Abstract
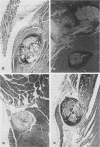
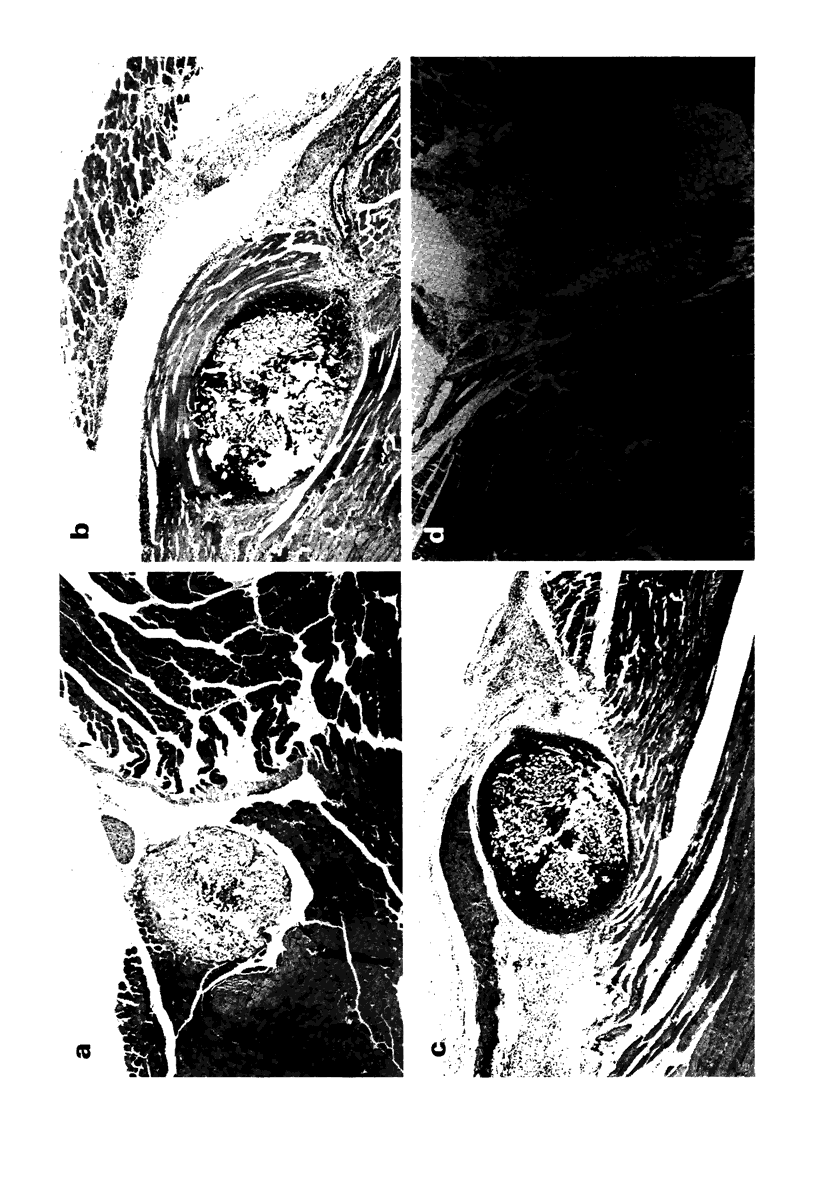
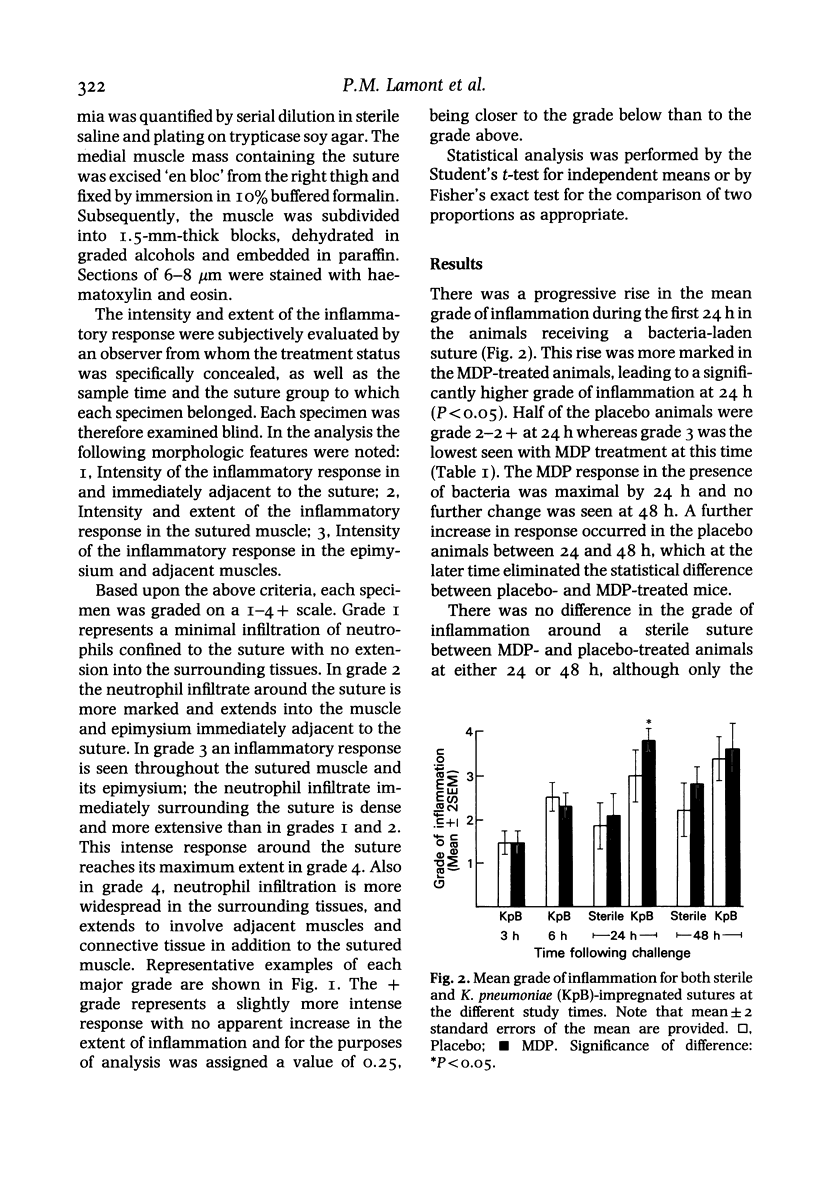
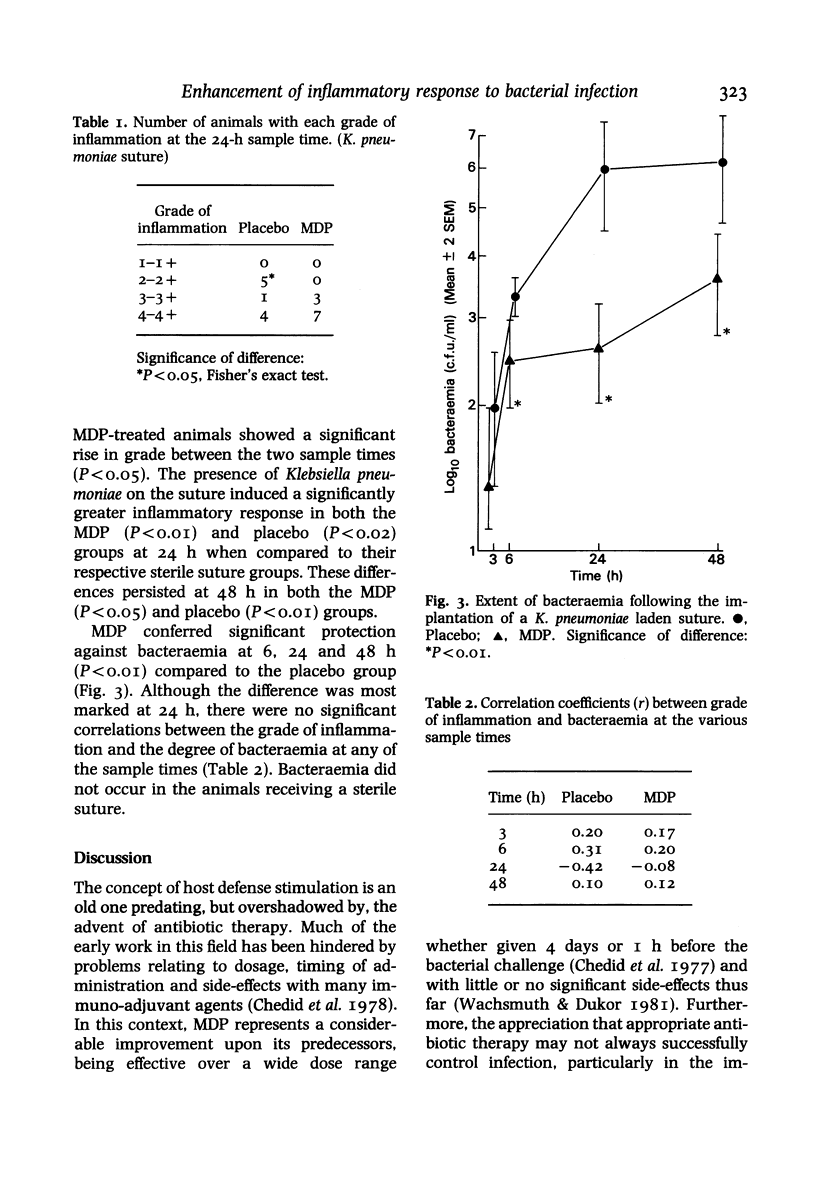
The effect of the synthetic immuno-adjuvant compound, muramyl dipeptide (MDP), upon the local inflammatory response to experimental bacterial infection was assessed by histological examination. Within 24 h of the insertion of a bacteria-laden suture into the medial thigh musculature of mice treated with either MDP or placebo, an enhanced degree of polymorphonuclear leucocyte infiltration in the muscle around the suture was observed in the MDP-treated animals. The inflammatory response around a sterile suture was less intense in both treatment groups and specific correlation between the degree of local inflammation and the extent of bacteraemia developing in either group of animals was not noted. The extent of bacteraemia developing in either group of animals was not noted. The previously observed protection conferred by MDP against the local impact of bacterial challenge appears to be mediated in part by enhancement of the acute local inflammatory response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., de Jong-Hoenderop J. Y., Michel M. F. Efficacy of antimicrobial therapy in experimental rat pneumonia: effects of impaired phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):366–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.366-375.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Audibert F., Johnson A. G. Biological activities of muramyl dipeptide, a synthetic glycopeptide analogous to bacterial immunoregulating agents. Prog Allergy. 1978;25:63–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Lefrancher P., Choay J., Lederer E. Enhancement of nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) and several analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2089–2093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevrier M., Birrien J. L., Leclerc C., Chedid L., Liacopoulos P. The macrophage, target cell of the synthetic adjuvant muramyl dipeptide. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):558–562. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galland R. B., Polk H. C. Non-specific stimulation of host defenses against a bacterial challenge in malnourished hosts. Br J Surg. 1982 Nov;69(11):665–668. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800691112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A. The inflammatory response in relation to local infections. Surg Clin North Am. 1980 Feb;60(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A., Yamamoto Y., Koga T., Onoue K., Shiba T., Kusumoto K., Kotani S. Inhibition of macrophage migration by muramyl peptides. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.308-312.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada Y., Mitsuyama M., Une T., Matsumoto K., Otani T., Satoh M., Ogawa H., Nomoto K. Effect of L18-MDP(Ala), a synthetic derivative of muramyl dipeptide, on nonspecific resistance of mice to microbial infections. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):292–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.292-300.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, Galland R. B., Ausobsky J. R. Nonspecific enhancement of resistance to bacterial infection: evidence of an effect supplemental to antibiotics. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):436–441. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Nagao R., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system of mice by muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]