Abstract
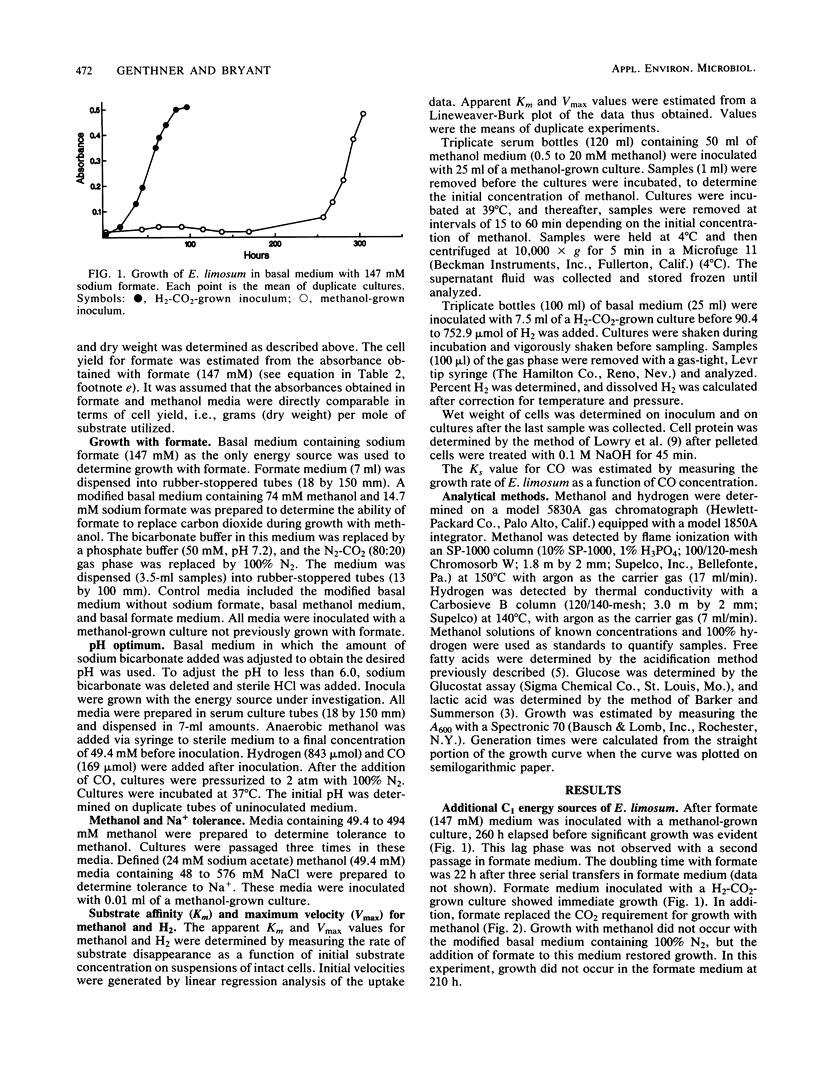
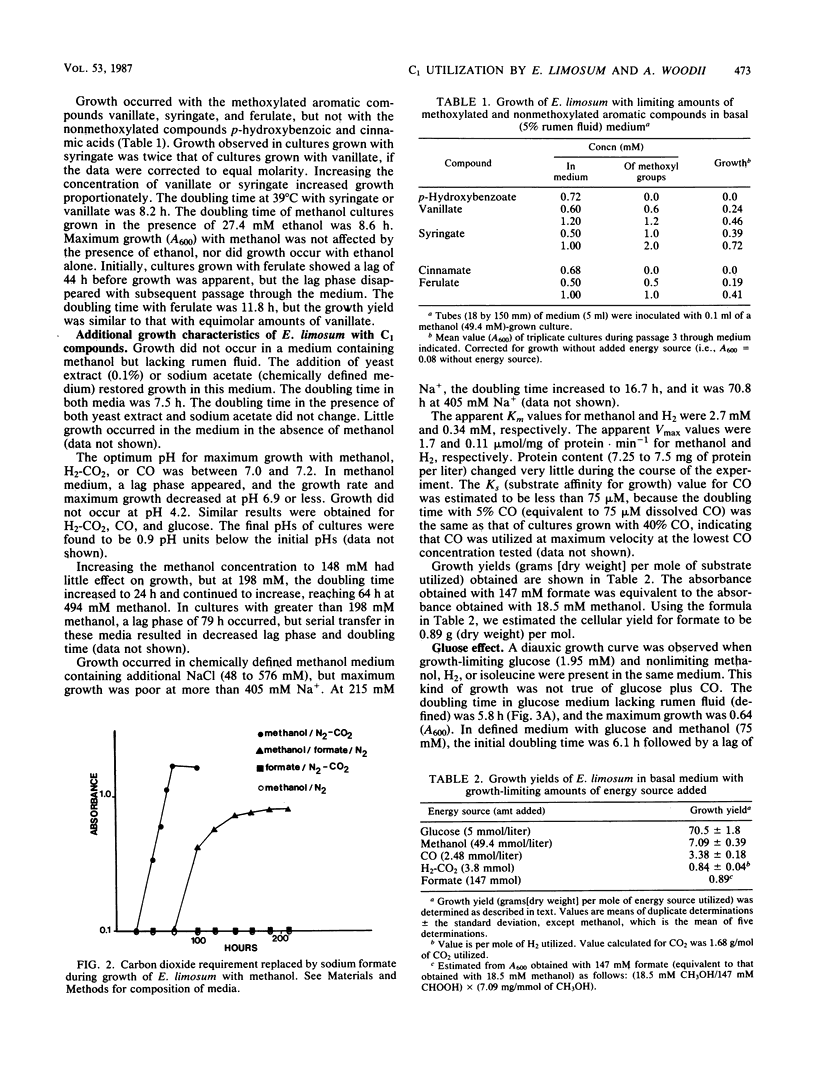
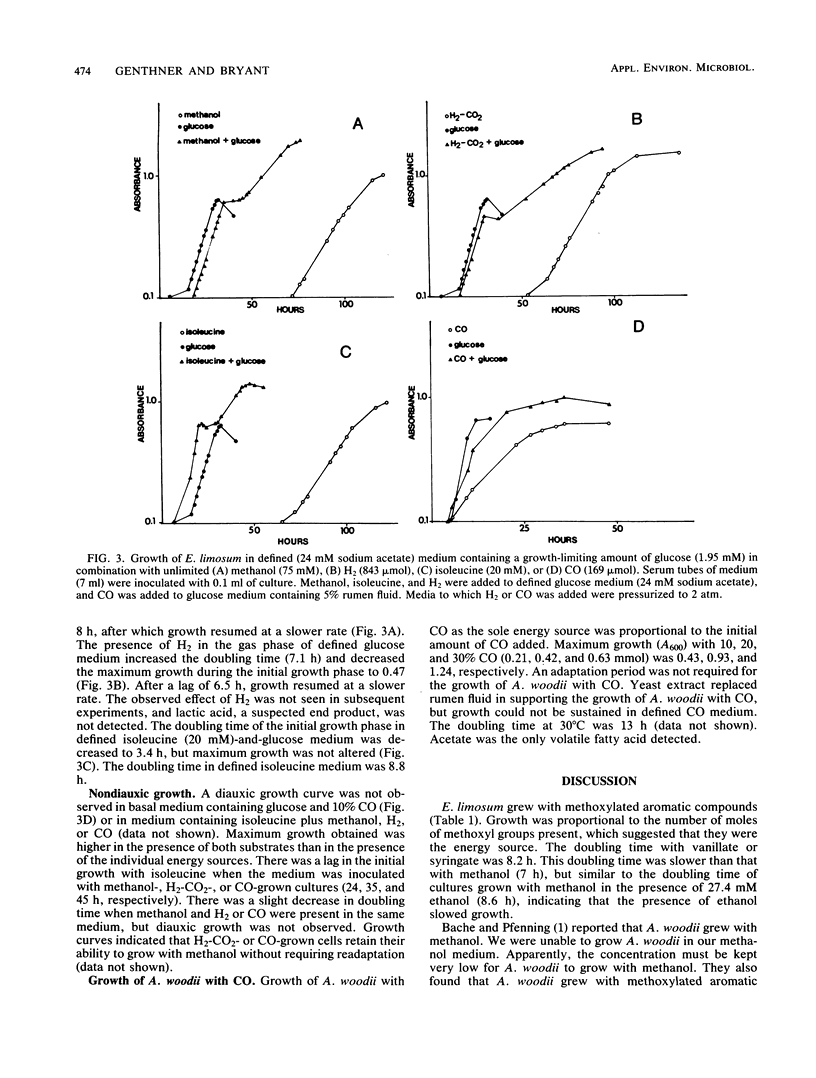
Growth characteristics of Eubacterium limosum and Acetobacterium woodii during one-carbon-compound utilization were investigated. E. limosum RF grew with formate as the sole energy source. Formate also replaced a requirement for CO2 during growth with methanol. Growth with methanol required either rumen fluid, yeast extract, or acetate, but their effects were not additive. Cultures were adapted to grow in concentrations of methanol of up to 494 mM. Growth occurred with methanol in the presence of elevated levels of Na+ (576 mM). The pH optima for growth with methanol, H2-CO2, and carbon monoxide were similar (7.0 to 7.2). Growth occurred with glucose at a pH of 4.7, but not at 4.0. The apparent Km values for methanol and hydrogen were 2.7 and 0.34 mM, respectively. The apparent Vmax values for methanol and hydrogen were 1.7 and 0.11 mumol/mg of protein X min-1, respectively. The Ks value for CO was estimated to be less than 75 microM. Cellular growth yields were 70.5, 7.1, 3.38, and 0.84 g (dry weight) per mol utilized for glucose, methanol, CO, and hydrogen (in H2-CO2), respectively. E. limosum was also able to grow with methoxylated aromatic compounds as energy sources. Glucose apparently repressed the ability of E. limosum to use methanol, hydrogen, or isoleucine but not CO. Growth with mixtures of methanol, H2, CO, or isoleucine was not diauxic. The results, especially the relatively high apparent Km values for H2 and methanol, may indicate why E. limosum does not usually compete with rumen methanogens for these energy sources.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Genthner B. R., Bryant M. P. Growth of Eubacterium limosum with Carbon Monoxide as the Energy Source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):70–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.70-74.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Smith W., Bauchop T., Yu I., Rabinowitz J. C. Formate as an intermediate in the bovine rumen fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.389-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby R., Niemczura W., Zeikus J. G. Single-carbon catabolism in acetogens: analysis of carbon flow in Acetobacterium woodii and Butyribacterium methylotrophicum by fermentation and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance measurement. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1208-1218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leedle J. A., Hespell R. B. Differential carbohydrate media and anaerobic replica plating techniques in delineating carbohydrate-utilizing subgroups in rumen bacterial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):709–719. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.709-719.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynd L., Kerby R., Zeikus J. G. Carbon monoxide metabolism of the methylotrophic acidogen Butyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):255–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.255-263.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Tiedje J. M. Kinetics of hydrogen consumption by rumen fluid, anaerobic digestor sludge, and sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1374–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1374-1384.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


