Abstract
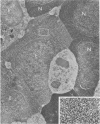
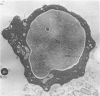
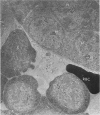
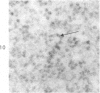
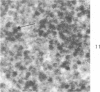
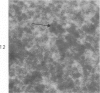
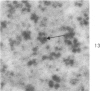
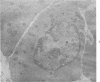
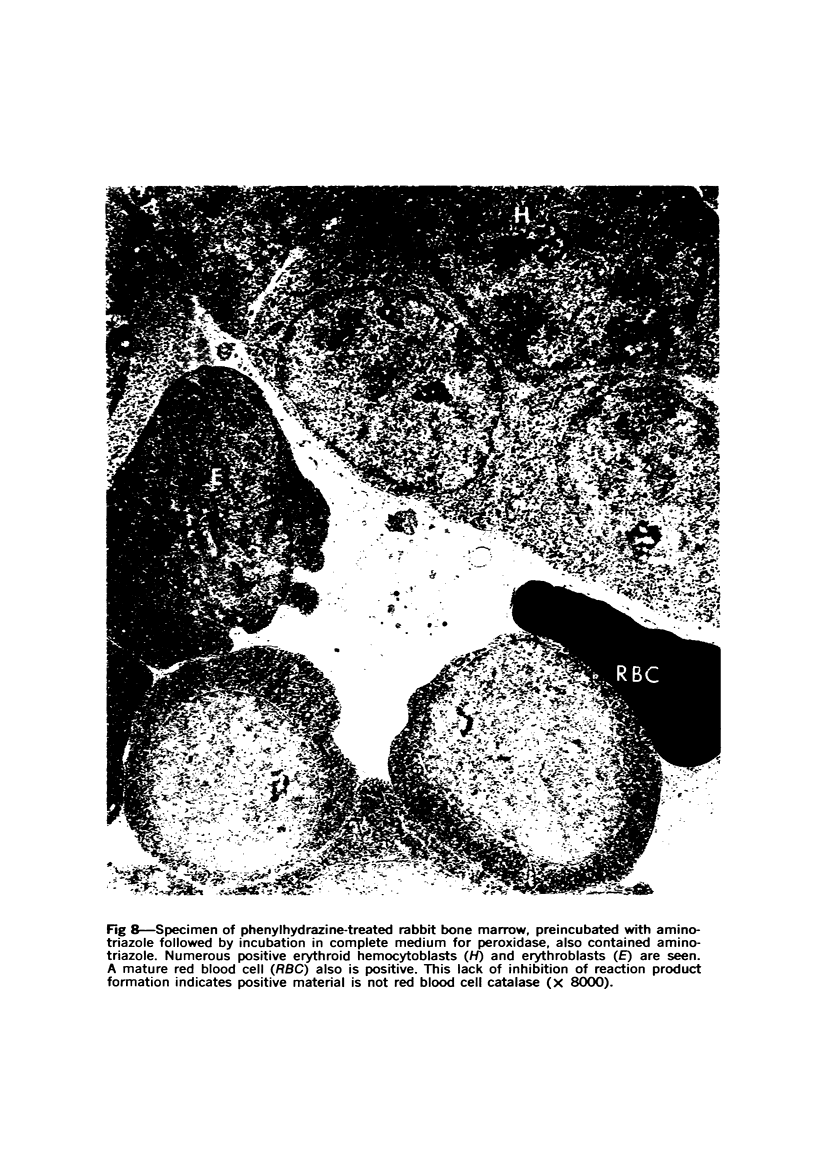
Peroxidase activity, demonstrated with diaminobenzidine as the electron donor according to the method of Graham and Karnovsky, was used as a cytochemical marker in a study of developing erythrocytes in guinea pig and rabbit bone marrow. Peroxidase activity was deposited diffusely in the cytoplasm and nuclear matrix of developing cells and was thought to represent hemoglobin, which others have shown by independent criteria to have a similar distribution. Diffuse localization was first observed in erythroblasts and at all subsequent stages of development. Another finding was the significant particulate localization of peroxidase activity apparently associated with cytoplasmic ribosomes and nuclear particles of immature erythrocytes. This activity differentiated the most primitive erythroid precursors from hemocytoblasts of other marrow cell lines, a distinction impossible by strictly morphologic criteria. Particulate peroxidase localization was identified in erythroid hemocytoblasts, erythroblasts, normoblasts and reticulocytes but not in mature erythrocytes. The nature of the particle-associated peroxidase activity was not determined with certainty. However, it could not be differentiated from the diffuse activity, thought to reflect hemoglobin, by several inhibitors and could not be attributed to erythrocyte catalase. The possibility is therefore raised that this activity represents hemoglobin, newly assembled either on or immediately adjacent to nuclear particles and cytoplasmic ribosomes.
Full text
PDF
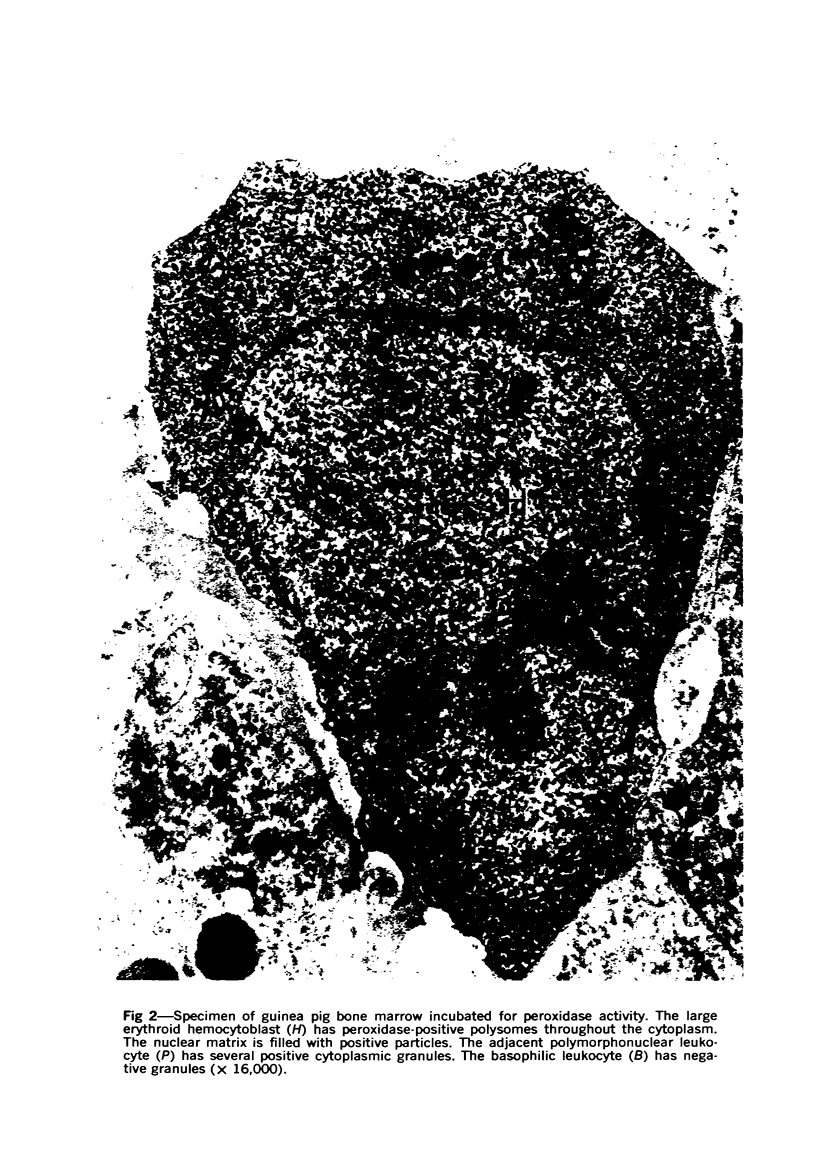
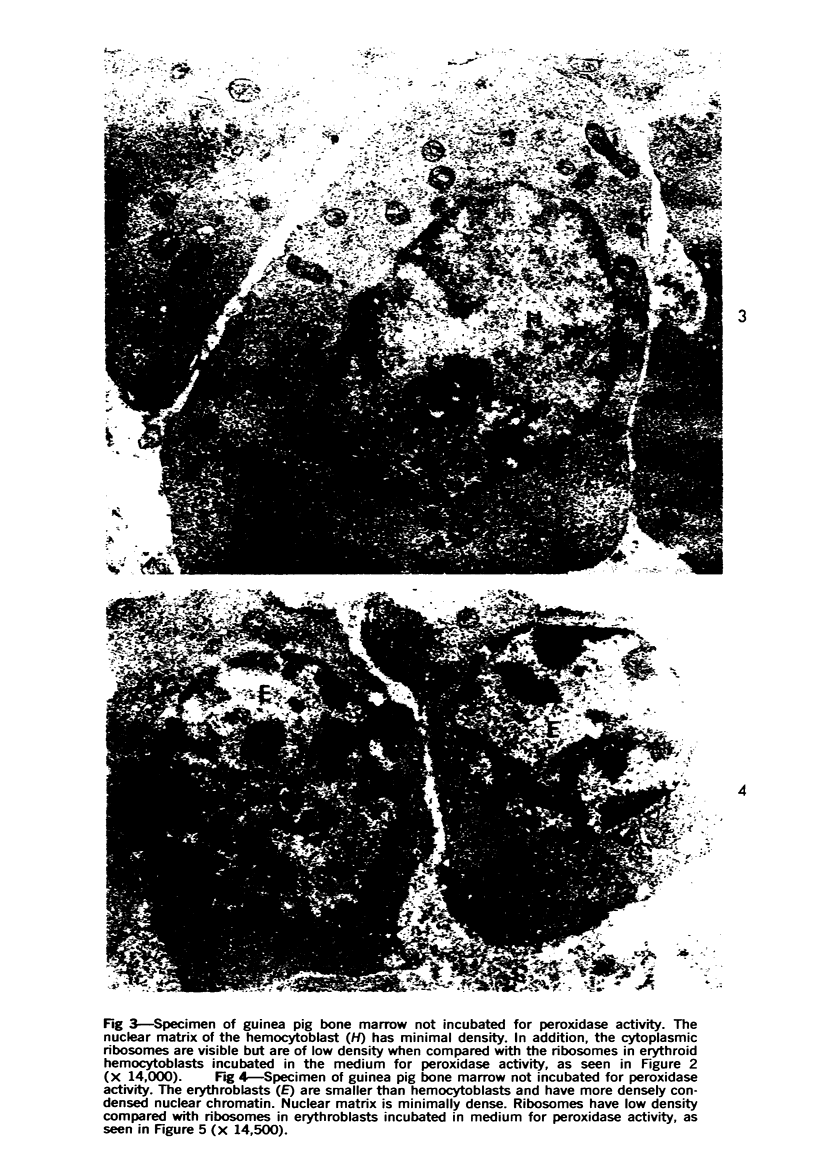













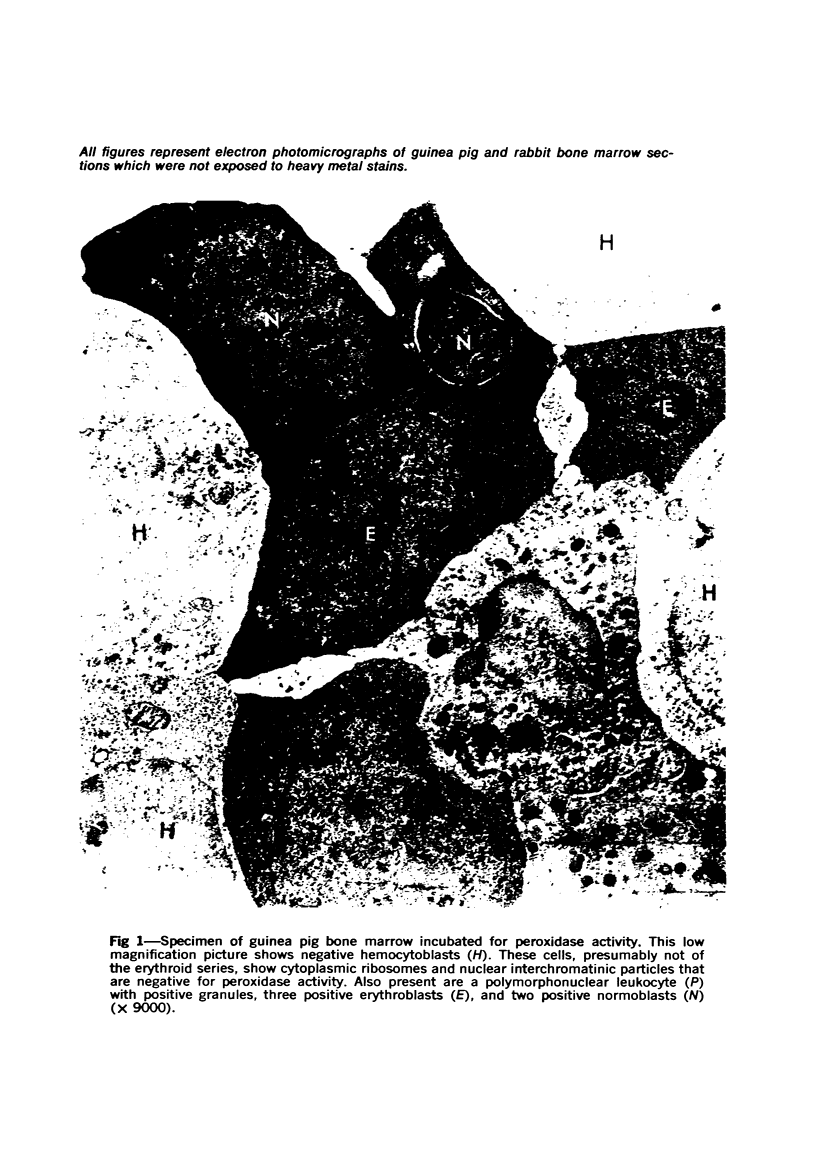


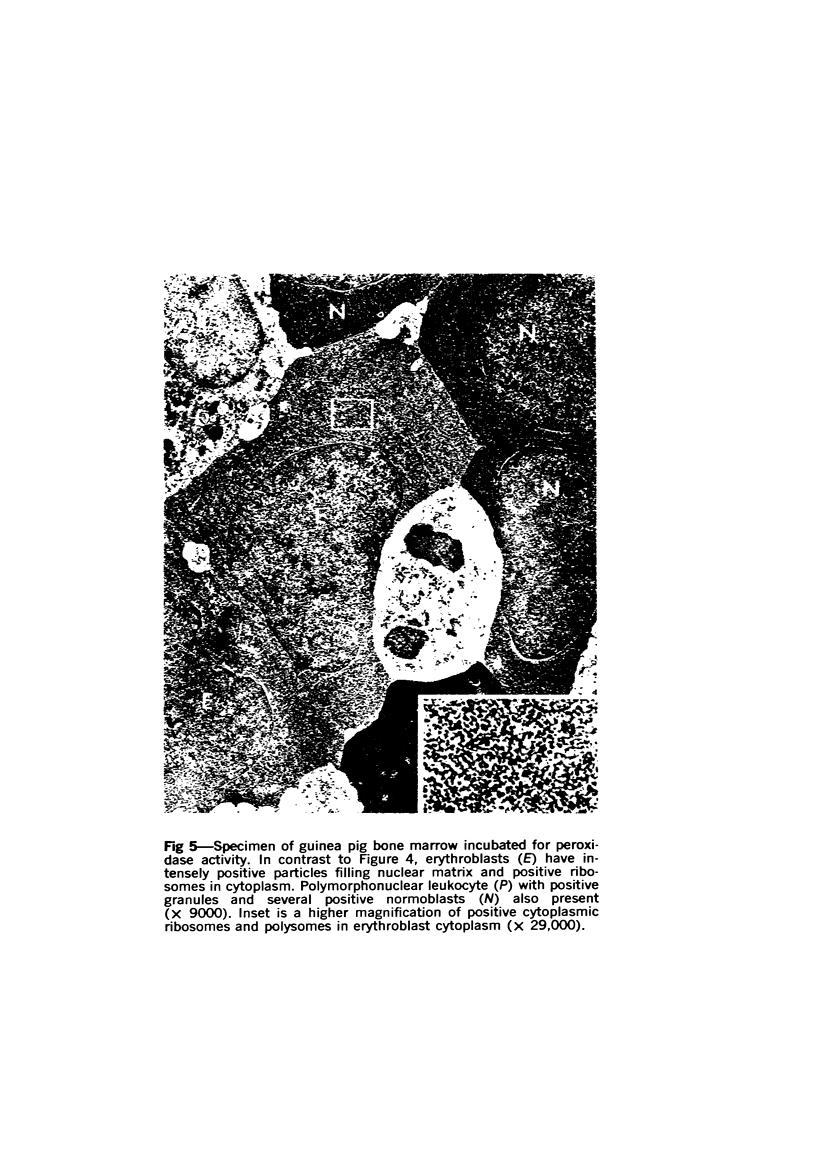
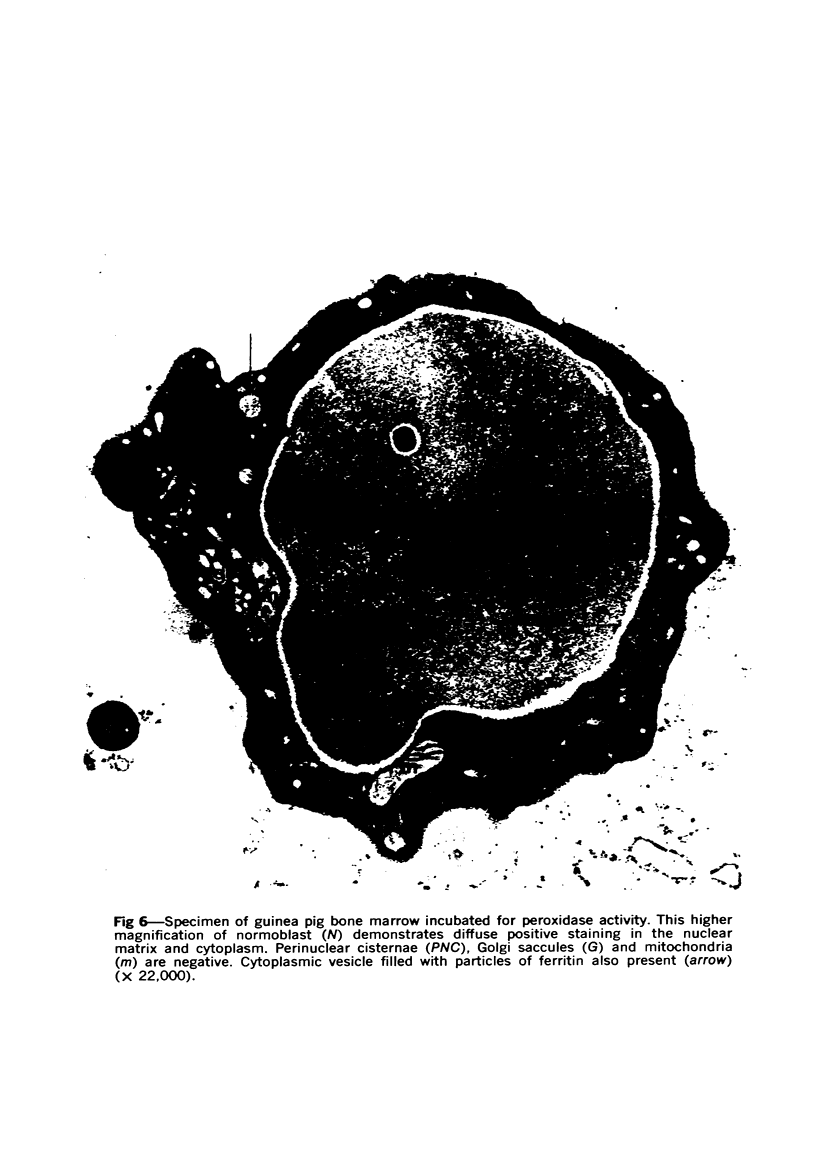
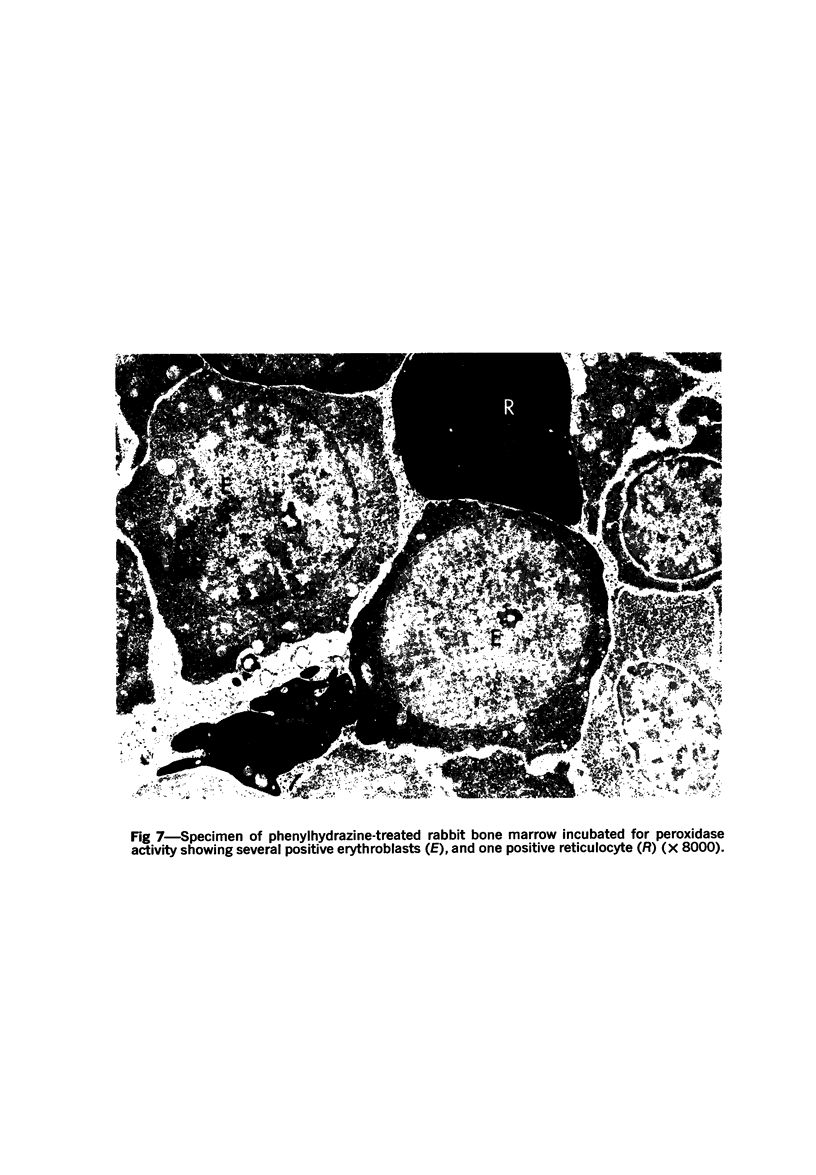

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Leduc E. H. Detection of simultaneous antibody synthesis in plasma cells and specialized lymphocytes in rabbit lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1137–1168. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSOOK H., DEASY C. L., HAAGENSMIT A. J., KEIGHLEY G., LOWY P. H. Incorporation in vitro of labeled amino acids into proteins of rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):669–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Segregation and packaging of granule enzymes in eosinophilic leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):54–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G., Elliott K. A. The distribution of peroxidase in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1934;28(5):1911–1919. doi: 10.1042/bj0281911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton-Gorius J. Utilisation de la diaminobenzidine pour la mise en évidence, au microscope électronique, de l'hémoglobine intracellulaire. La réactivité des différents organelles des érythroblastes. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1970 Mar-Apr;10(2):243–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Litt M. The entry of granule-associated peroxidase into the phagocytic vacuoles of eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1291–1306. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES H. G. Structure in nucleated erythrocytes. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Mar;9:671–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT D. W. SURFACE SPECIALIZATIONS OF ABSORBING CELLS. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Feb;13:75–91. doi: 10.1177/13.2.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenster J. H., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. METABOLISM AND MORPHOLOGY OF RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN PARTICLES FROM THE CELL NUCLEUS OF LYMPHOCYTES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Apr;46(4):432–444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.4.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMEL C. L., BESSMAN S. P. HEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS IN AVIAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2228–2238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya T., Morrison M. A study of the hemoproteins of thyroid microsomes with emphasis on the thyroid peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1967 Apr;6(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1021/bi00856a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANZANI G. A., GALANTE E. PEROXIDASE ACTIVITIES FROM WHEAT EMBRYO RIBOSOMES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:20–24. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., NOVOGRODSKY A. A study of the inhibition of catalase by 3-amino-1:2:4:-triazole. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):468–475. doi: 10.1042/bj0680468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS G. C. The purification and properties of glutathione peroxidase of erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):502–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B., Goldfischer S. Visualization of peroxisomes (microbodies) and mitochondria with diaminobenzidine. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Oct;17(10):675–680. doi: 10.1177/17.10.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlic D. The use of 55Fe in high-resolution radioautography of developing red cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):201–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHICHI H., KAMIRYO T., FUNAHASHI S. HAEMOPROTEINS IN HEART MICROSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 18;99:381–383. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon L. M., Kay E., Lew J. Y. Peroxidase isozymes from horseradish roots. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):2166–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skutelsky E., Danon D. An electron microscopic study of nuclear elimination from the late erythroblast. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):625–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum J. M., Karnovsky M. J. Cytochemical localization of endogenous peroxidase in thyroid follicular cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):655–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum J. M., Karnovsky M. J. Ultrastructural localization of peroxidase in submaxillary acinar cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 May;31(3):323–336. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Fahimi H. D. The use of beef liver catalase as a protein tracer for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):480–489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Soltani M. H., Fahimi H. D. Fine structural localization of peroxidase activity in the epithelium of large intestine of rat. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):168–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman H. S., Freedman M. L., Rabinovitz M. Studies with 59Fe-labeled hemin on the control of polyribosome formation in rabbit reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]