Abstract
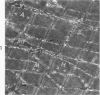
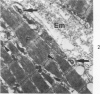
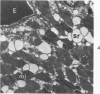
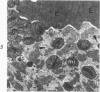
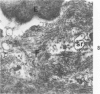
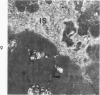
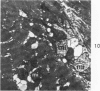
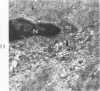
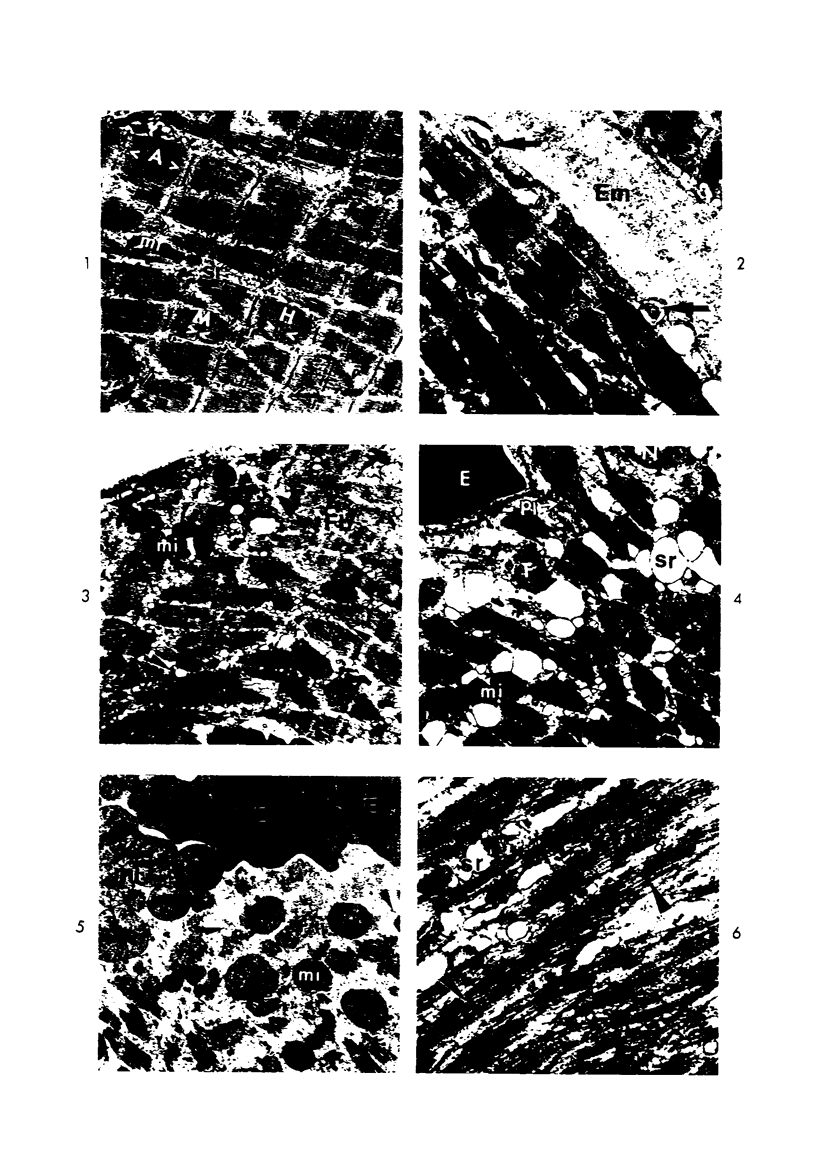
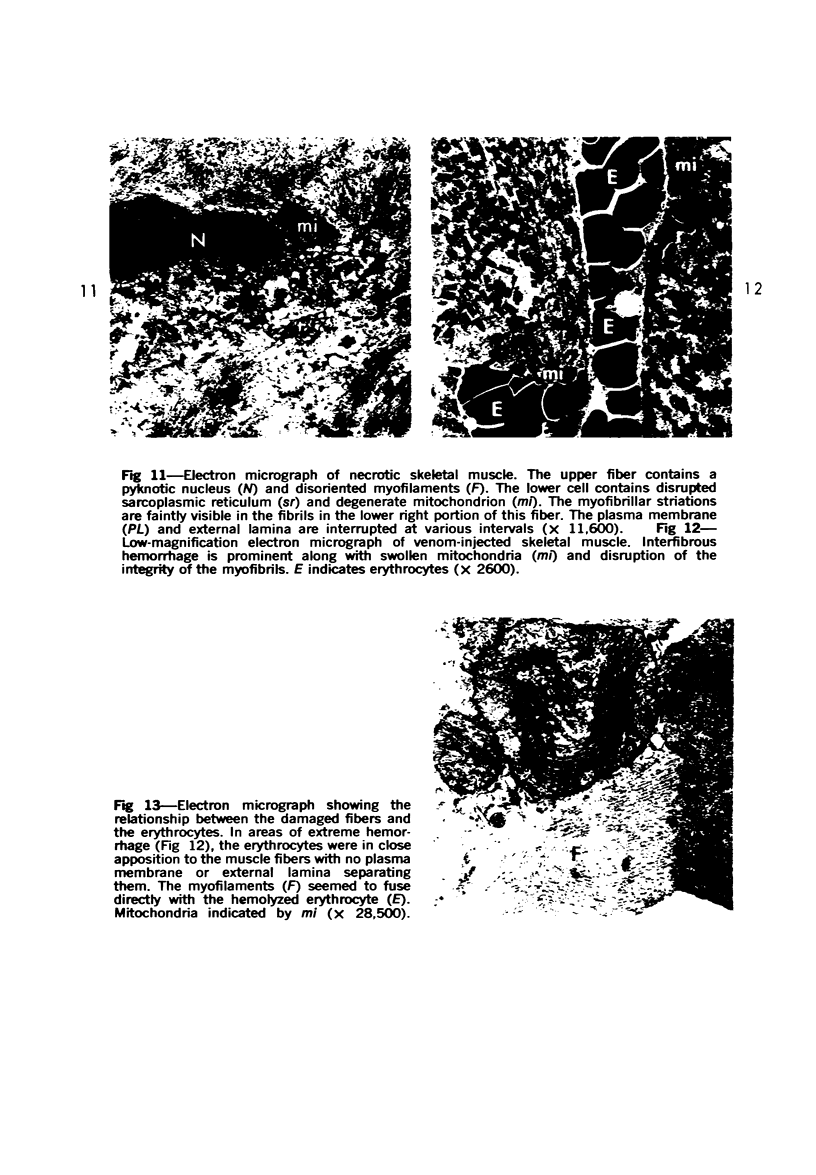
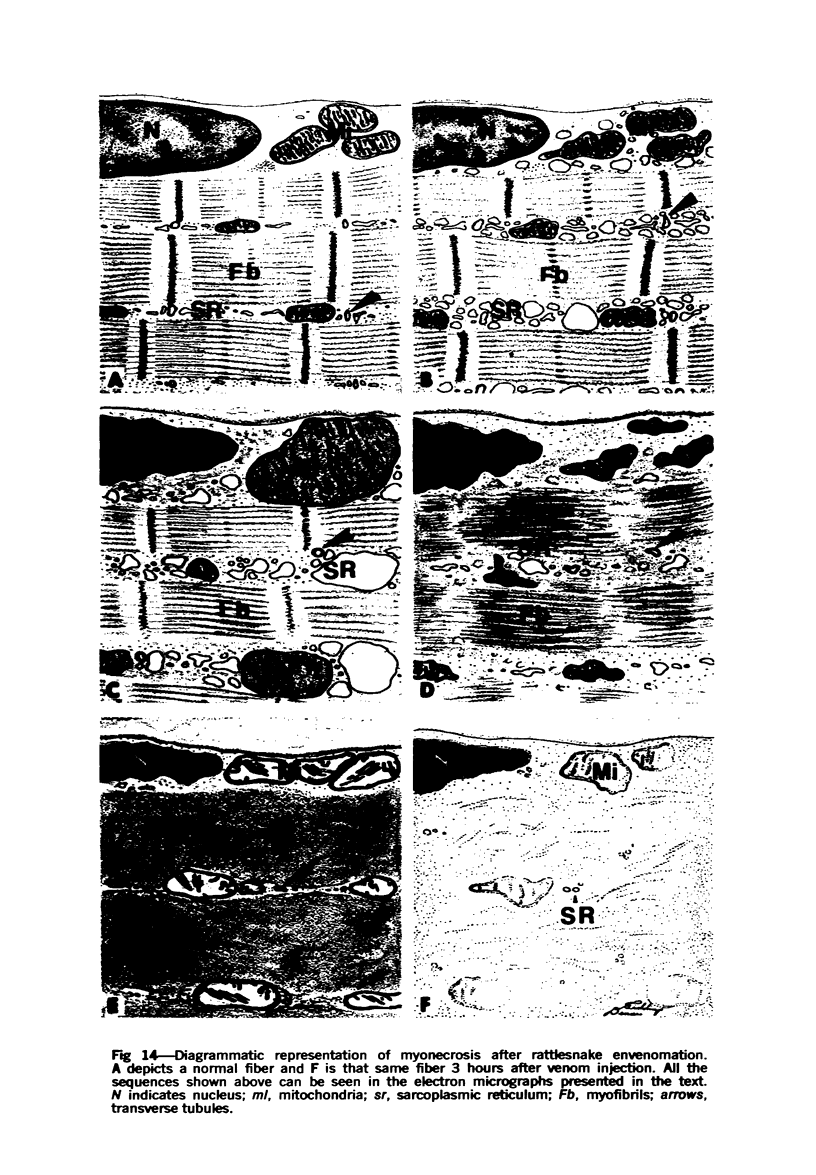
The myonecrotic effect of rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis) venom on mouse skeletal muscle was studied. The biceps femoris muscle was examined with the electron microscope after one-fourth the LD50 of the crude venom was injected into the gracilis and semimembranosus muscles. Focal areas of myonecrosis were abundant. Injured fibers contained dilated sarcoplasmic reticulum, disoriented, coagulated myofilamentous components and condensed, rounded and enlarged mitochondria. The external lamina and sarcolemma remained intact in many fibers. Hemorrhage was apparent in the endomysial connective tissue, and hemolysis was discernible. In areas where the erythrocytes were tightly packed between the muscle fibers, there was disruption of the external lamina and sarcolemma. Degeneration of the fibers in these areas was pronounced. These findings correlate well with the breakdown of muscle fibers by various methods described in the literature. Myonecrosis induced by snake venom may serve as a useful model for studying muscle necrosis because of its rapid onset and relative ease of induction.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews C. E., Dees J. E., Edwards R. O., Jackson K. W., Snyder C. C., Moseley T., Gennaro J. F., Jr, Gehres G. W. Venomous snakebite in Florida. J Fla Med Assoc. 1968 Apr;55(4):308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustyn J. M., Parsa B., Elliott W. B. Structural and respiratory effects of Agkistrodon piscivorus phospholipase A on rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 3;197(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D AGOSTINO A. N. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF SKELETAL AND CARDIAC MUSCLE OF THE RAT POISONED BY PLASMOCID. Lab Invest. 1963 Nov;12:1060–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahimi H. D., Cotran R. S. Permeability studies in heat-induced injury of skeletal muscle using lanthanum as fine structural tracer. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jan;62(1):143–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. The contraction of muscle. Sci Am. 1958 Nov;199(5):67–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A. K., Murphy F. A., Gary G. W., Jr Ultrastructural pathology of coxsackie A4 virus infection of mouse striated muscle. Exp Mol Pathol. 1971 Feb;14(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(71)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNN J. A. RAPID TOLUIDINE BLUE STAINING OF EPON-EMBEDDED AND MOUNTED "ADJACENT" SECTIONS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jul;44:57–58. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCollough N. C., Gennaro J. F. Treatment of venomous snakebite in the United States. Clin Toxicol. 1970 Sep;3(3):483–500. doi: 10.3109/15563657008990121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRISH H. M., SILBERG S. L., GOLDNER J. C. SNAKEBITE A PEDIATRIC PROBLEM. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1965 Apr;4:237–241. doi: 10.1177/000992286500400413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PALADE G. E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. III. Its form and distribution in striated muscle cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Mar 25;3(2):269–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE H. M., HOWES E. L., Jr, BLUMBERG J. M. ULTRASTRUCTURAL ALTERATIONS IN SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS INJURED BY COLD. I. THE ACUTE DEGENERATIVE CHANGES. Lab Invest. 1964 Oct;13:1264–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE H., PEASE D. C., PEARSON C. M. Selective actin filament and Z-band degeneration induced by plasmocid. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1962 Jul;11:549–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodin A. E., Harris L. C., Nghiem Q. X. Idiopathic, nonobstructive cardiomyopathy. Electron microscopic, histochemical, and autopsy observations. Arch Pathol. 1971 Jan;91(1):62–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENGER R. J., SPIRO D., SCULLY R. E., SHANNON J. M. Ultrastructural and physiologic alterations in ischemic skeletal muscle. Am J Pathol. 1962 Jan;40:1–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. M., Kainer R. A., Tu A. T. Ultrastructural studies of myonecrosis induced by cobra venom in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;18(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk S. W., Smith C. W., Blumberg J. M. Ultrastructural studies on the lesion produced in skeletal muscle fibers by crude type A Clostridium perfringens toxin and its purified alpha fraction. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):89–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENERY J. H., KOEFOOT R. R. Snake bite; a case with observations on early and late treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1955 Jun;15(6):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarom R., Braun K. Electron microscopic studies of the myocardial changes produced by scorpion venom injections in dogs. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]