Abstract
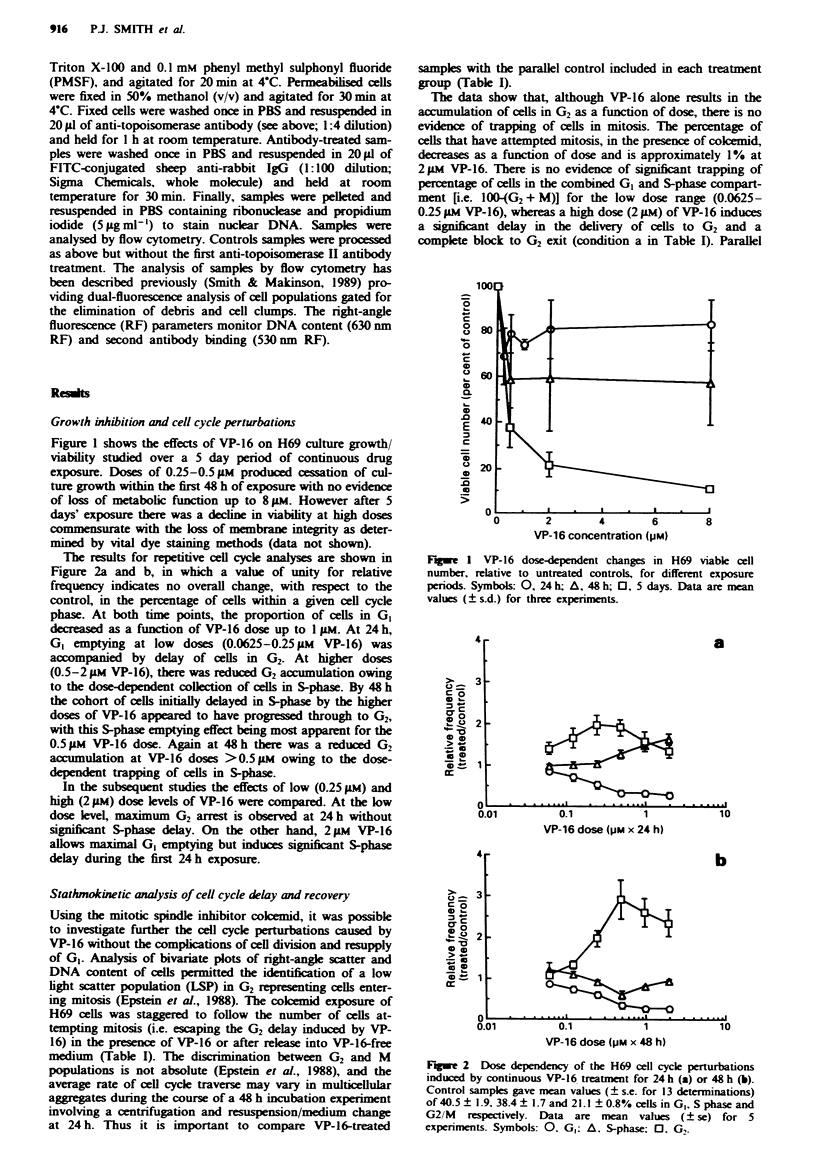
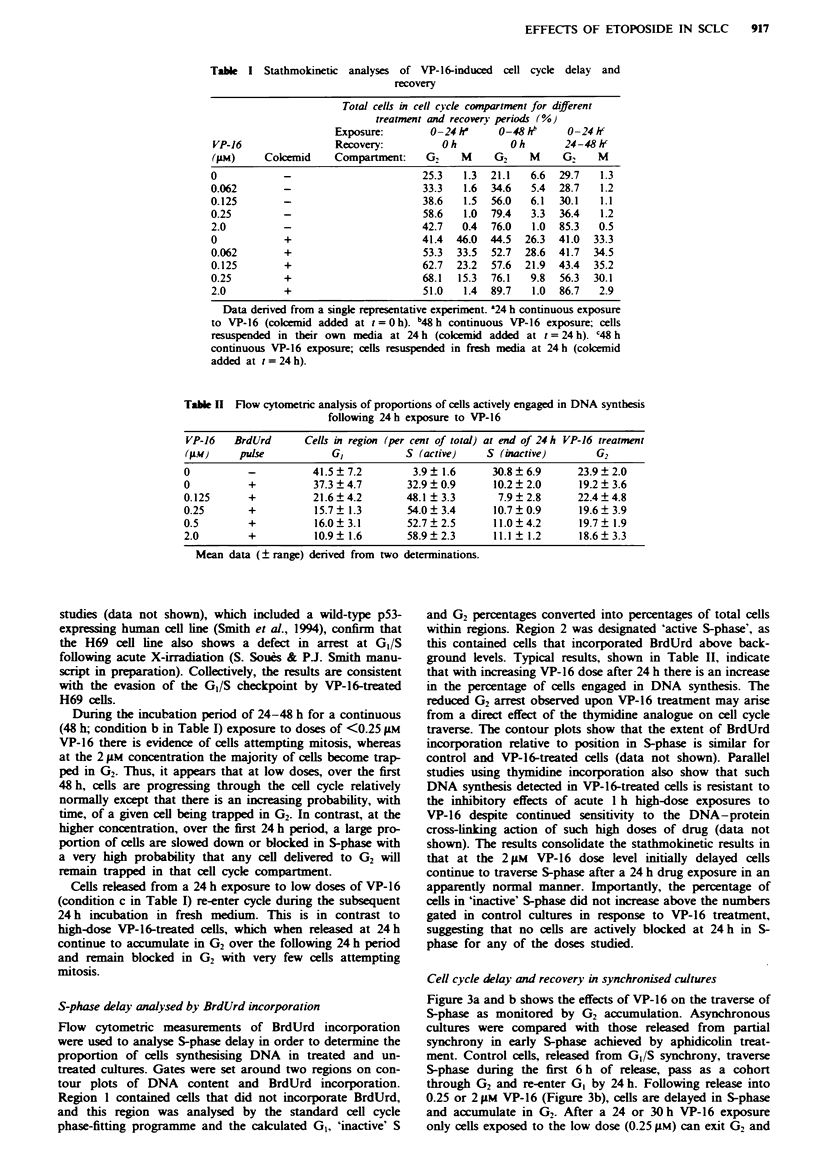
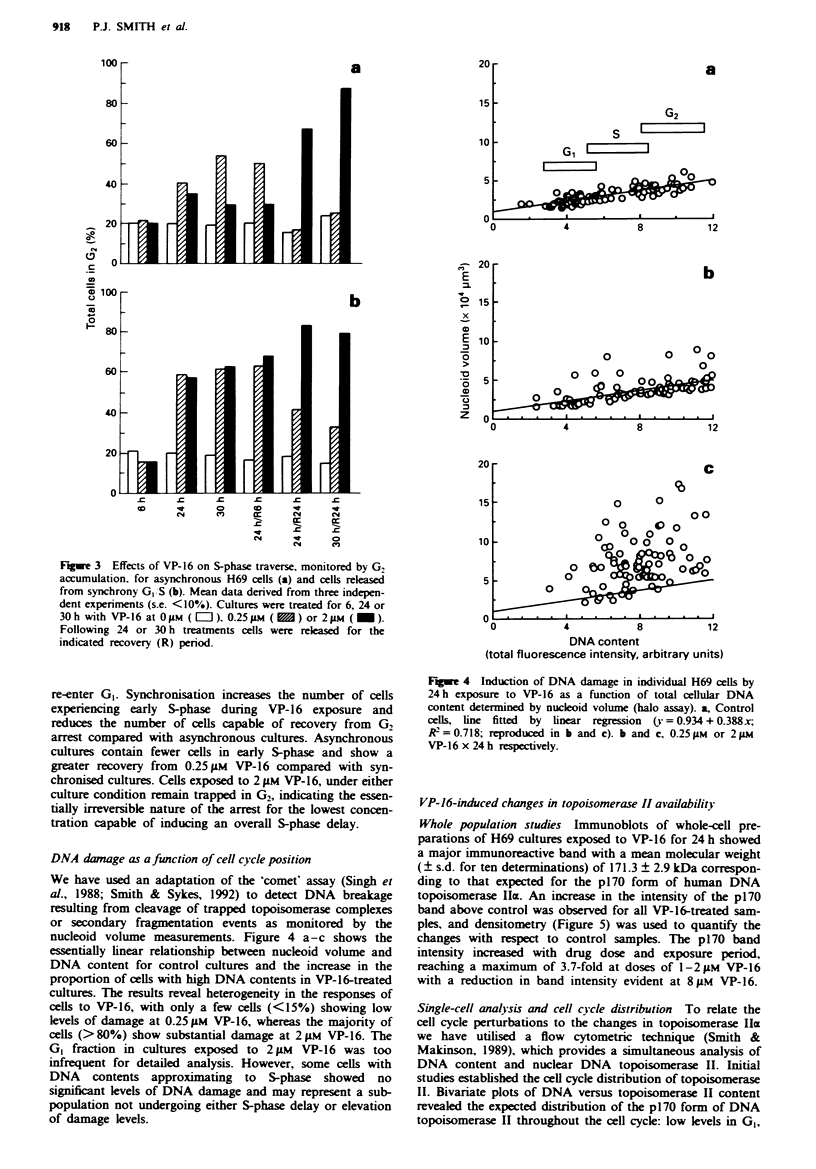
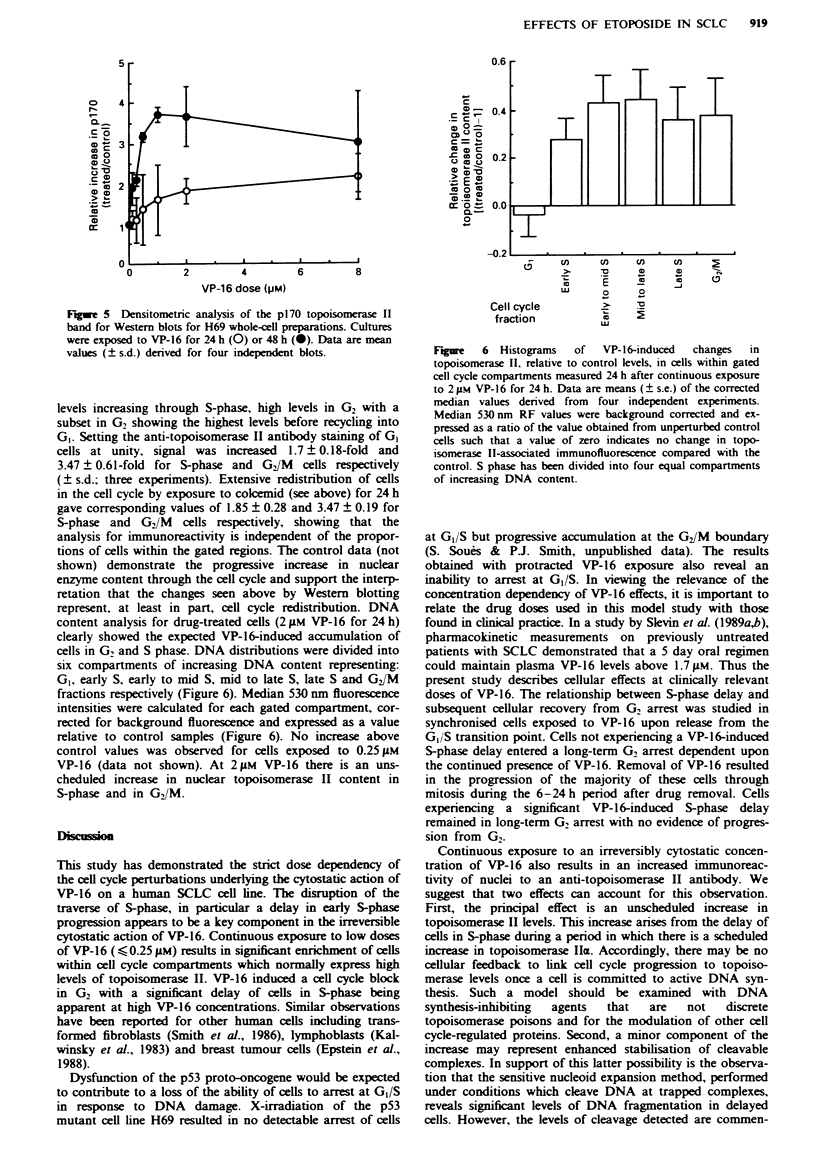
As an approach to the rational design of combination chemotherapy involving the anti-cancer DNA topoisomerase II poison etoposide (VP-16), we have studied the dynamic changes occurring in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell populations during protracted VP-16 exposure. Cytometric methods were used to analyse changes in target enzyme availability and cell cycle progression in a SCLC cell line, mutant for the tumour-suppressor gene p53 and defective in the ability to arrest at the G1/S phase boundary. At concentrations up to 0.25 microM VP-16, cells became arrested in G2 by 24 h exposure, whereas at concentrations 0.25-2 microM G2 arrest was preceded by a dose-dependent early S-phase delay, confirmed by bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. Recovery potential was determined by stathmokinetic analysis and was studied further in aphidicolin-synchronised cultures released from G1/S and subsequently exposed to VP-16 in early S-phase. Cells not experiencing a VP-16-induced S-phase delay entered G2 delay dependent upon the continued presence of VP-16. These cells could progress to mitosis during a 6-24 h period after drug removal. Cells experiencing an early S-phase delay remained in long-term G2 arrest with greatly reducing ability to enter mitosis up to 24 h after removal of VP-16. Irreversible G2 arrest was delimited by the induction of significant levels of DNA cleavage or fragmentation, not associated with overt apoptosis, in the majority of cells. Western blotting of whole-cell preparations showed increases in topoisomerase II levels (up to 4-fold) attributable to cell cycle redistribution, while nuclei from cells recovering from S-phase delay showed enhanced immunoreactivity with an anti-topoisomerase II alpha antibody. The results imply that traverse of G1/S and early S-phase in the presence of a specific topoisomerase II poison gives rise to progressive low-level trapping of topoisomerase II alpha, enhanced topoisomerase II alpha availability and the subsequent irreversible arrest in G2 of cells showing limited DNA fragmentation. We suggest that protracted, low-dose chemotherapeutic regimens incorporating VP-16 are preferentially active towards cells attempting G1/S transition and have the potential for increasing the subsequent action of other topoisomerase II-targeted agents through target enzyme modulation. Combination modalities which prevent such dynamic changes occurring would act to reduce the effectiveness of the VP-16 component.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callahan R. p53 mutations, another breast cancer prognostic factor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):826–827. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombernowsky P., Nissen N. I. Schedule dependency of the antileukemic activity of the podophyllotoxin-derivative VP 16-213 (NSC-141540) in L1210 leukemia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1973 Sep;81(5):715–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb03564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn L. H., Pennington K., McClean J. Phase II trial of daily oral VP-16 in refractory small cell lung cancer: a Hoosier Oncology Group study. Semin Oncol. 1990 Feb;17(1 Suppl 2):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. J., Watson J. V., Smith P. J. Subpopulation analysis of drug-induced cell-cycle delay in human tumor cells using 90 degrees light scatter. Cytometry. 1988 Jul;9(4):349–358. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. E., Smith P. J. Long-term inhibition of DNA synthesis and the persistence of trapped topoisomerase II complexes in determining the toxicity of the antitumor DNA intercalators mAMSA and mitoxantrone. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 15;50(18):5813–5818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisson B. S., Ross W. E. DNA topoisomerase II: a primer on the enzyme and its unique role as a multidrug target in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;32(2):89–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainsworth J. D., Johnson D. H., Frazier S. R., Greco F. A. Chronic daily administration of oral etoposide--a phase I trial. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Mar;7(3):396–401. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Hittelman W. N., Earnshaw W. C. Differential expression of DNA topoisomerases I and II during the eukaryotic cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1086–1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. H., Greco F. A., Strupp J., Hande K. R., Hainsworth J. D. Prolonged administration of oral etoposide in patients with relapsed or refractory small-cell lung cancer: a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Oct;8(10):1613–1617. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.10.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalwinsky D. K., Look A. T., Ducore J., Fridland A. Effects of the epipodophyllotoxin VP-16-213 on cell cycle traverse, DNA synthesis, and DNA strand size in cultures of human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1592–1597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Watson J. V., Lowe A. D., Green S. M., Vedeckis W. Regulation of cell cycle duration by c-myc levels. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):773–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone L. R., White A., Sprouse J., Livanos E., Jacks T., Tlsty T. D. Altered cell cycle arrest and gene amplification potential accompany loss of wild-type p53. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):923–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R. B., Ross W. E. Possible role for p34cdc2 kinase in etoposide-induced cell death of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3767–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. A., Stewart C. F., Tolley E. A. Clinical pharmacodynamics of continuous-infusion etoposide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990;25(5):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00686238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minford J., Pommier Y., Filipski J., Kohn K. W., Kerrigan D., Mattern M., Michaels S., Schwartz R., Zwelling L. A. Isolation of intercalator-dependent protein-linked DNA strand cleavage activity from cell nuclei and identification as topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):9–16. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. B., Hainsworth J. D., Greco F. A., Hande K. R., DeVore R. F., Johnson D. H. A phase II trial of cisplatin and prolonged administration of oral etoposide in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 1992 Jan 15;69(2):370–375. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920115)69:2<370::aid-cncr2820690217>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto-Kubo S., Nishio K., Heike Y., Yoshida M., Ohmori T., Saijo N. Apoptosis induced by etoposide in small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1994;33(5):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00686267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfilippo F., Vaughn W. K., Spees E. K., Light J. A., LeFor W. M. Benefits of HLA-A and HLA-B matching on graft and patient outcome after cadaveric-donor renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):358–364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. P., McCoy M. T., Tice R. R., Schneider E. L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Mar;175(1):184–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slevin M. L., Clark P. I., Joel S. P., Malik S., Osborne R. J., Gregory W. M., Lowe D. G., Reznek R. H., Wrigley P. F. A randomized trial to evaluate the effect of schedule on the activity of etoposide in small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Sep;7(9):1333–1340. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.9.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Anderson C. O., Watson J. V. Predominant role for DNA damage in etoposide-induced cytotoxicity and cell cycle perturbation in human SV40-transformed fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5641–5645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Makinson T. A. Cellular consequences of overproduction of DNA topoisomerase II in an ataxia-telangiectasia cell line. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 1;49(5):1118–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Morgan S. A., Fox M. E., Watson J. V. Mitoxantrone-DNA binding and the induction of topoisomerase II associated DNA damage in multi-drug resistant small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 1;40(9):2069–2078. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90237-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Sykes H. R. Simultaneous measurement of cell cycle phase position and ionizing radiation-induced DNA strand breakage in single human tumour cells using laser scanning confocal imaging. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Apr;61(4):553–560. doi: 10.1080/09553009214551331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Takahashi T., Suzuki H., Hida T., Sekido Y., Ariyoshi Y., Ueda R. The p53 gene is very frequently mutated in small-cell lung cancer with a distinct nucleotide substitution pattern. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1775–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. N., Grosh W. W., Prater K., Hande K. R. In vitro pharmacodynamic evaluation of VP-16-213 and implications for chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1987;19(3):246–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00252980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


