Abstract
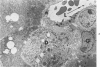
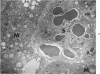
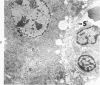
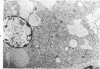
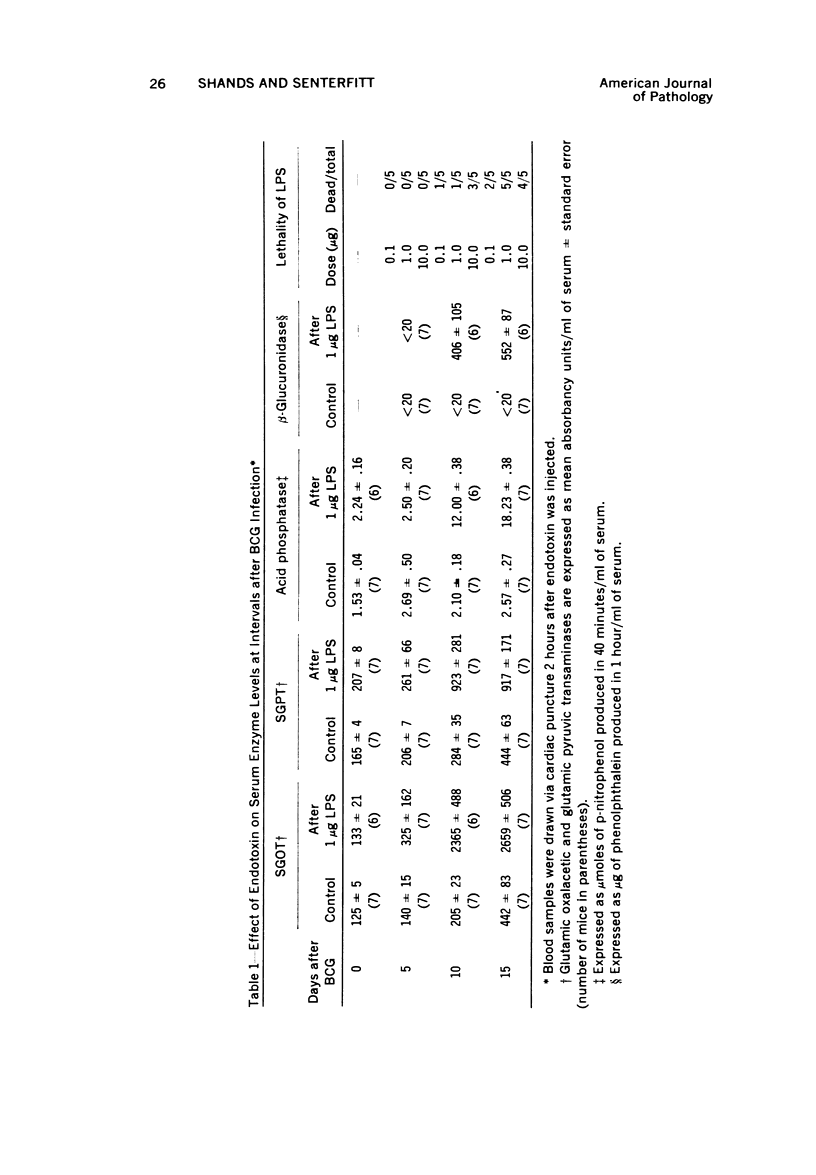
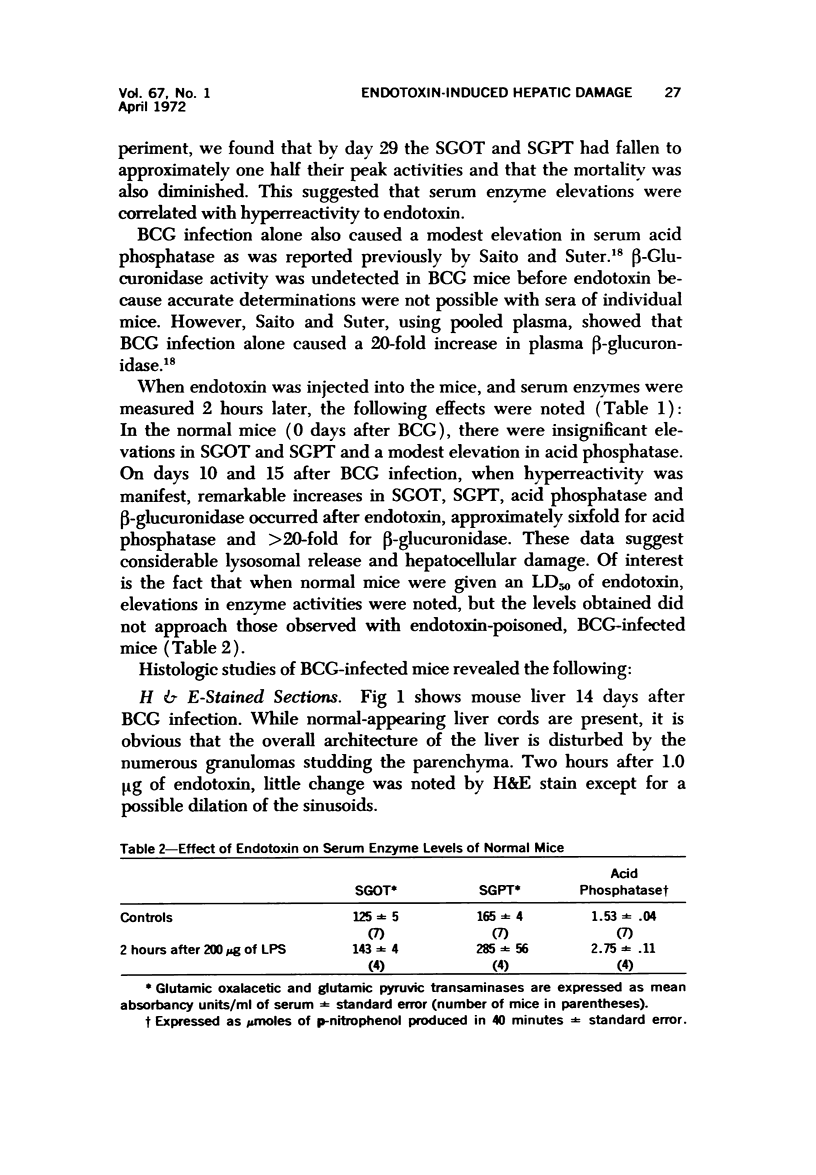
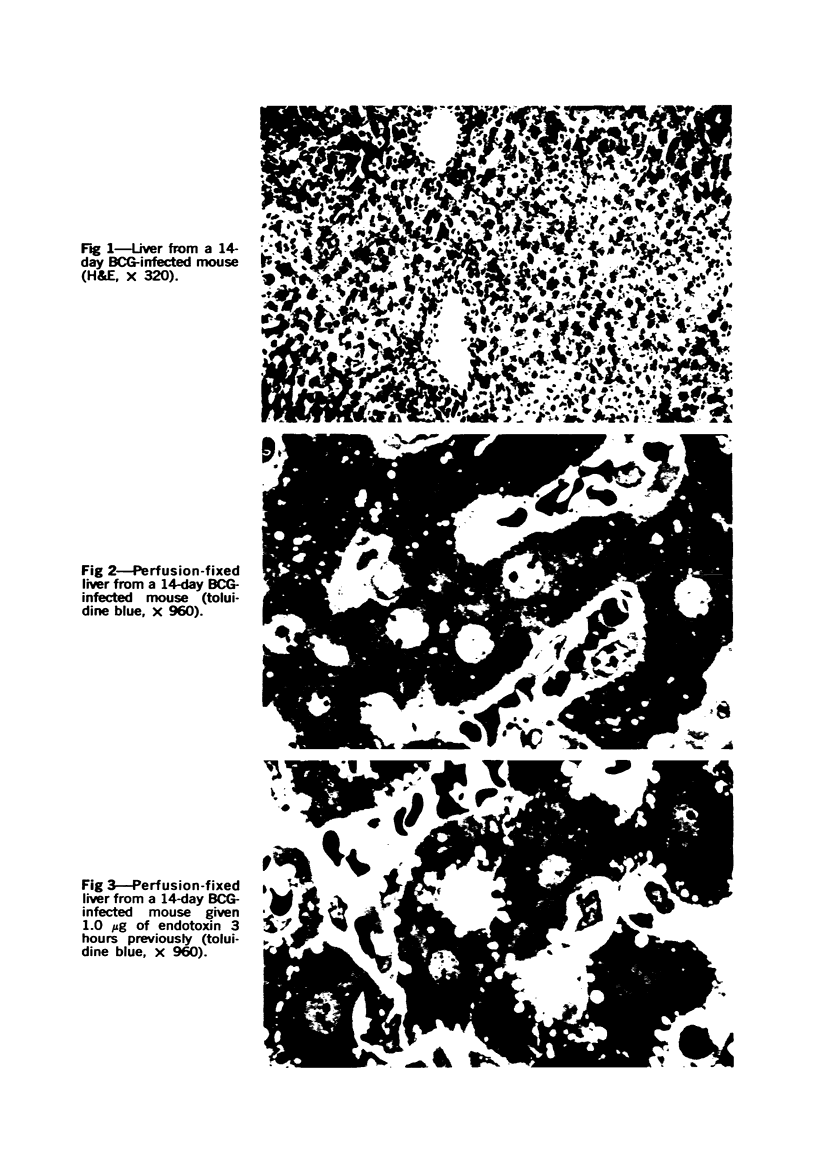
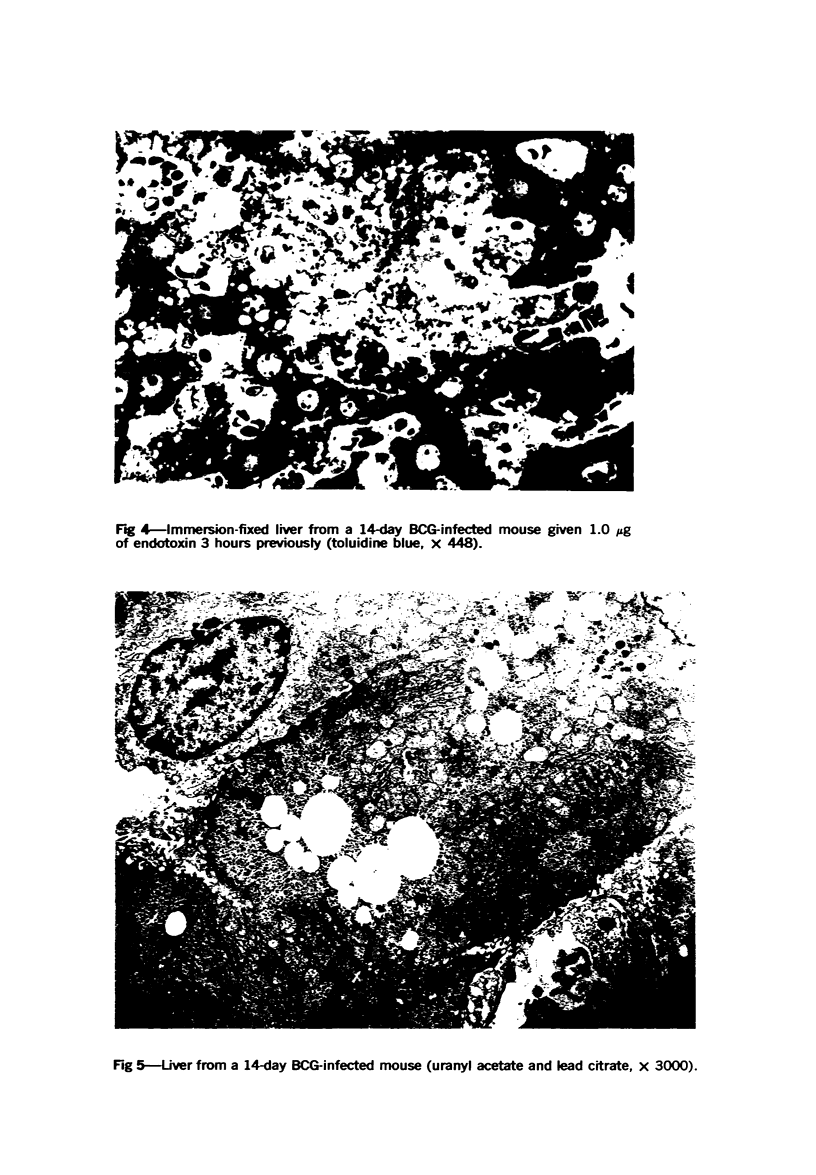
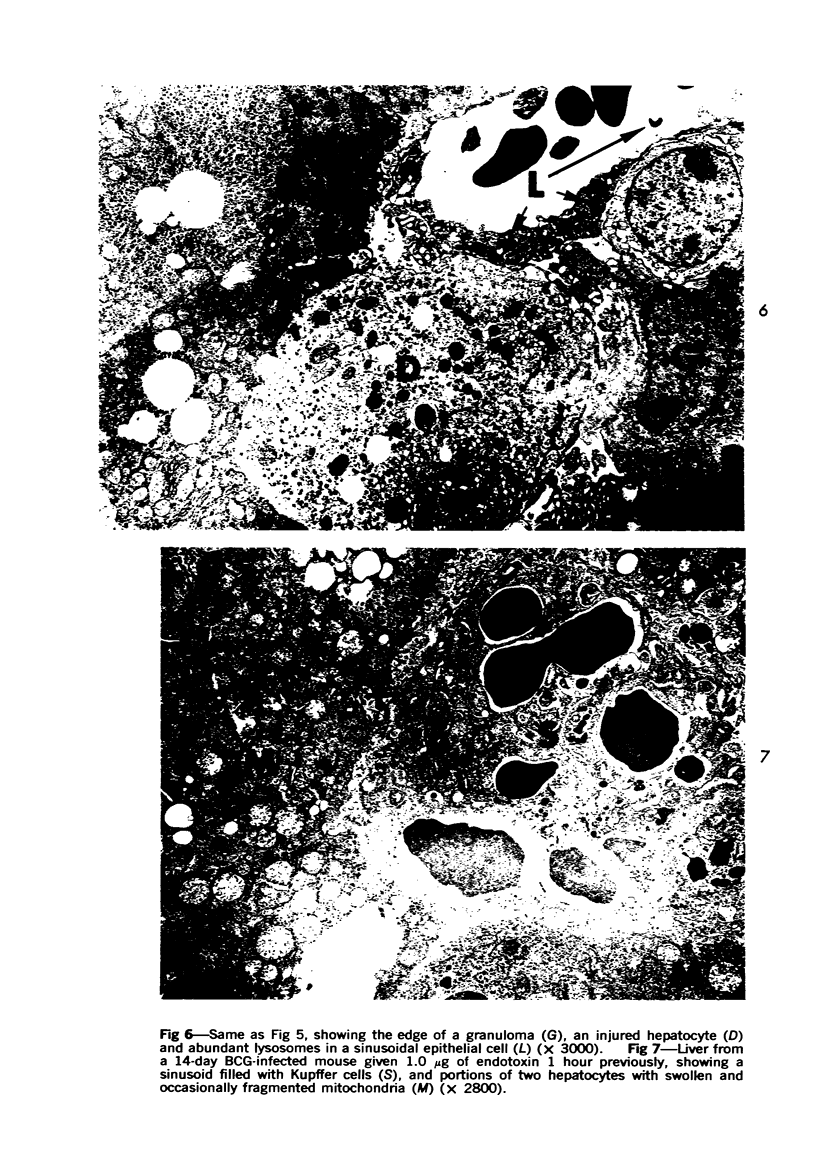
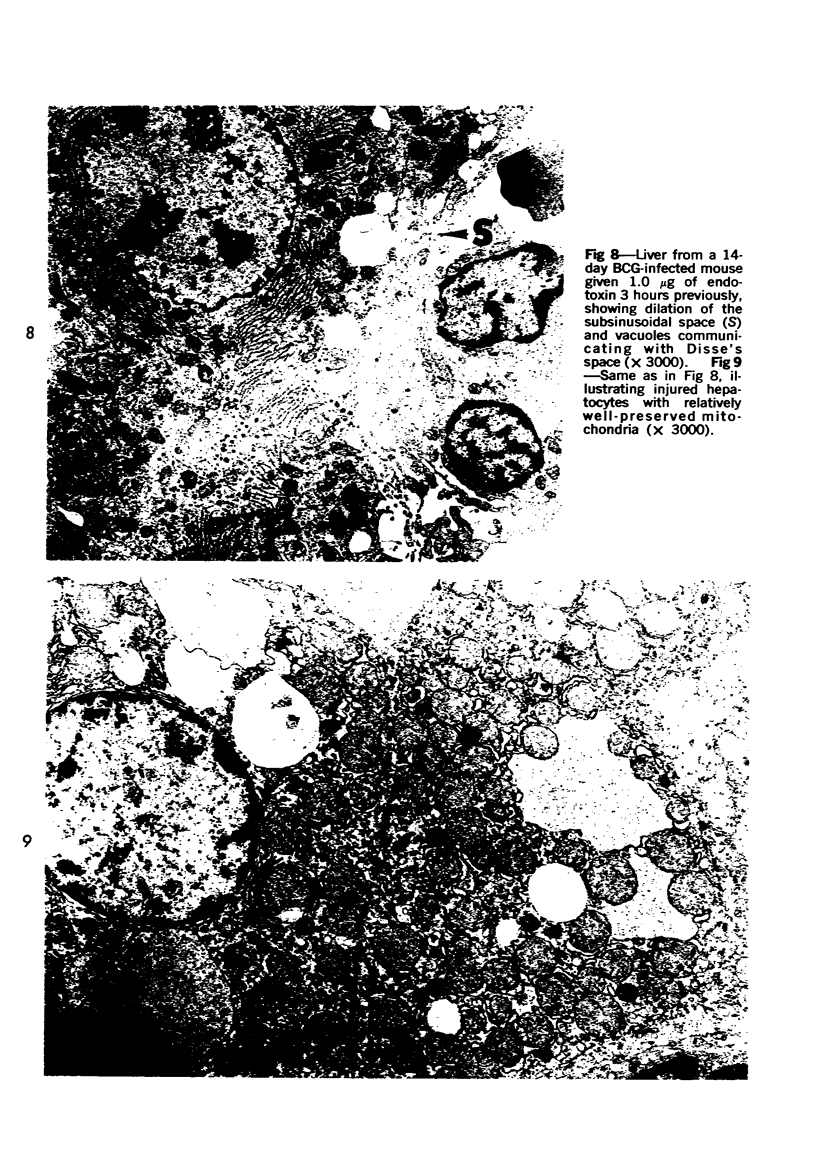
Systemic infection of mice with Mycobacterium BCG leads to focal liver damage by producing many granulomas. By undefined mechanisms, this infection markedly enhances the animal's susceptibility to the lethal effect of endotoxin. Small doses of endotoxin given to BCG-infected mice were found to cause acute hepatic damage, as demonstrated by elevated activities of liver enzymes in serum and by morphologic alterations documented by light and electron microscopy and by histochemical technics. The morphologic alterations caused by endotoxin included glycogen depletion, mitochondrial swelling, disruption of the continuity of sinusoidal endothelium and focal injury characterized by marked vacuolization of hepatocytes and distension and fragmentation of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Histochemical studies revealed the apparent release of acid phosphatase from granules in the central portions of granulomas, and the release of β-glucuronidase from the cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER J. R., FISHMAN W. H. Cellular localization of beta-glucuronidase in rat tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1956 Nov;4(6):570–587. doi: 10.1177/4.6.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY L. J., SMYTHE D. S., YOUNG L. G. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on metabolism. I. Carbohydrate depletion and the protective role of cortisone. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:389–405. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTONE M. S. Histochemical comparison of naphthol AS-phosphates for the demonstration of phosphatases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1958 Mar;20(3):601–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciznár I., Shands J. W. Effect of Alkali on the Immunological Reactivity of Lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):549–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.549-555.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRAR W. E., Jr, WATSON J. G. HYPOGLYCEMIA FOLLOWING ENDOTOXIN ADMINISTRATION IN ANIMALS WITH LIVER DAMAGE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:833–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUDA T. On the mechanism of endotoxin intoxication in rabbits. Jpn J Physiol. 1963 Apr 15;13:155–168. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.13.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Goldman S. S., DeLellis R. Dual localization of beta-glucuronidase in endoplasmic reticulum and in lysosomes. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):457–460. doi: 10.1038/213457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROGG E., PEARSE A. G. E. The enzymic and lipid histochemistry of experimental tuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Dec;33(6):567–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., WU M. L., HIXON W. S., CRAWFORD E. J. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. II. Enzyme measurements. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):19–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Mason A. D., Jr, Daniels J. P. The impairment of glucogenesis by gram negative infection. Metabolism. 1968 Jul;17(7):606–611. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Ruebner B. H. Hepatic changes produced by a single dose of endotoxin in the germfree mouse. Histochemistry, light microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1968 Jan;52(1):97–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Ruebner B. H. Hepatic changes produced by a single dose of endotoxin in the mouse. Light microscopy and histochemistry. Am J Pathol. 1967 Aug;51(2):269–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Slusser R. J., Ruebner B. H. Hepatic changes produced by a single dose of endotoxin in the mouse. Electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):477–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel D. M., Byfield J. E., Adomian G. E., Stevens G. H., Fonkalsrud E. W. Hepatic ultrastructural response to endotoxin shock. Surgery. 1970 Sep;68(3):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO K., SUTER E. LYSOSOMAL ACID HYDROLASES AND HYPERREACTIVITY TO ENDOTOXIN IN MICE INFECTED WITH BCG. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:739–749. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO K., SUTER E. LYSOSOMAL ACID HYDROLASES IN MICE INFECTED WITH BCG. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:727–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E., KIRSANOW E. M. Hyperreactivity to endotoxin in mice infected with mycobacteria. Induction and elicitation of the reactions. Immunology. 1961 Oct;4:354–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Miller V., Martin H., Senterfitt V. Hypoglycemic activity of endotoxin. II. Mechanism of the phenomenon in BCG-infected mice. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.494-501.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Miller V., Martin H. The hypoglycemic activity of endotoxin. I. Occurrence in animals hyperreactive to endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):413–417. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J. Effect of endotoxin on the ultrastructure of liver and blood cells of hamsters. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Apr;51(2):114–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]