Abstract
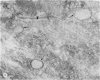
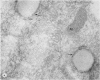
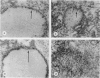
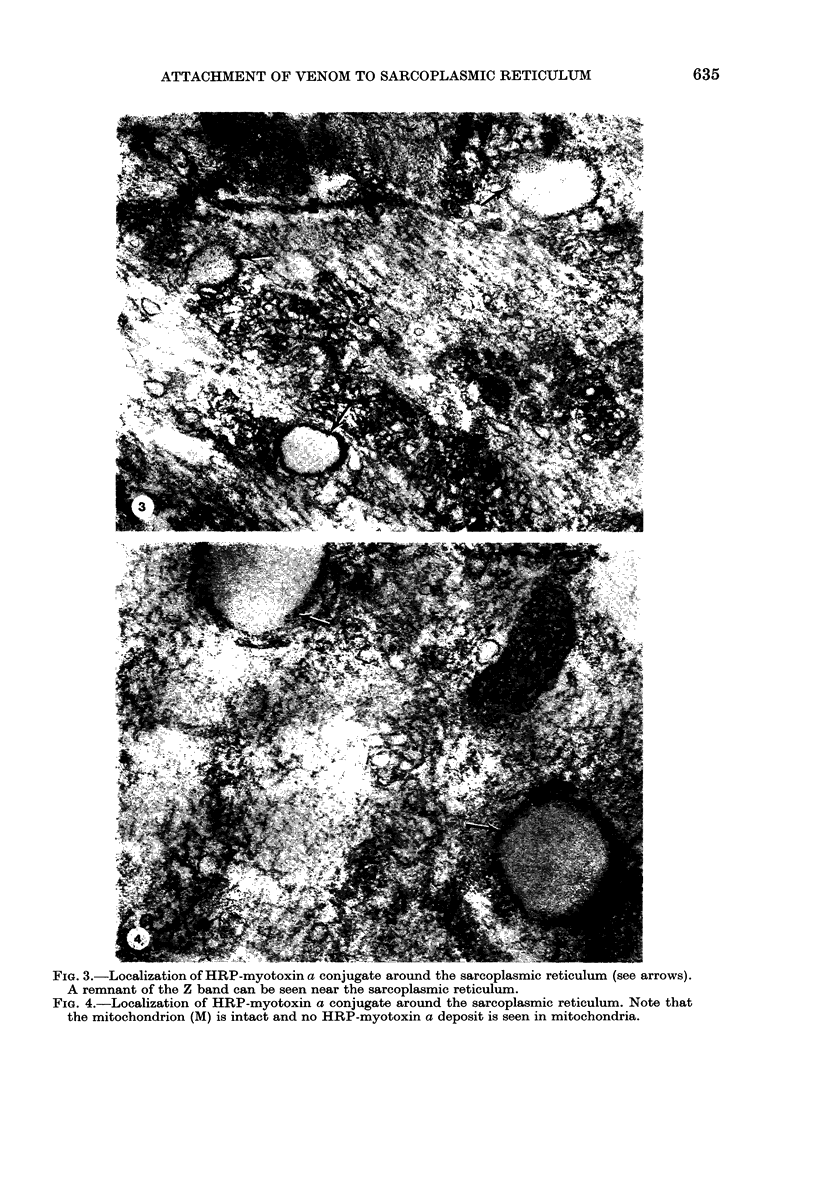
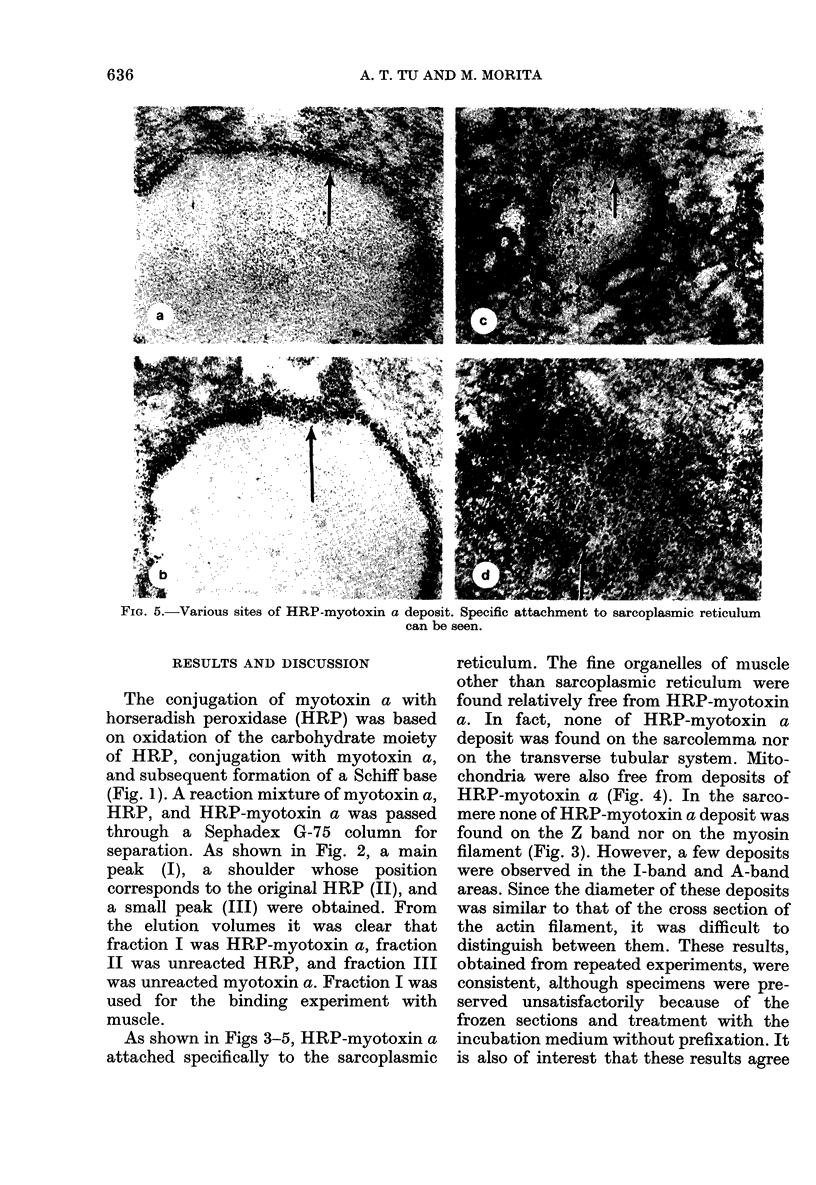
Myotoxin a is a muscle-damaging toxin isolated from the venom of Crotalus atrox (western diamondback rattlesnake) and is composed of 42 amino acid residues. Earlier electron microscopic observation indicated that the toxin causes extensive swelling of the sarcoplasmic reticulum followed by disorganization of the sarcomers. In the present paper we describe the evidence for the attachment of peroxidase-conjugated myotoxin a to the membrane of sarcoplasmic reticulum of human muscle. It is thus suggested that the attachment of the toxin to the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the subsequent swelling are the first steps in myonecrosis induced by myotoxin a.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey G. S., Lee J., Tu A. T. Conformational analysis of myotoxin alpha (muscle degenerating toxin) of Prairie rattlesnake venom. Predictions from amino acid sequence, circular dichroism, and Raman spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8922–8926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. L., Tu A. T. Characterization of myotoxin a from the venom of prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis). Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2546–2553. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Elzinga M., Tu A. T. Amino acid sequence and disulfide bond assignment of myotoxin a isolated from the venom of Prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis). Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):678–684. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Bjarnason J., Tu A. T. Hemorrhagic toxins from rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom. Pathogenesis of hemorrhage induced by three purified toxins. Am J Pathol. 1978 Oct;93(1):201–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Cameron D., Tu A. T. Isolation of myotoxic component from rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis) venom. Electron microscopic analysis of muscle damage. Am J Pathol. 1976 Oct;85(1):149–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Gutiérrez J. M., Colberg T. R., Odell G. V. Quantitation of myonecrosis induced by myotoxin a from prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis) venom. Toxicon. 1982;20(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Woods W. M., Odell G. V. Antiserum to myotoxin from prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis) venom. Toxicon. 1979;17(4):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]