Abstract
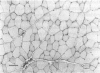
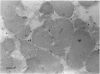
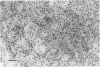
A number of amphiphilic and lipid-soluble drugs of heterogeneous pharmacological properties, when injected into rat anterior tibial muscles, induced acute muscle fibre necrosis. The myotoxic agents were: penicillin, cloxacillin, phenobarbital, haloperidol, diazepam, hydantoin, metoclopramide, pentazocine and chlorpromazine. The regenerative process, studied using the latter three medications, showed rapid regeneration, complete within 3 weeks. Injection of the water-soluble drugs aminophylline, tranexamic acid and vitamins B6 and B12 produced no tissue damage. The pathogenesis of muscle fibre necrosis is suggested to involve direct damage to cell membranes by lipid soluble drugs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberfeld D. C., Bienenstock H., Shapiro M. S., Namba T., Grob D. Diffuse myopathy related to meperidine addiction in a mother and daughter. Arch Neurol. 1968 Oct;19(4):384–389. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480040050004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit P. W., Yagiela A., Fort N. F. Pharmacologic correlation between local anesthetic-induced myotoxicity and disturbances of intracellular calcium distribution. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;52(2):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeson P. S., Singer S. A., Kaplan A. M. Intramuscular injections in children. Pediatrics. 1982 Dec;70(6):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choucair A. K., Ziter F. A. Pentazocine abuse masquerading as familial myopathy. Neurology. 1984 Apr;34(4):524–527. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.4.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gove C. D., Hems D. A. Fatty acid synthesis in the regenerating liver of the rat. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj1700001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Craggs E. C. Rapid degeneration and regeneration of a whole skeletal muscle following treatment with bupivacaine (Marcain). Exp Neurol. 1974 May;43(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Shimomura J., Tsuyuhara S., Mogi M., Ishizaki S., Nagai Y. Differential reactivities of fucosyl GM1 and GM1 gangliosides on rat erythrocyte membrane revealed by analysis with anti-fucosyl GM1 and GM1 antisera. J Biochem. 1983 Jul;94(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. H. Protein synthesis in bupivacaine (marcaine)-treated, regenerating skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Apr;5(4):281–290. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuncl R. W., Wiggins W. W. Toxic myopathies. Neurol Clin. 1988 Aug;6(3):593–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Engel W. K. Iatrogenic muscle fibrosis. Arm levitation as an initial sign. JAMA. 1975 Nov 10;234(6):621–624. doi: 10.1001/jama.234.6.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifenberick D. H., Koski C. L., Max S. R. Metabolic studies of skeletal muscle regeneration. Exp Neurol. 1974 Dec;45(3):527–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadeh M., Czyewski K., Stern L. Z. Chronic myopathy induced by repeated bupivacaine injections. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Feb;67(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz E., Lipton B. H. The effect of Marcaine on muscle and non-muscle cells in vitro. Anat Rec. 1978 Jul;191(3):351–369. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091910308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibel H. R., Dolwick M. F., Bush F. M., Craig S. S. Electron-microscopic study of the rat masseter muscle following injection of lidocaine. Acta Anat (Basel) 1978;100(3):354–364. doi: 10.1159/000144916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer J. H., Mastaglia F. L. Protein degradation in bupivacaine-treated muscles. The role of extracellular calcium. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Oct;75(3):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner J. C., Winkelman A. C., De Jesus P. V., Jr Pentazocine-induced myopathy. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):408–409. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240068012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K. R., Max S. R., Grollman E. M., Koski C. L. Glycolysis in skeletal muscle regeneration. Exp Neurol. 1976 Jul;52(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]