Abstract
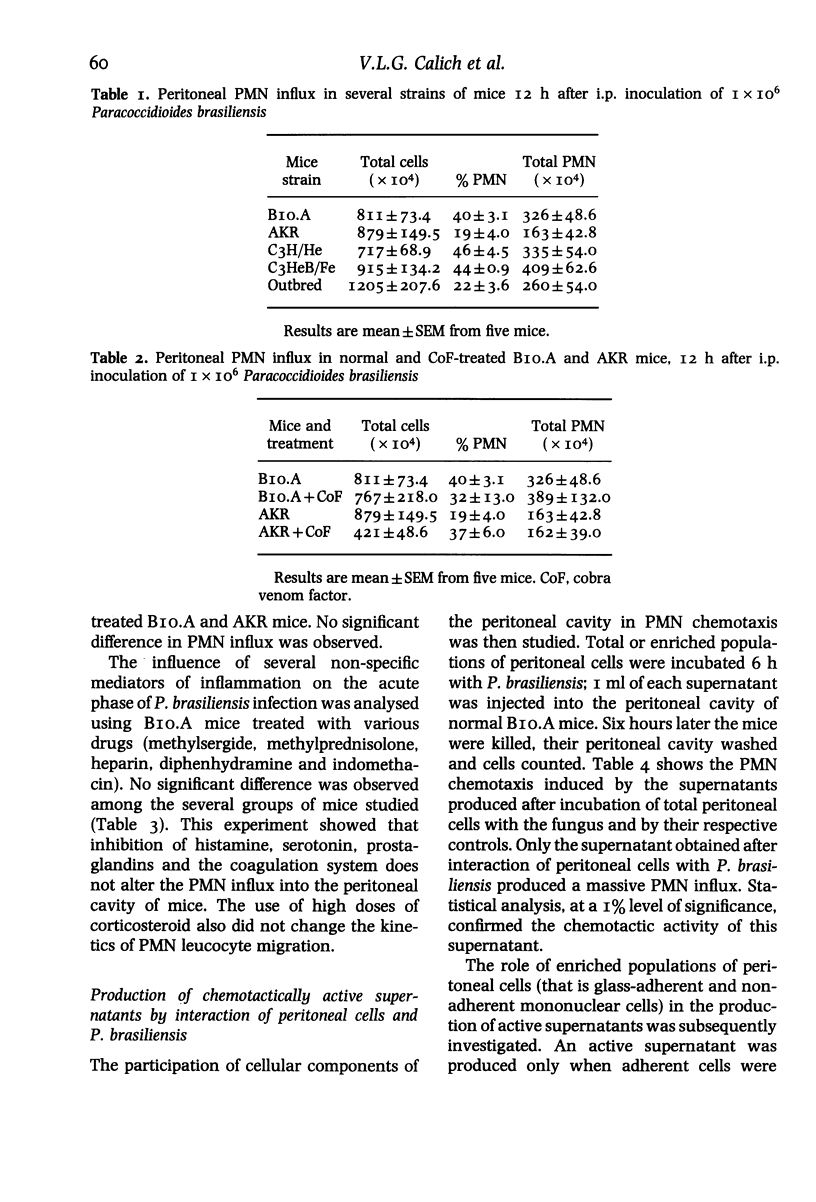
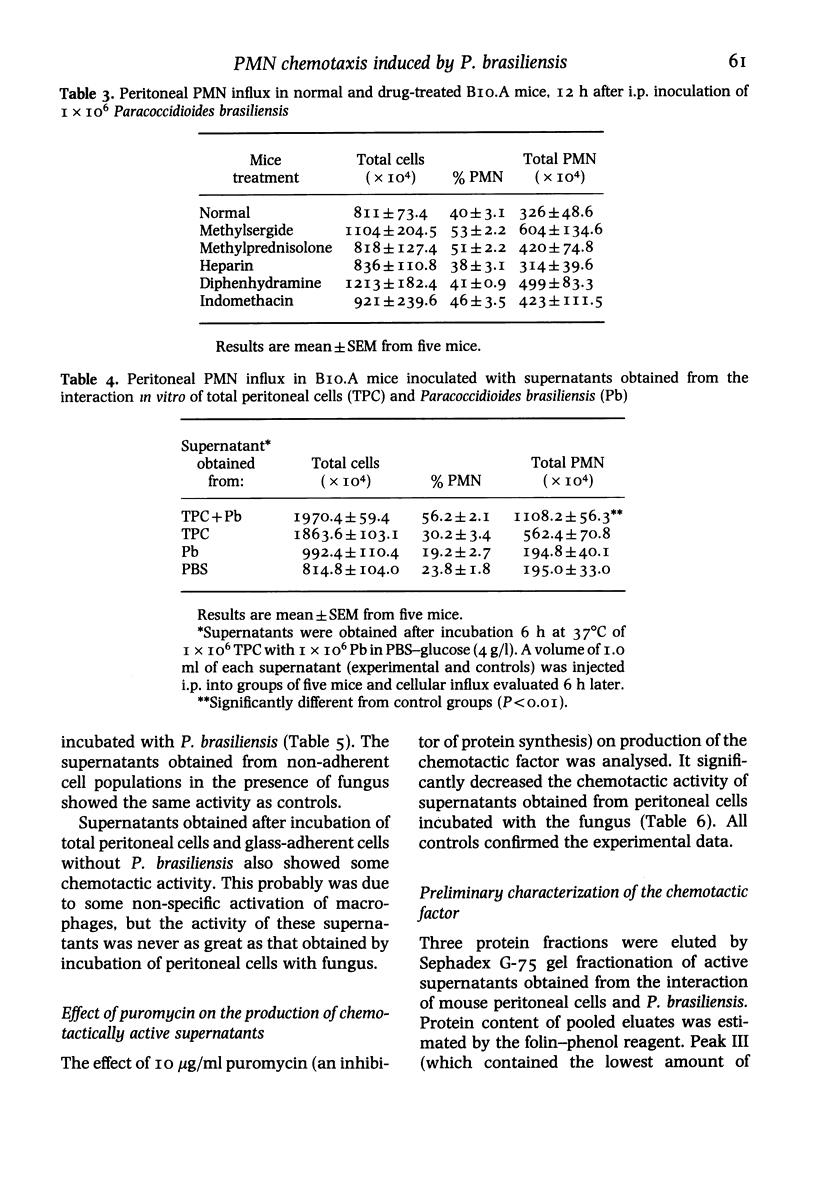
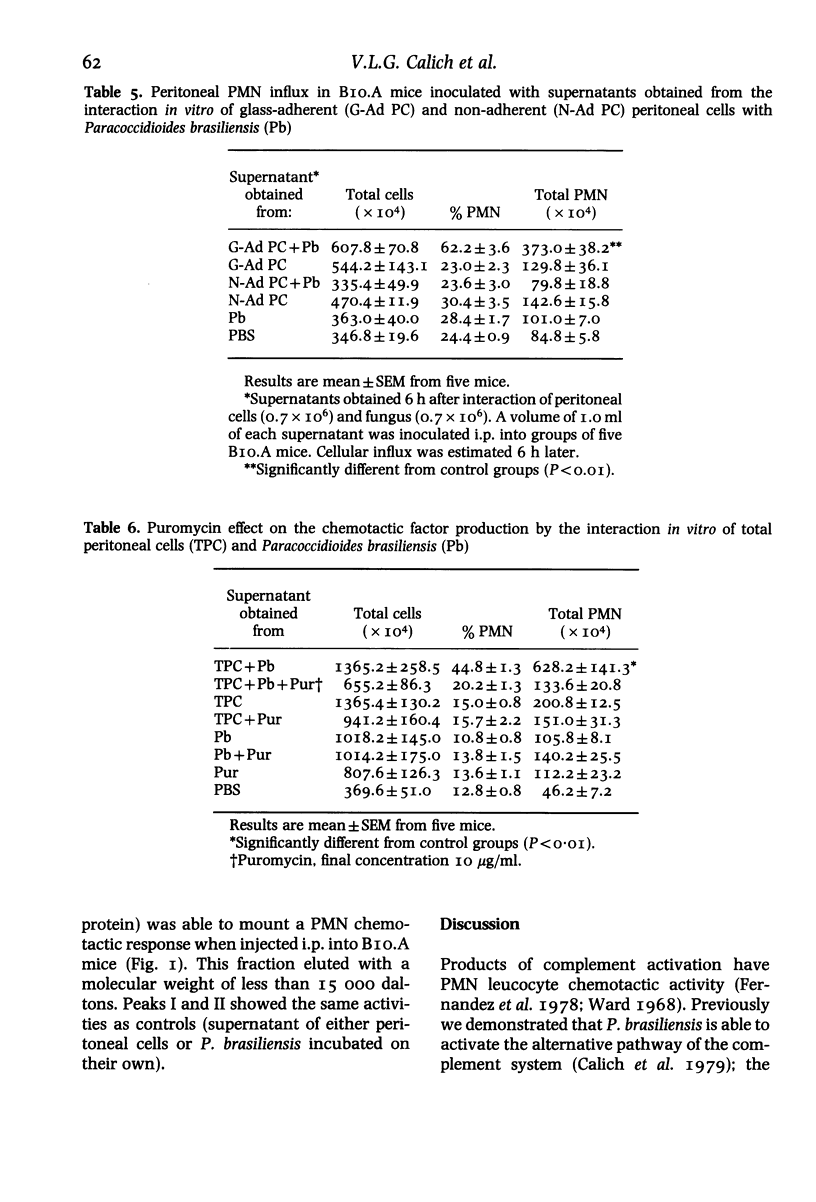
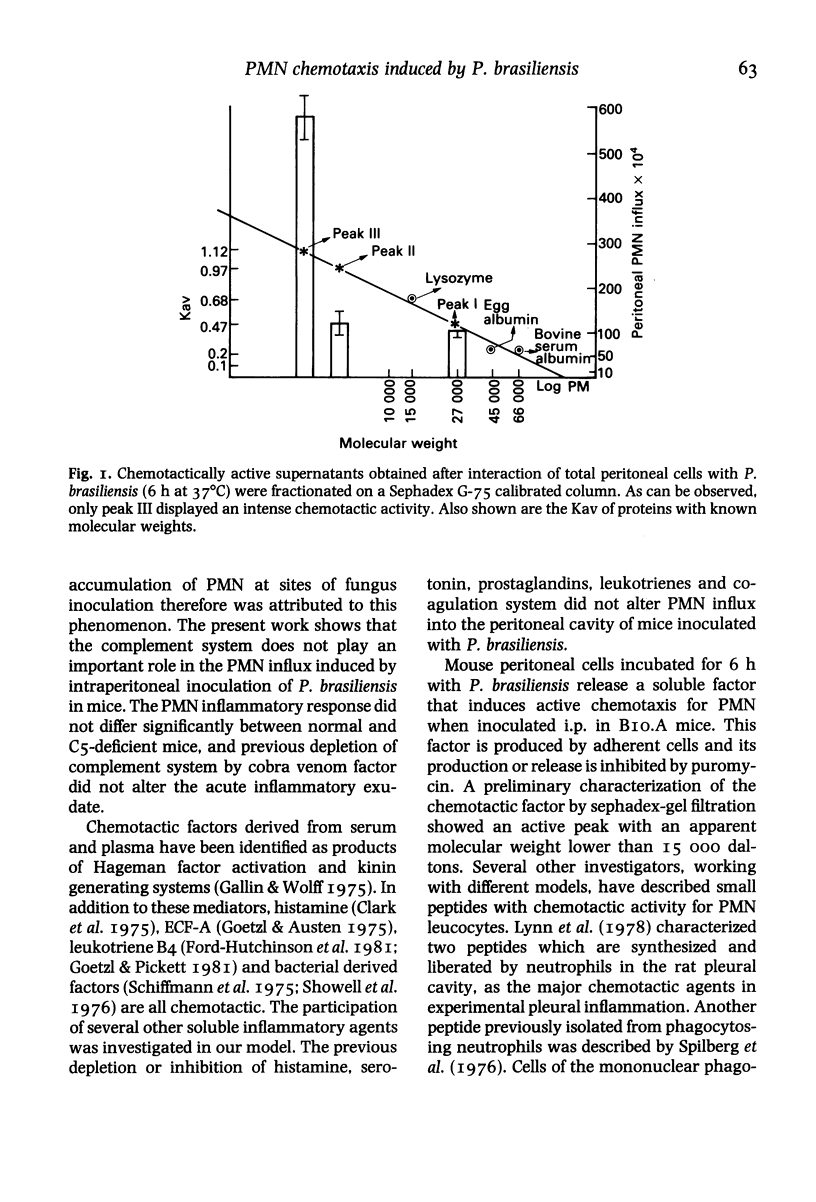
Intraperitoneal inoculation of BIO.A mice with P. brasiliensis induces an acute inflammatory infiltrate in which 40-50% of the cells are PMN leucocytes. Previous depletion of serotonin, prostaglandin, histamine and complement does not alter the course of inflammation. Complement-derived factors appear to have no active participation in the process since C5-deficient mice depleted or not by Cobra venom factor (CoF) show the same kind of cellular influx. On the other hand, peritoneal cells incubated (6 h) with the fungus release a soluble factor that induces in vivo an active chemotaxis of PMN cells when inoculated i.p. The factor has the following characteristics: a) it is produced by adherent cells; b) it is protein in nature; c) its production is inhibited by incubation of peritoneal cells with 10 micrograms/ml puromycin and d) it has a molecular weight less than 15 000 daltons, as determined by gel filtration through a Sephadex G-75 column.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. The selective eosinophil chemotactic activity of histamine. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1462–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Cunningham F. M., Davidson E. M., Smith M. J. Isomers of leukotriene B4 possess different biological potencies. Prostaglandins. 1981 Jan;21(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wolff S. M. Leucocyte chemotaxis: physiological considerations and abnormalities. Clin Haematol. 1975 Oct;4(3):567–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Immunologic reactivity of the lung: the in vivo and in vitro generation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):15–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., DeStefano M. J. Cell shape changes induced by cationic anesthetics. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):290–304. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo M. The role of macrophages in the chemotactic response of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jul;164(3):326–330. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilbert I., Gallacher A., Mehta J. M., Mandell B. Urate crystal-induced chemotactic factor: isolation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):815–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI108533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


