Abstract
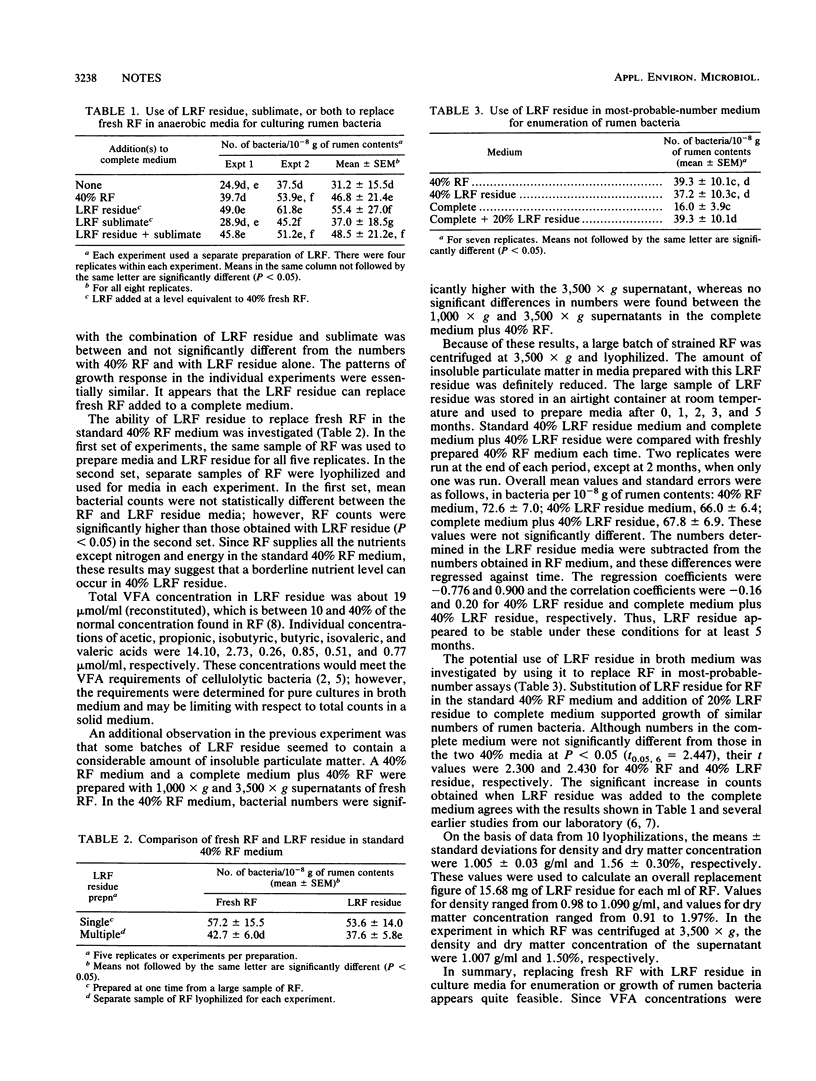
The supernatant from centrifugation at 1,000 x g of strained rumen fluid was lyophilized, and the residue and sublimate fractions were used to replace fresh rumen fluid in a complete roll tube medium for enumeration of total rumen bacteria. Most of the growth-supporting nutrients in fresh rumen fluid were found in the residue fraction. With one exception, no significant differences were found in total bacterial numbers either by roll tube or most-probable-number procedures when lyophilized rumen fluid residue was substituted for fresh rumen fluid. Lyophilized rumen fluid residue was stable for at least 5 months at room temperature. Rumen fluid supernatant from centrifugation at 1,000 x g had a mean density of 1.005 +/- 0.03 g/ml and contained 1.56% +/- 0.30% dry matter. On the basis of these values, 15.68 mg of lyophilized rumen fluid residue is equivalent to 1 ml of rumen fluid supernatant from centrifugation at 1,000 x g.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Scott H. W., Kowaluk P. Volatile fatty acid requirements of cellulolytic rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.537-543.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Tirabasso P. A., Grifo A. P., Jr Most-probable-number procedures for enumerating ruminal bacteria, including the simultaneous estimation of total and cellulolytic numbers in one medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2789–2792. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2789-2792.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb J. A., Dehority B. A. Variation in colony counts of total viable anaerobic rumen bacteria as influenced by media and cultural methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.262-267.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


