Abstract
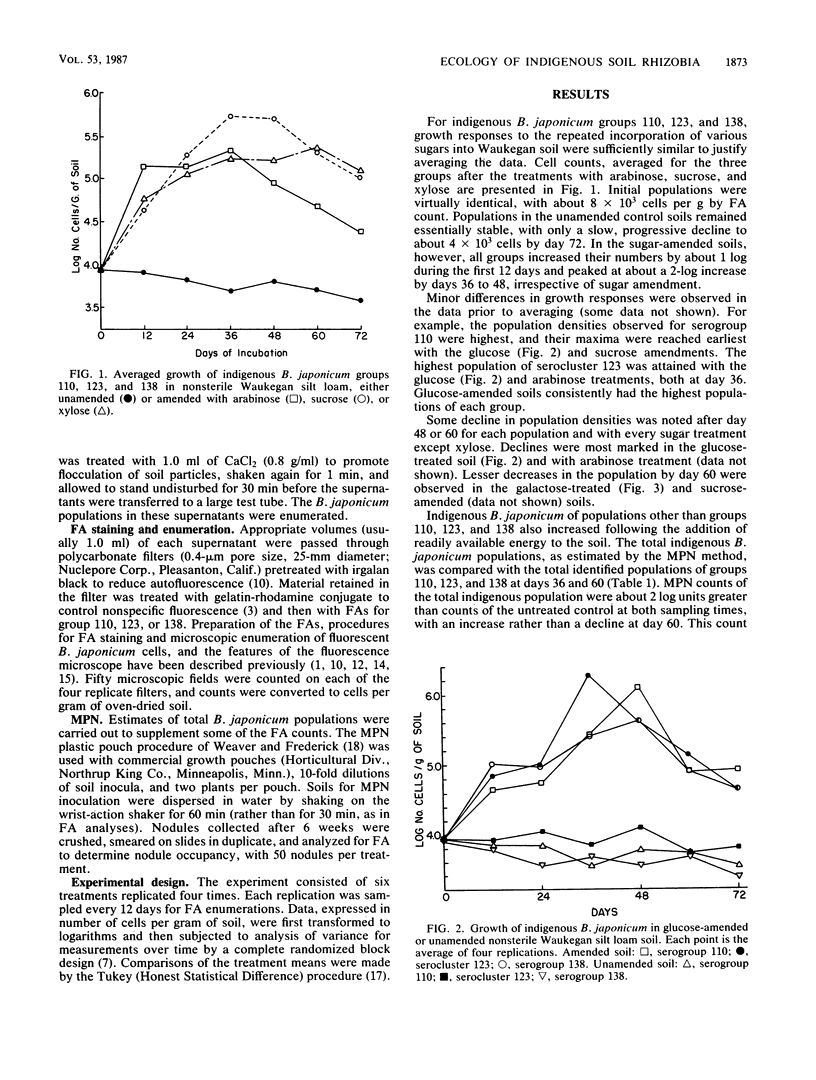
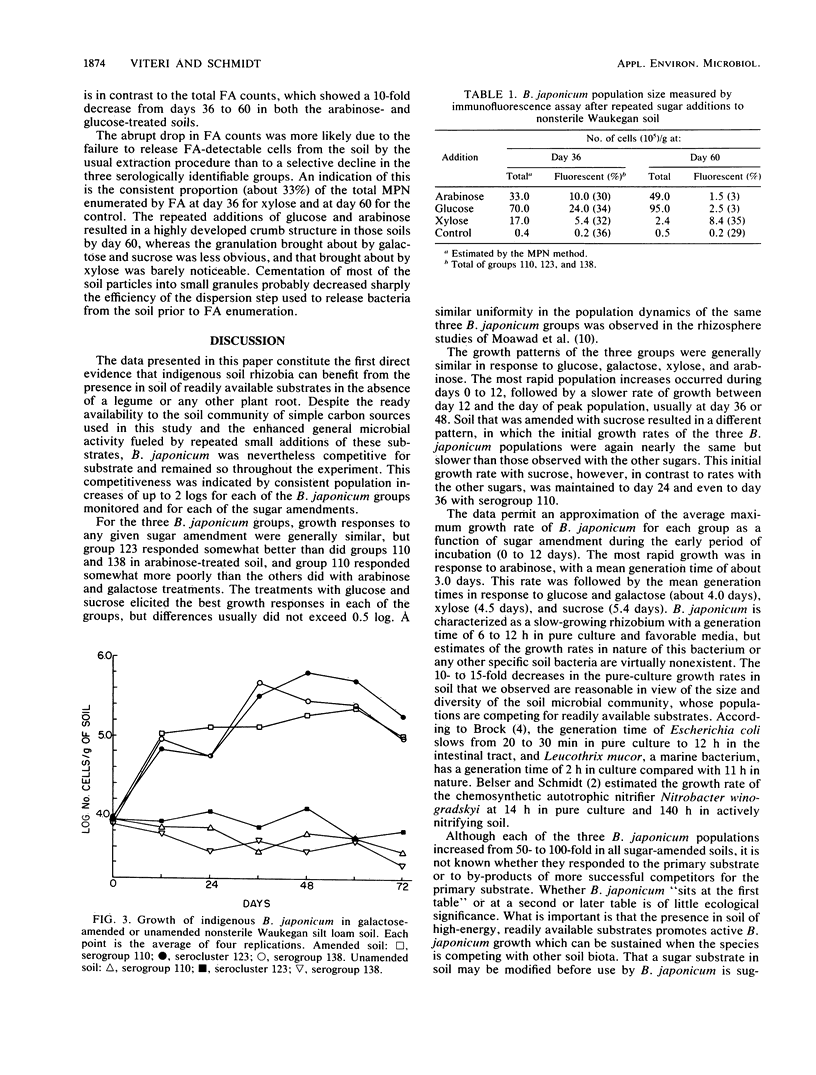
Populations of indigenous Bradyrhizobium japonicum serocluster 123 and serogroups 110 and 138 were studied after various sugars were added to their soil habitat. Loam soil with approximately 104 cells of each group per g of soil were amended every 3 days with 0.1% glucose, sucrose, arabinose, xylose, or galactose. Enumerations of the populations were made every 12 days by immunofluorescence assay. Each B. japonicum population in the sugar-treated soils increased by about 1 log during the first 12 days, to a maximum of about 106 cells by day 36 or 48, irrespective of the sugar added. Maximum growth rates were similar for each group and occurred during the 12-day incubation period. The most rapid growth was in response to arabinose, with a mean generation time of about 3.0 days. Other mean doubling times were 4.0 days with glucose and galactose treatments, 4.5 days with xylose treatment, and 5.4 days with sucrose amendment. These data provide the first direct evidence that indigenous soil rhizobia can compete successfully with other soil bacteria for readily available substrates in soil in the absence of host legume roots or other rhizospheres. The growth rates in soil of the specific B. japonicum populations studied were nearly the same with a given sugar treatment but varied considerably with different sugars. The mean generation times of 3 to 5 days are among the first reported growth rates for heterotrophic bacteria in natural soil.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belser L. W., Schmidt E. L. Serological diversity within a terrestrial ammonia-oxidizing population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):589–593. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.589-593.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Nonspecific staining: its control in immunofluorescence examination of soil. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1012–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkan G. H., Kwik I. Nitrogen, energy and vitamin nutrition of Rhizobium japonicum. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;31(4):399–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley M. T., Bohlool B. B. Release of Rhizobium spp. from Tropical Soils and Recovery for Immunofluorescence Enumeration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):241–248. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.241-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-de Drets G., Arias A., Rovira de Cutinella M. Fast- and slow-growing rhizobia: differences in sucrose utilization and invertase activity. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Apr;20(4):605–609. doi: 10.1139/m74-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moawad H. A., Ellis W. R., Schmidt E. L. Rhizosphere Response as a Factor in Competition Among Three Serogroups of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum for Nodulation of Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):607–612. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.607-612.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert F. M., Schmidt E. L. Population Changes and Persistence of Rhizobium phaseoli in Soil and Rhizospheres. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.550-556.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Zidwick M. J., Abebe H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 and Diversity among Member Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1212-1215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


