Abstract
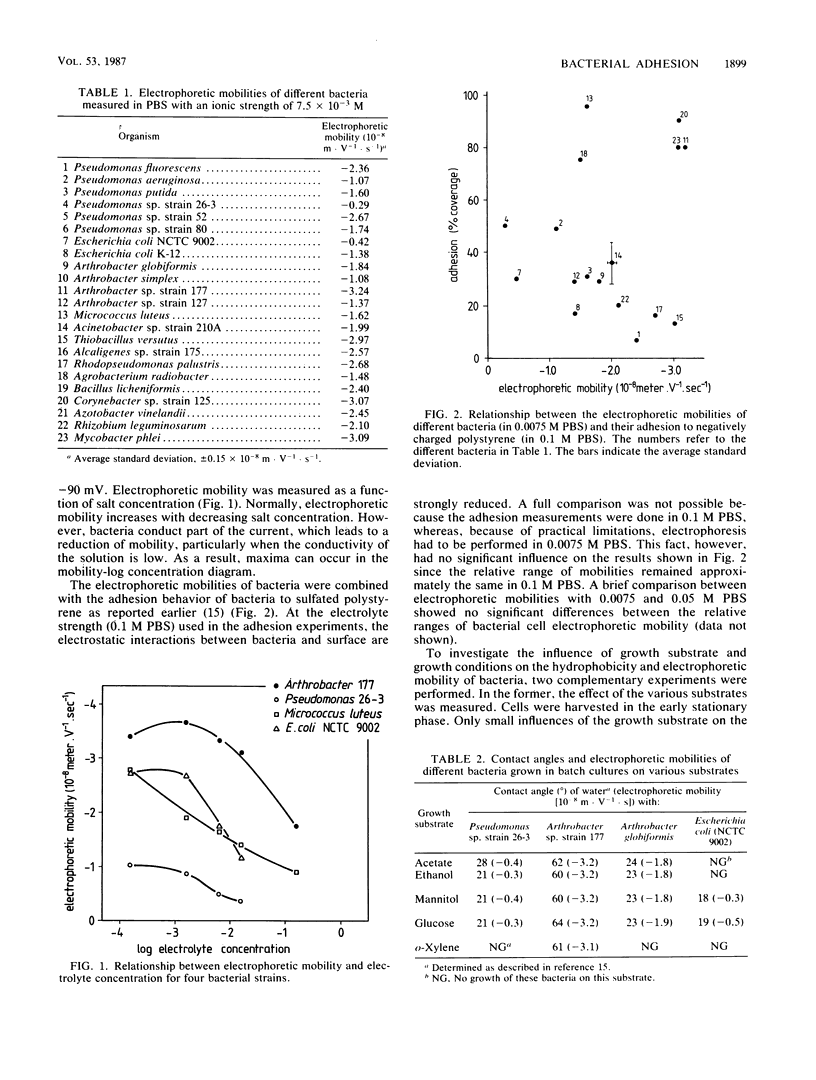
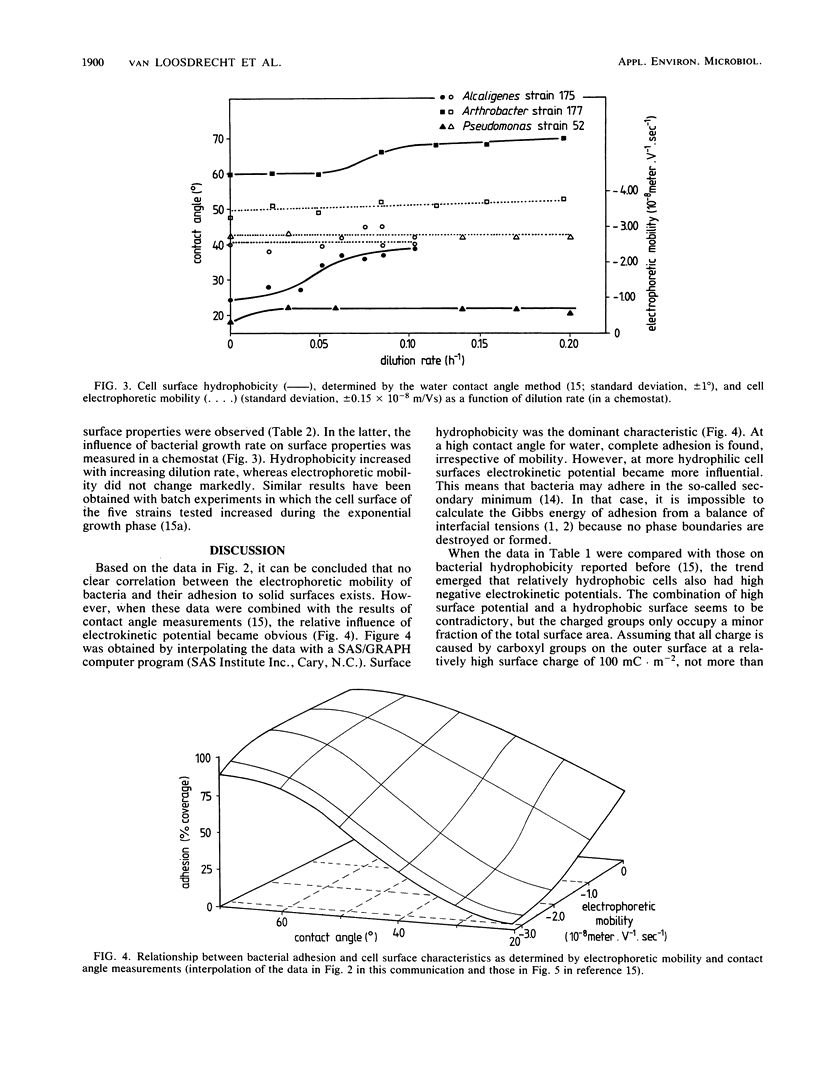
The relationship between physiochemical surface parameters and adhesion of bacterial cells to negatively charged polystyrene was studied. Cell surface hydrophobicity and electrokinetic potential were determined by contact angle measurement and electrophoresis, respectively. Both parameters influence cell adhesion. The effect of the electrokinetic potential increases with decreasing hydrophobicity. Cell surface characteristics determining adhesion are influenced by growth conditions. At high growth rates, bacterial cells tend to become more hydrophobic. This fact can be of ecological significance for controlling the spread of bacteria throughout the environment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Bacterial conductivity in the determination of surface charge by microelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):506–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Shilo M. Hydrophobicity as an adhesion mechanism of benthic cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.135-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Millero F. J. Electrolyte effects on attachment of an estuarine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):495–499. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.495-499.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insupova D. V., Kireeva N. A., Beliaeva M. I., Vinogradova V. S., Gareishina A. Z. Izuchenie prodigiozina kak vozmozhnogo ingibitora nukleazy Serratia marcescens. Mikrobiologiia. 1977 Mar-Apr;46(2):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M. Starvation-induced effects on bacterial surface characteristics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.497-503.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson K., Glantz P. O. Microbial adhesion to surfaces with different surface charges. Acta Odontol Scand. 1981;39(2):79–82. doi: 10.3109/00016358109162263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist T. Bacterial hydrophobicity measured as partition of palmitic acid between the two immiscible phases of cell surface and buffer. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Feb;91(1):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrangstadh M., Conway P. L., Kjelleberg S. The production and release of an extracellular polysaccharide during starvation of a marine Pseudomonas sp. and the effect thereof on adhesion. Arch Microbiol. 1986 Aug;145(3):220–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00443649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. The role of bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1893–1897. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1893-1897.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


