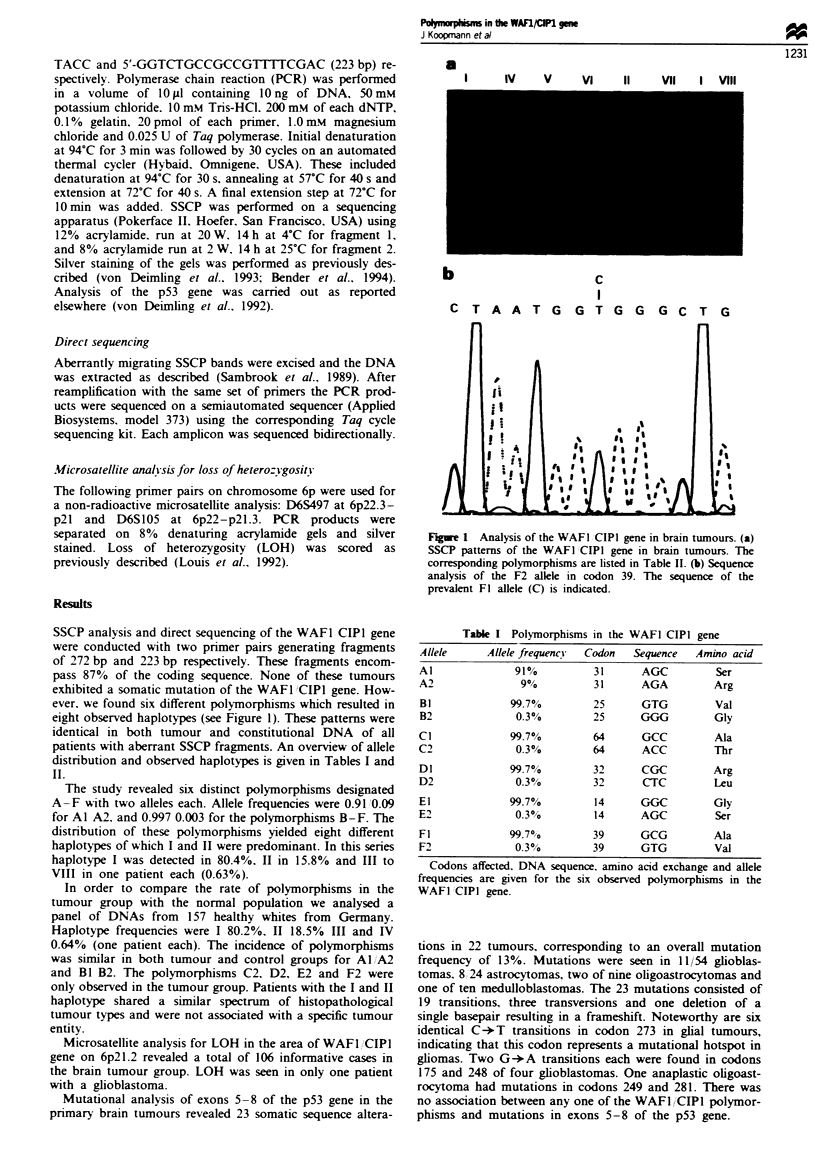
Abstract
The cyclin kinase inhibitor WAF1/CIP1, also termed CDKN1, mediates p53-induced cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. This property makes it an attractive tumour-suppressor candidate for a p53-associated tumour-suppressor gene. In order to investigate the role of WAF1/CIP1 in the pathogenesis of primary human brain tumours we performed single-stranded conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis and direct sequencing of exon 2 of the gene in a representative series of 158 brain tumours and corresponding blood samples. In addition, all tumours were examined for mutations in exons 5-8 of the p53 gene. Analysis of WAF1/CIP1 revealed multiple polymorphisms, the most abundant being AGC-->AGA (Ser-->Arg) at codon 31 with an allele frequency of 8.5%. Less common polymorphisms included GTG-->GGG (Val-->Gly) at codon 25, GCC-->ACC (Ala-->Thr) at codon 64, CGC-->CTC (Arg-->Leu) at codon 32, GGC-->AGC (Gly-->Ser) at codon 14 and GCG-->GTG (Ala-->Val) at codon 39 each with an allele frequency of 0.3%. These polymorphisms were all located in a conserved region of exon 2. Two of the polymorphisms were also seen in a group of 157 healthy controls indicating that WAF1/CIP1 polymorphisms do not predispose to cancer. None of the tumours included in our series showed a somatic mutation in WAF1/CIP1. All samples were also analysed for loss of heterozygosity on the short arm of chromosome 6 in the region of the WAF1/CIP1 locus. Allelic loss was observed in only one patient with a glioblastoma. Mutations in the p53 gene were found in 22 of 158 tumours. No association was found between any polymorphism of the WAF1/CIP1 gene, p53 mutations and histopathological tumour type. Our data indicate that WAF1/CIP1 mutations are probably not involved in the formation of primary human brain tumours.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender B., Wiestler O. D., von Deimling A. A device for processing large acrylamide gels. Biotechniques. 1994 Feb;16(2):204–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid M., Michieli P., Lengel C., Huppi K., Givol D. A single nucleotide substitution at codon 31 (Ser/Arg) defines a polymorphism in a highly conserved region of the p53-inducible gene WAF1/CIP1. Oncogene. 1994 Oct;9(10):3021–3024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Jackson P. K., Kirschner M. W., Dutta A. Separate domains of p21 involved in the inhibition of Cdk kinase and PCNA. Nature. 1995 Mar 23;374(6520):386–388. doi: 10.1038/374386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Leonardo A., Linke S. P., Clarkin K., Wahl G. M. DNA damage triggers a prolonged p53-dependent G1 arrest and long-term induction of Cip1 in normal human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2540–2551. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppi K., Siwarski D., Dosik J., Michieli P., Chedid M., Reed S., Mock B., Givol D., Mushinski J. F. Molecular cloning, sequencing, chromosomal localization and expression of mouse p21 (Waf1). Oncogene. 1994 Oct;9(10):3017–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. A death in the life of p53. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):786–787. doi: 10.1038/362786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis D. N. The p53 gene and protein in human brain tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 Jan;53(1):11–21. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis D. N., von Deimling A., Seizinger B. R. A (CA)n dinucleotide repeat assay for evaluating loss of allelic heterozygosity in small and archival human brain tumor specimens. Am J Pathol. 1992 Oct;141(4):777–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgaki H., Eibl R. H., Schwab M., Reichel M. B., Mariani L., Gehring M., Petersen I., Höll T., Wiestler O. D., Kleihues P. Mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in neoplasms of the human nervous system. Mol Carcinog. 1993;8(2):74–80. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger G., Liu L., Ichimura K., Schmidt E. E., Collins V. P. Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2 gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2736–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio M. P., von Deimling A., Yandell D. W., Wiestler O. D., Gusella J. F., Louis D. N. Accumulation of wild type p53 protein in human astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3465–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiohara M., el-Deiry W. S., Wada M., Nakamaki T., Takeuchi S., Yang R., Chen D. L., Vogelstein B., Koeffler H. P. Absence of WAF1 mutations in a variety of human malignancies. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3781–3784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Chen I. T., Zhan Q., Bae I., Chen C. Y., Gilmer T. M., Kastan M. B., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Interaction of the p53-regulated protein Gadd45 with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1376–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.7973727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Deimling A., Bender B., Louis D. N., Wiestler O. D. A rapid and non-radioactive PCR based assay for the detection of allelic loss in human gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993 Dec;19(6):524–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Deimling A., Eibl R. H., Ohgaki H., Louis D. N., von Ammon K., Petersen I., Kleihues P., Chung R. Y., Wiestler O. D., Seizinger B. R. p53 mutations are associated with 17p allelic loss in grade II and grade III astrocytoma. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2987–2990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



