Abstract
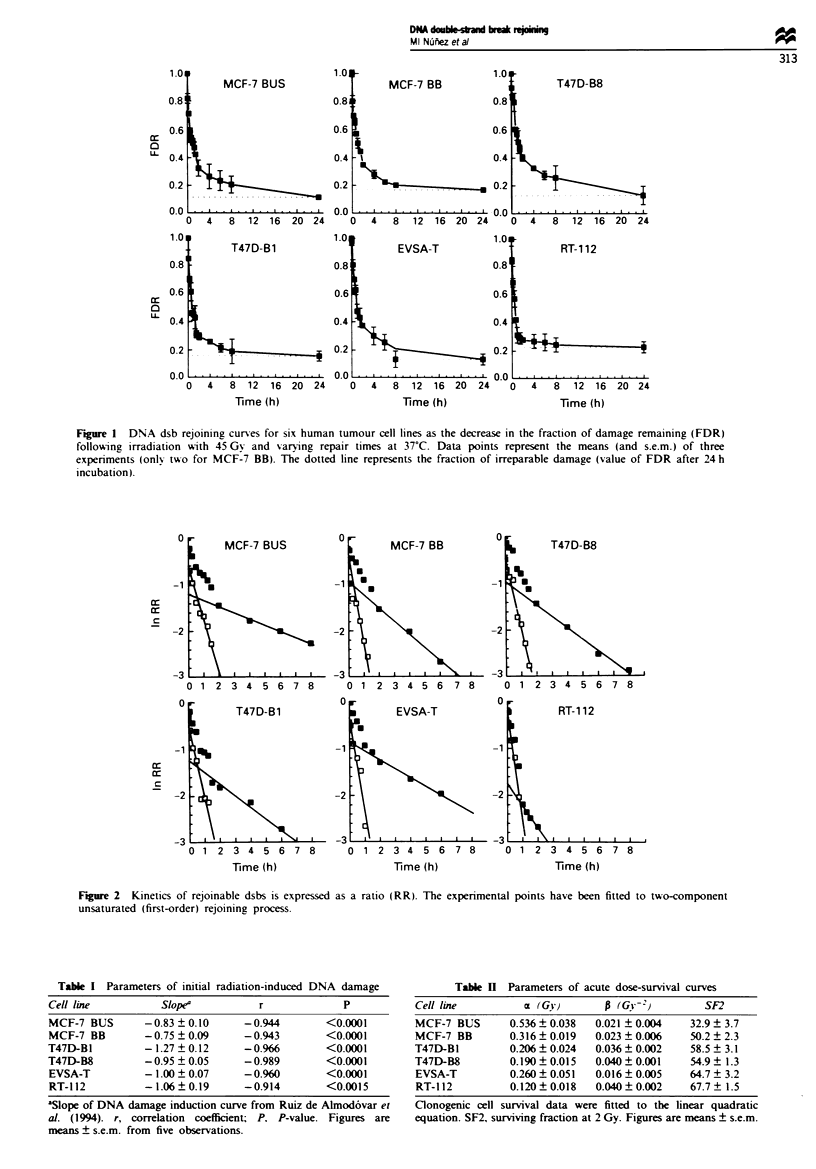
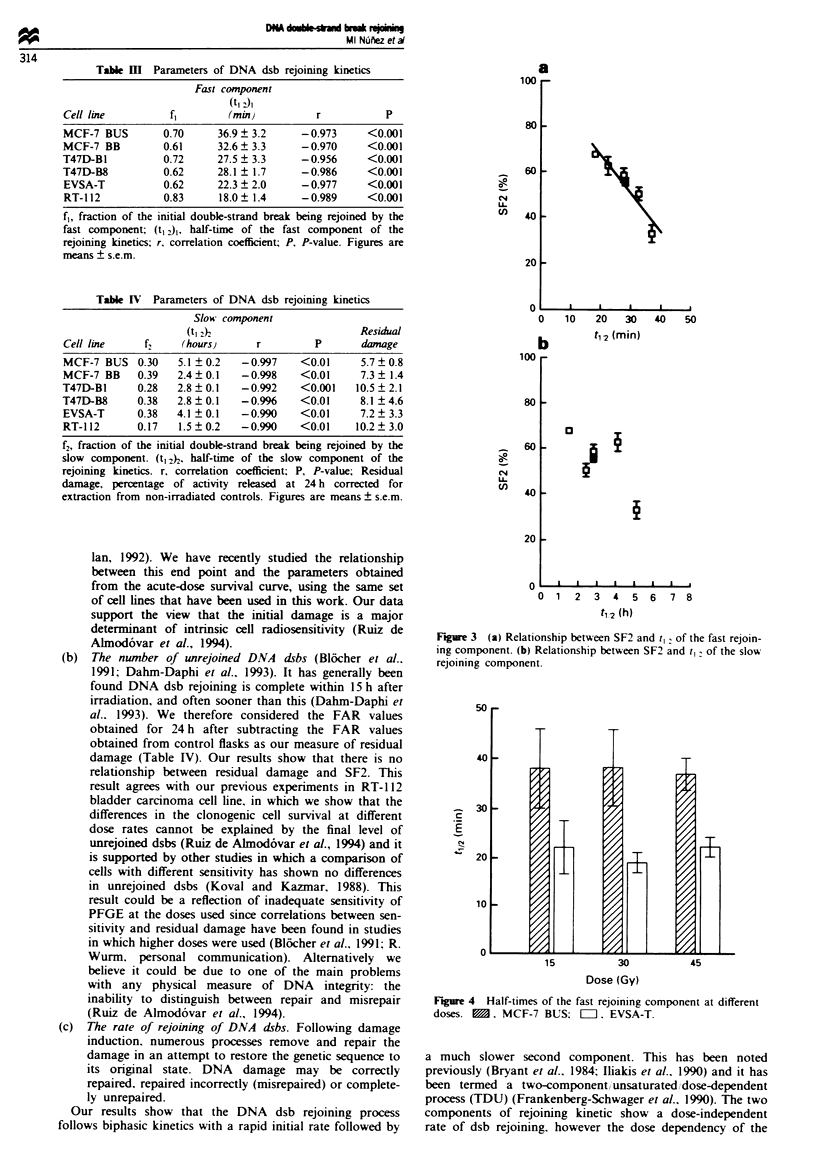
Five established human breast cancer cell lines and one established human bladder cancer cell line of varying radiosensitivity have been used to determine whether the rejoining of DNA double-strand breaks (dsbs) shows a correlation with radiosensitivity. The kinetics of dsb rejoining was biphasic and both components proceeded exponentially with time. The half-time (t1/2) of rejoining ranged from 18.0 +/- 1.4 to 36.4 +/- 3.2 min (fast rejoining process) and from 1.5 +/- 0.2 to 5.1 +/- 0.2 h (slow rejoining process). We found a statistically significant relationship between the survival fraction at 2 Gy (SF2) and the t1/2 of the fast rejoining component (r = 0.949, P = 0.0039). Our results suggest that cell lines which show rapid rejoining are more radioresistant. These results support the view that, as well as the level of damage induction that we have reported previously, the repair process is a major determinant of cellular radiosensitivity. It is possible that the differences found in DNA dsb rejoining and the differences in DNA dsb induction are related by a common mechanism, e.g. conformation of chromatin in the cell.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barendsen G. W. Radiation-induced DNA damage in relation to linear and quadratic terms of dose-effect relationships for cell reproductive death. BJR Suppl. 1992;24:53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blöcher D., Sigut D., Hannan M. A. Fibroblasts from ataxia telangiectasia (AT) and AT heterozygotes show an enhanced level of residual DNA double-strand breaks after low dose-rate gamma-irradiation as assayed by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Nov;60(5):791–802. doi: 10.1080/09553009114552601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothman D. A., Bouvard I., Hughes E. N. Identification and characterization of X-ray-induced proteins in human cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2871–2878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. E., Warring R., Ahnström G. DNA repair kinetics after low doses of X-rays. A comparison of results obtained by the unwinding and nucleoid sedimentation methods. Mutat Res. 1984 Jan;131(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm-Daphi J., Dikomey E., Pyttlik C., Jeggo P. A. Reparable and non-reparable DNA strand breaks induced by X-irradiation in CHO K1 cells and the radiosensitive mutants xrs1 and xrs5. Int J Radiat Biol. 1993 Jul;64(1):19–26. doi: 10.1080/09553009314551071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg-Schwager M., Frankenberg D., Harbich R., Adamczyk C. A comparative study of rejoining of DNA double-strand breaks in yeast irradiated with 3.5 MeV alpha-particles or with 30 MeV electrons. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Jun;57(6):1151–1168. doi: 10.1080/09553009014551261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg-Schwager M., Frankenberg D. Shouldered survival curves in accordance with the unsaturated rejoining kinetics of DNA double-strand breaks. BJR Suppl. 1992;24:23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccia A. J., Schwartz J., Shieh J., Brown J. M. The use of asymmetric-field inversion gel electrophoresis to predict tumor cell radiosensitivity. Radiother Oncol. 1992 Aug;24(4):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(92)90229-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovitz-Friedman A., Vlodavsky I., Chaudhuri A., Witte L., Fuks Z. Autocrine effects of fibroblast growth factor in repair of radiation damage in endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2552–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hittelman W. N., Pollard M. A comparison of the DNA and chromosome repair kinetics after gamma irradiation. Radiat Res. 1982 Dec;92(3):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliakis G., Mehta R., Jackson M. Level of DNA double-strand break rejoining in Chinese hamster xrs-5 cells is dose-dependent: implications for the mechanism of radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Mar;61(3):315–321. doi: 10.1080/09553009214550991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliakis G., Metzger L., Muschel R. J., McKenna W. G. Induction and repair of DNA double strand breaks in radiation-resistant cells obtained by transformation of primary rat embryo cells with the oncogenes H-ras and v-myc. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6575–6579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliakis G. Radiation-induced potentially lethal damage: DNA lesions susceptible to fixation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Apr;53(4):541–584. doi: 10.1080/09553008814550901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelland L. R., Edwards S. M., Steel G. G. Induction and rejoining of DNA double-strand breaks in human cervix carcinoma cell lines of differing radiosensitivity. Radiat Res. 1988 Dec;116(3):526–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Sedgwick S. G., Jeggo P. A. X-ray sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells defective in double-strand break rejoining. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov-Dec;132(5-6):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval T. M., Kazmar E. R. DNA double-strand break repair in eukaryotic cell lines having radically different radiosensitivities. Radiat Res. 1988 Feb;113(2):268–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L., Chiu S. M., Friedman L. R. Gamma radiation as a probe of chromatin structure: damage to and repair of active chromatin in the metaphase chromosome. Radiat Res. 1984 Jun;98(3):629–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive P. L. DNA organization affects cellular radiosensitivity and detection of initial DNA strand breaks. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Oct;62(4):389–396. doi: 10.1080/09553009214552261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil M. S., Locher S. E., Hariharan P. V. Radiation-induced thymine base damage and its excision repair in active and inactive chromatin of HeLa cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Nov;48(5):691–700. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. H., Eady J. J., Edwards S. M., McMillan T. J., Steel G. G. The intrinsic alpha/beta ratio for human tumour cells: is it a constant? Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Apr;61(4):479–487. doi: 10.1080/09553009214551241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford I. R. Effect of cell-cycle position and dose on the kinetics of DNA double-strand breakage repair in X-irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1987 Oct;52(4):555–564. doi: 10.1080/09553008714552051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford I. R. The level of induced DNA double-strand breakage correlates with cell killing after X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Jul;48(1):45–54. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Almodóvar J. M., Bush C., Peacock J. H., Steel G. G., Whitaker S. J., McMillan T. J. Dose-rate effect for DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation in human tumor cells. Radiat Res. 1994 Apr;138(1 Suppl):S93–S96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Almodóvar J. M., Núez M. I., McMillan T. J., Olea N., Mort C., Villalobos M., Pedraza V., Steel G. G. Initial radiation-induced DNA damage in human tumour cell lines: a correlation with intrinsic cellular radiosensitivity. Br J Cancer. 1994 Mar;69(3):457–462. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. L., Rotmensch J., Giovanazzi S., Cohen M. B., Weichselbaum R. R. Faster repair of DNA double-strand breaks in radioresistant human tumor cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988 Oct;15(4):907–912. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(88)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel G. G. The ESTRO Breur lecture. Cellular sensitivity to low dose-rate irradiation focuses the problem of tumour radioresistance. Radiother Oncol. 1991 Feb;20(2):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(91)90140-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker S. J., McMillan T. J. Oxygen effect for DNA double-strand break induction determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Jan;61(1):29–41. doi: 10.1080/09553009214550591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodek D., Hittelman W. N. The repair of double-strand DNA breaks correlates with radiosensitivity of L5178Y-S and L5178Y-R cells. Radiat Res. 1987 Oct;112(1):146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


