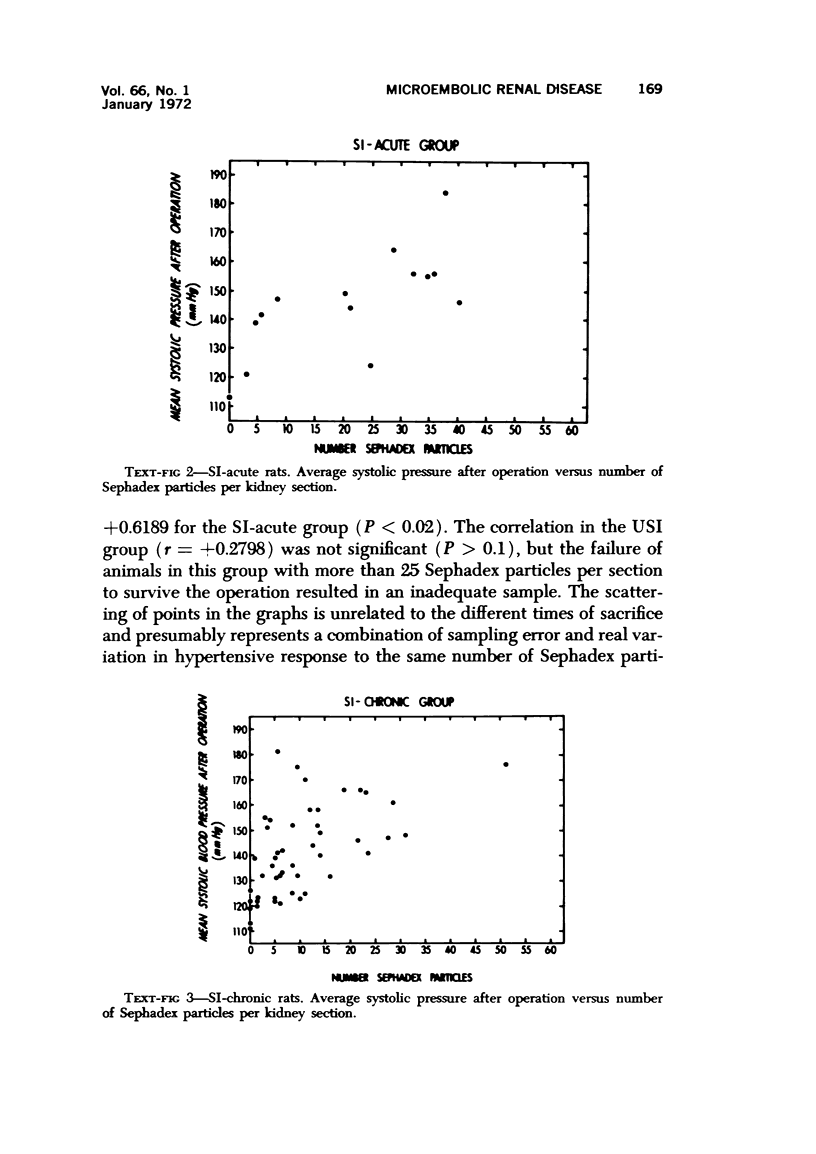
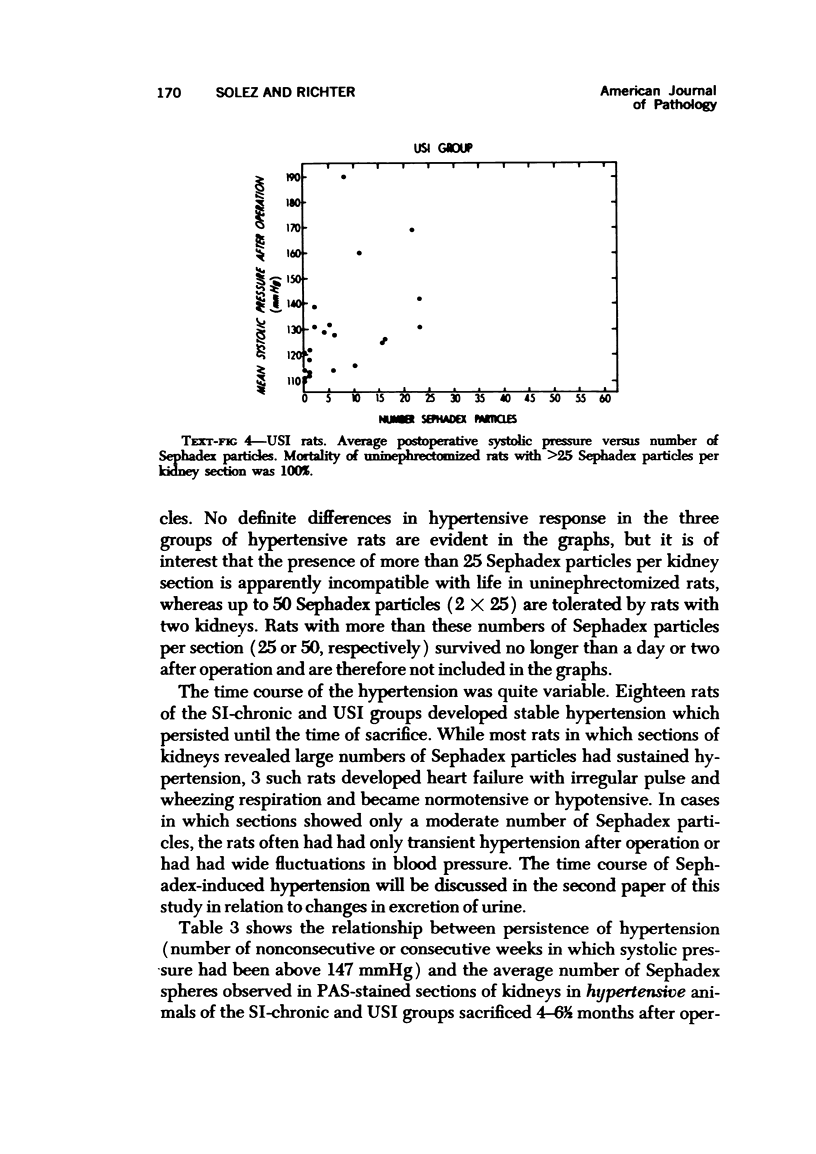
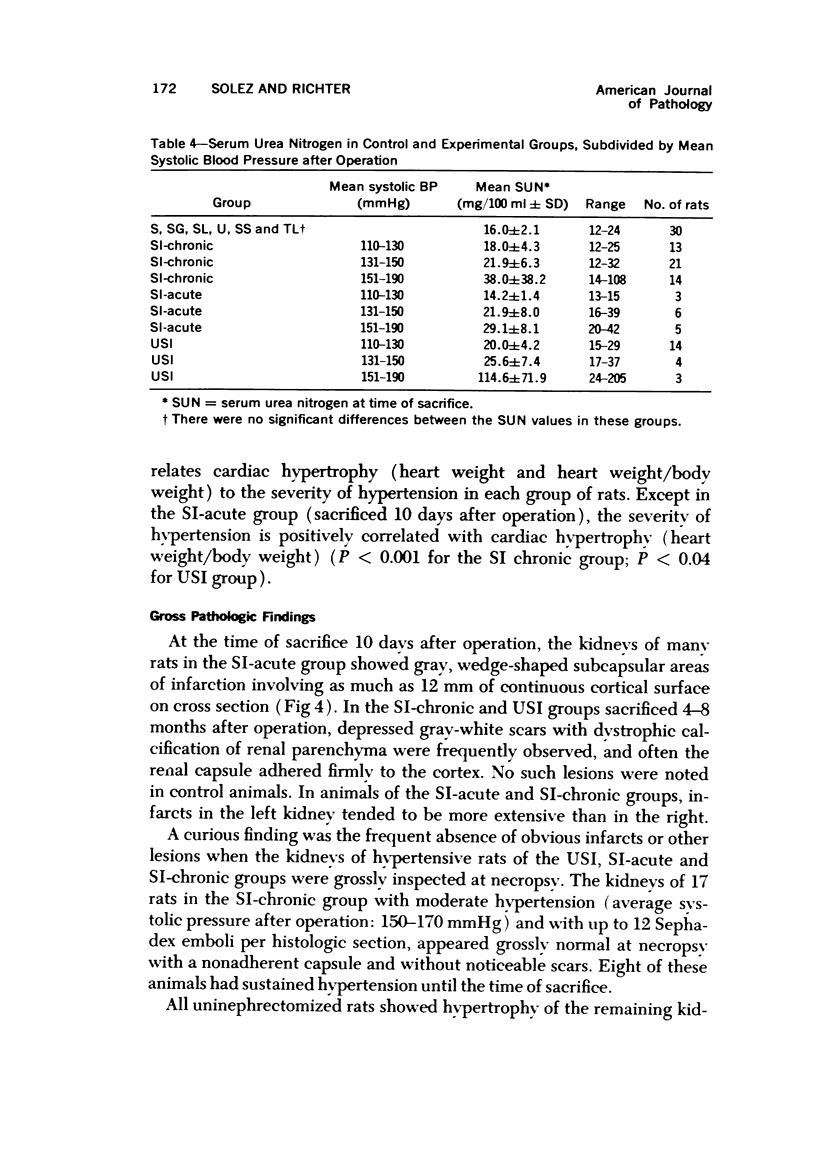
Sephadex particles (20-80 μ in size) were injected into the abdominal aorta of 134 male Sprague-Dawley rats near the renal arteries. In 31 rats, the right kidney was then removed. The Sephadex particles lodged in glomerular capillaries, afferent glomerular arterioles and interlobular arteries, creating renal infarcts, some of which were grossly visible. Shortly after injection, arterial blood pressure rose significantly in most animals. The hypertension in uninephrectomized rats was not demonstrably different from that in rats with two Kidneys. Severity and duration of hypertension (up to 8 months) were positively correlated with the number of Sephadex particles in renal vessels, and there was also a positive correlation between the degree of hypertension and serum urea nitrogen levels, and between degree of hypertension and degree of cardiac hypertrophy. The vascular permeability in acutely hypertensive rats was abnormal, as judged from penetration of iron-dextran into vessel walls. This experimental model resembles atheromatous microembolic renovascular disease, which may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of unexplained hypertension in patients with advanced aortic atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF




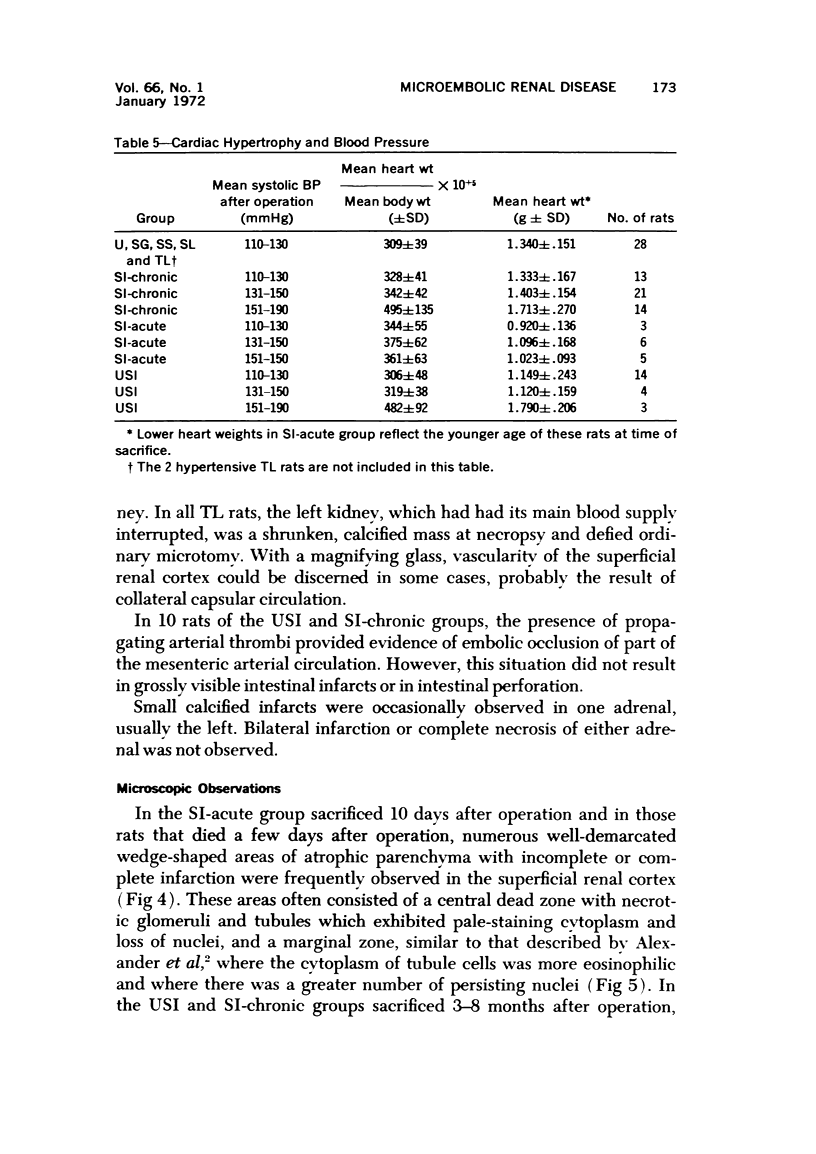







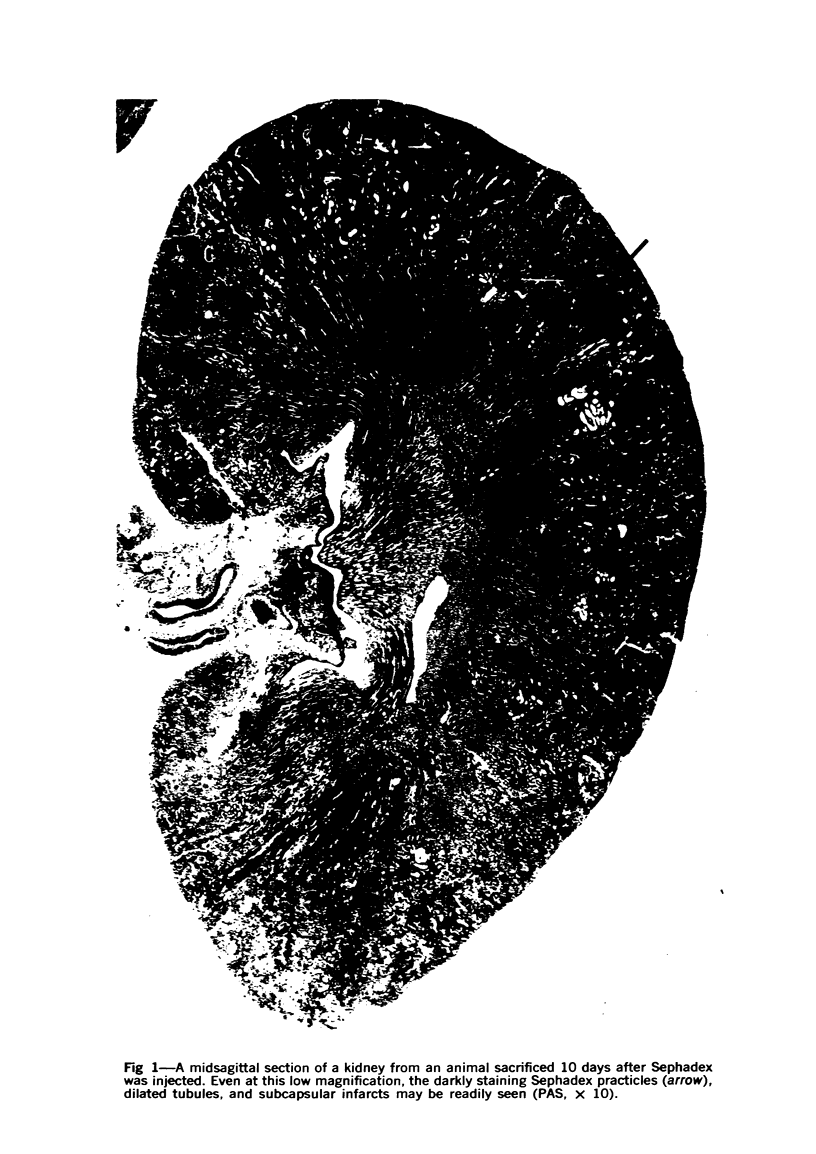
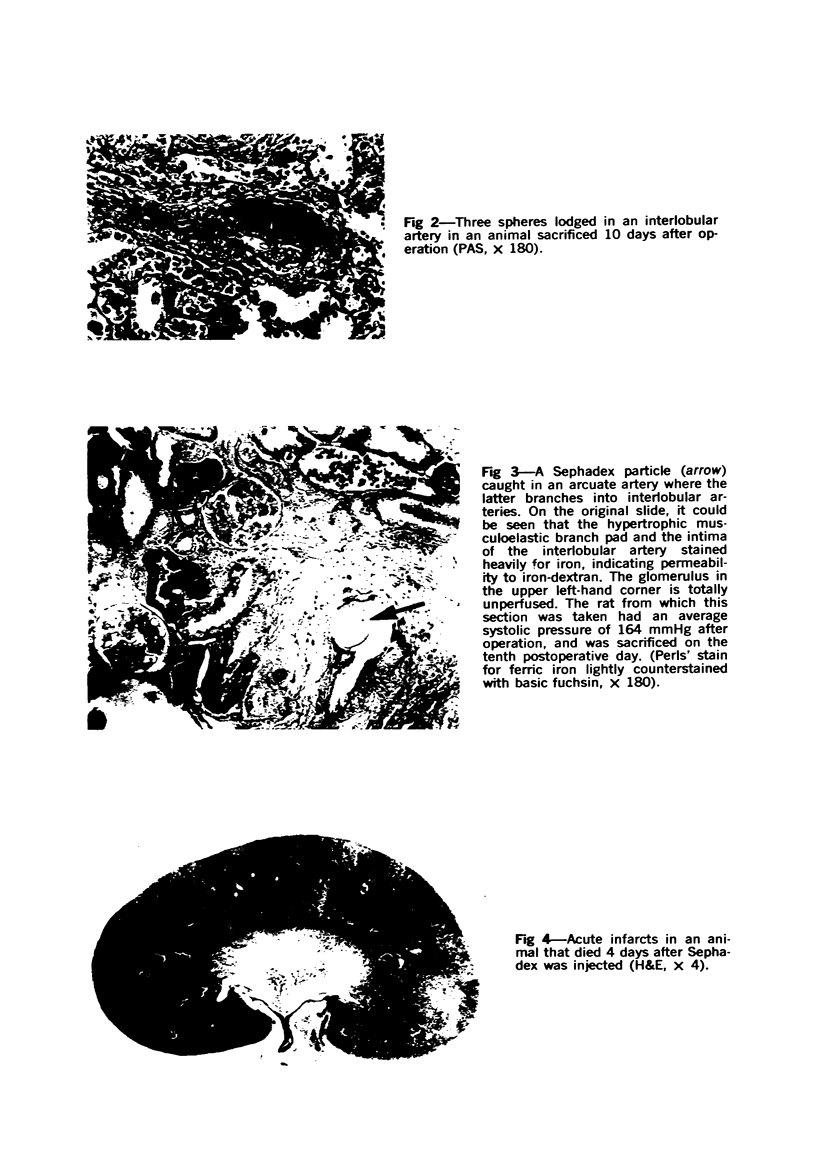
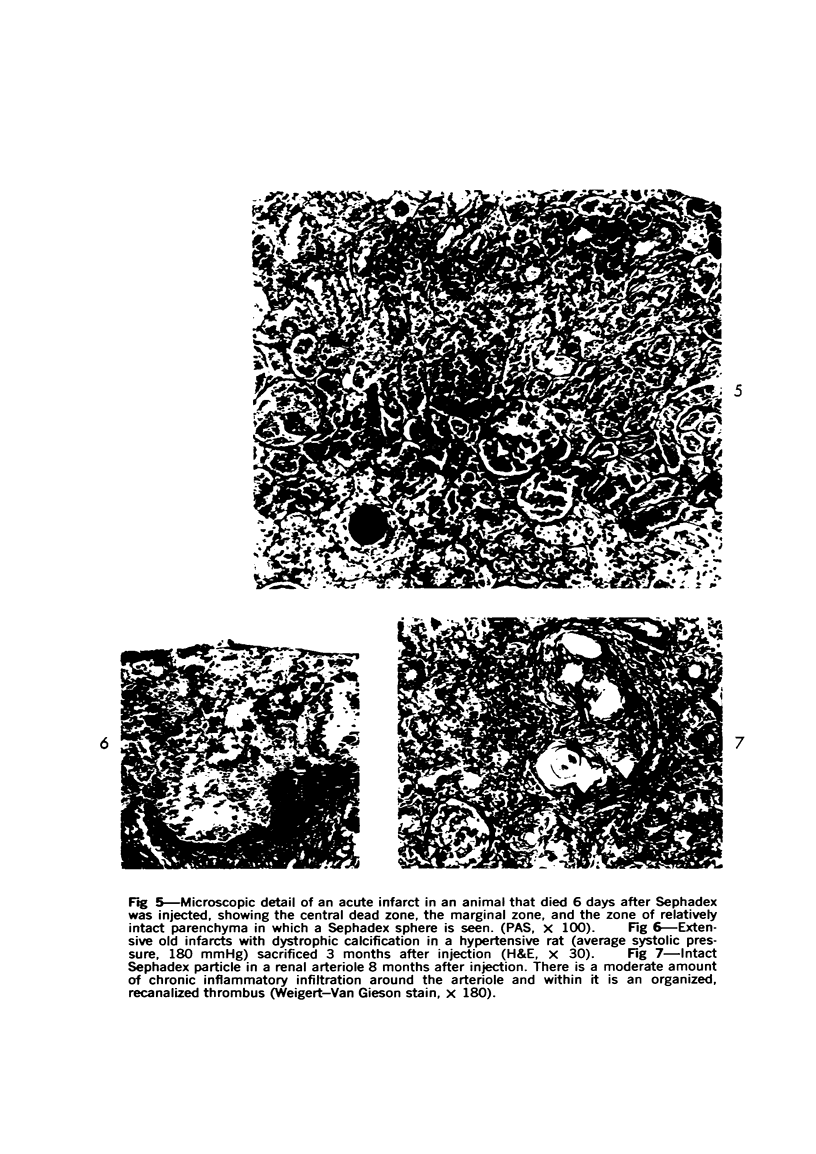


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER N., HEPTINSTALL R. H., PICKERING G. W. The effects of embolic obstruction of intrarenal arteries in the rabbit. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:225–237. doi: 10.1002/path.1700810125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNOLD M. W., GOODWIN W. E., COLSTON J. A. C. Renal infarction and its relation to hypertension. Urol Surv. 1951 Jun;1(3):191–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. E. Renal microvasculatures and microenvironments. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 4;284(9):498–499. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103042840910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. K., Knudsen K. D., Heine M., Leitl G. Effects of chronic excess salt ingestion. Genetic influence on the development of salt hypertension in parabiotic rats: evidence for a humoral factor. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):687–699. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon A. C., Glenn G. C., Burham W. A., Owen T. L., Goldstein J. D. The pathologic changes associated with the intravenous use of Sephadex. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Nov;52(5):587–592. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTERLY J. A., GLAGOV S. ALTERED PERMEABILITY OF THE RENAL ARTERY OF THE HYPERTENSIVE RAT: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:619–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER C. M. Observations of the fundus oculi in transient monocular blindness. Neurology. 1959 May;9(5):333–347. doi: 10.1212/wnl.9.5.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESE J. ACUTE HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE. 2. STUDIES ON VASCULAR REACTION PATTERNS AND PERMEABILITY CHANGES BY MEANS OF VITAL MICROSCOPY AND COLLOIDAL TRACER TECHNIQUE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;62:497–515. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.62.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORE I., MCCOMBS H. L., LINDQUIST R. L. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FATE OF CHOLESTEROL EMBOLI. J Atheroscler Res. 1964 Nov-Dec;4:527–535. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(64)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Wiener J., Spiro D. The cellular pathology of experimental hypertension. V. Increased permeability of cerebral arterial vessels. Am J Pathol. 1970 Apr;59(1):133–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLER J. A., Jr, RADIGAN L. R., MORROW A. G. Hypertension due to segmental infarction of the kidney. Am J Med. 1957 Feb;22(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffé D., Sutherland L. E., Barker D. M., Dahl L. K. Effects of chronic excess salt ingestion. Morphologic findings in kidneys of rats with differing genetic susceptibilities to hypertension. Arch Pathol. 1970 Jul;90(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek H., Nagy Z., Hüttner I., Bálint A., Kóczé A., Kerényi T. Investigations of the permeability changes of the vascular wall in experimental malignant hypertension by means of a colloidal iron preparation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Feb;50(1):13–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen L., Glynn M. F., Hovig T., Murphy E. A., Buchanan M. R., Mustard J. F. Renal lesions and rise in blood pressure caused by adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in rabbits. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):347–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P. Atheroembolic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 10;280(15):812–818. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904102801506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletsky S., Pavlicko K. M., Rivera-Velez J. M. Renin-angiotensin activity in hypertensive rats with a single ischemic kidney. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletsky S., Rivera-Velaz J. M. Renin-angiotensin system in microembolic renal hypertension. Arch Pathol. 1968 Jan;85(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S. THE RELATION OF SUPERFICIAL CORTICAL SCARS OF THE KIDNEY TO AORTIC ATHEROSCLEROSIS; A HYPOTHESIS OF RENAL ISCHAEMIA. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:471–478. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNay J. L., Abe Y. Pressure-dependent heterogeneity of renal cortical blood flow in dogs. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):571–587. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNay J. L., Abe Y. Redistribution of cortical blood flow during renal vasodilatation in dogs. Circ Res. 1970 Dec;27(6):1023–1032. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.6.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Mersereau W. A. Microembolic renal ischemia, hypertension, and nephrosclerosis. Arch Pathol. 1968 Jun;85(6):623–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Mersereau W. A. Platelet embolism and renal ischaemia. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(2):579–588. doi: 10.1002/path.1700900226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTKEN L. B., Jr Experimental production of atheromatous embolization. Arch Pathol. 1959 Dec;68:685–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS A. M., ELIOT R. S., KANJUH V. I., BLOEMENDAAL R. D., EDWARDS J. E. CHOLESTEROL EMBOLISM: A MULTIPLE-SYSTEM DISEASE MASQUERADING AS POLYARTERITIS NODOSA. Am J Cardiol. 1965 May;15:696–707. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(65)90359-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retan J. W., Miller R. E. Microembolic complications of atherosclerosis. Literature review and report of a patient. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Dec;118(6):534–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. W. The source of retinal emboli. Lancet. 1968 Oct 12;2(7572):789–792. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieniewicz D. J., Moore S., Moir F. D., McDade D. F. Atheromatous emboli to the kidneys. Radiology. 1969 May;92(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1148/92.6.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotkoff L. M., Logan A., Jose P., D'Avella J., Eisner G. M. Microsphere measurement of intrarenal circulation of the dog. Circ Res. 1971 Feb;28(2):158–166. doi: 10.1161/01.res.28.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swales J. D., Blake J. The relation between blood-pressure level and ischaemic renal contraction in the rat. J Pathol. 1970 Mar;100(3):149–154. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBURN G. D., KOPALD H. H., HERD J. A., HOLLENBERG M., O'MORCHOE C. C., BARGER A. C. INTRARENAL DISTRIBUTION OF NUTRIENT BLOOD FLOW DETERMINED WITH KRYPTON 85 IN THE UNANESTHETIZED DOG. Circ Res. 1963 Oct;13:290–307. doi: 10.1161/01.res.13.4.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J., Lattes R. G., Meltzer B. G., Spiro D. The cellular pathology of experimental hypertension. IV. Evidence for increased vascular permeability. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):187–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK F. G., ELIAS K. Embolization with material from atheromata. Am J Med Sci. 1949 Nov;218(5):510–515. doi: 10.1097/00000441-194911000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]