Abstract
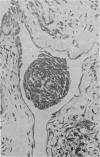
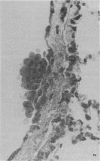
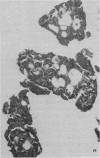
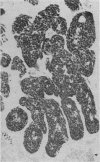
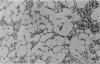
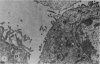
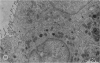
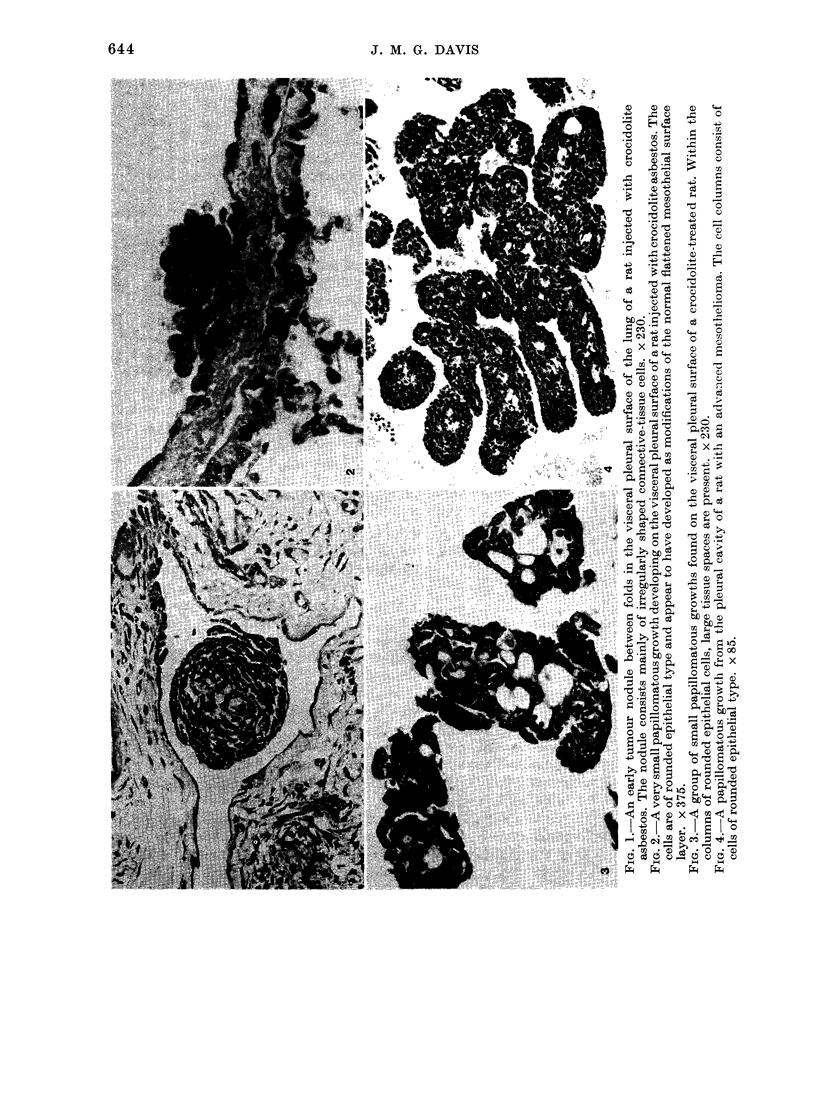
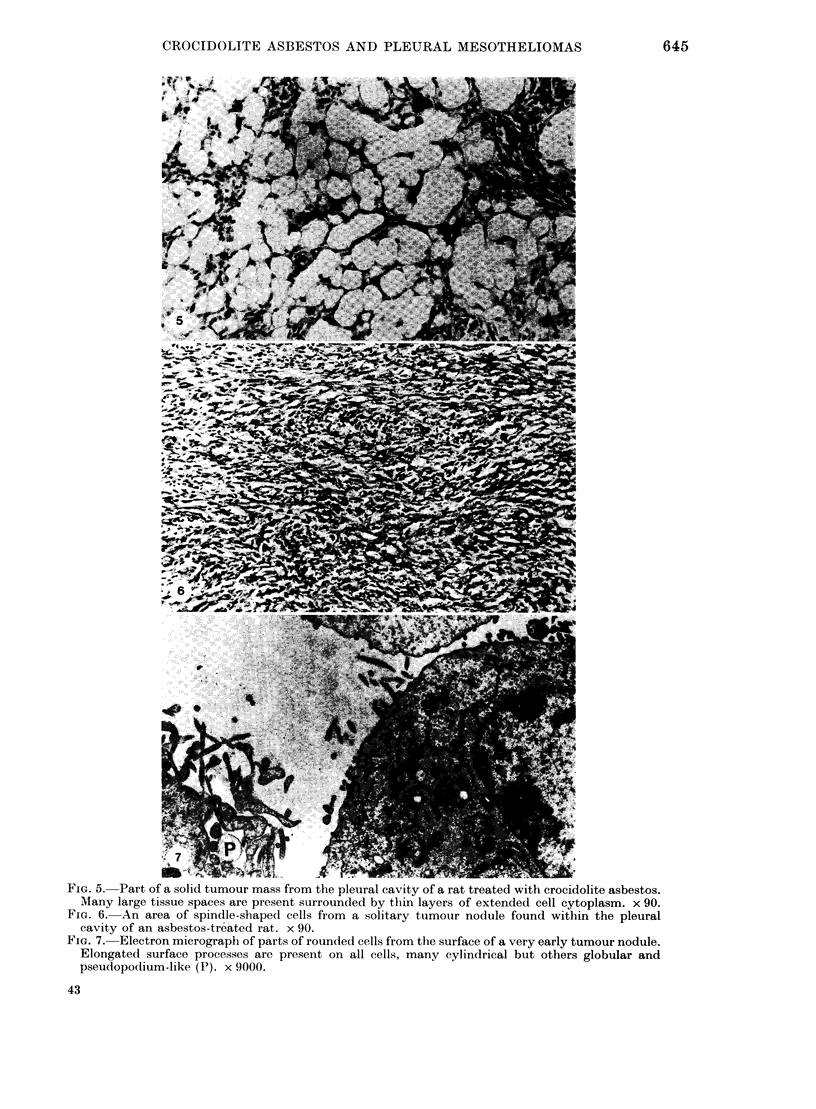
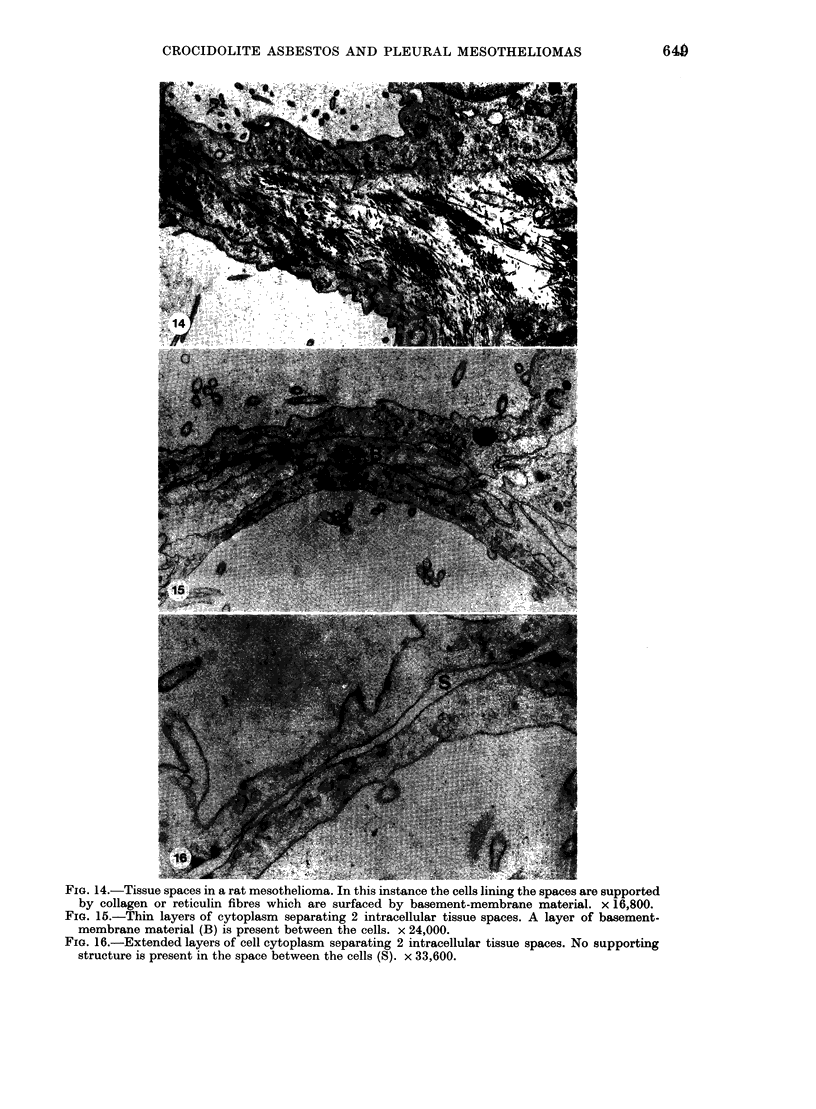
Primary tumours of the pleural cavity were produced in rats by the intrapleural injection of crocidolite asbestos. Their histological structure as seen with both light and electron microscopy was very variable and tumours frequently contained elements of both connective-tissue and epithelial type. In some instances the connective-tissue elements predominated from the start and the earliest tumour nodules consisted mainly of pleomorphic connective-tissue cells with only a few layers of cells more nearly epithelial in type on the surface. This pattern was largely retained when tumour nodules increased in size and coalesced, but in the deeper layers of advanced tumours the pleomorphic connective-tissue pattern was often replaced by a more uniform spindle-cell form. Other tumours were more predominantly epithelial in type, showing either a papillary pattern with rounded epithelial cells growing in solid columns, or a vesicular form in which large tissue spaces, often intracellular, were lined by very thin layers of extended cell cytoplasm. Whereas early tumours showed only one histological pattern, the more advanced stages often exhibited areas of all 3, so that there seemed to be some degree of histological mutability. The spindle-cell areas of advanced tumours frequently showed evidence of direct invasion of the surrounding tissue but this was never seen with the epithelial forms of rat mesothelioma.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand K. G., Buoen L. C., Brand I. Foreign body tumorigenesis: timing and location of preneoplastic events. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):829–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M. Histogenesis and fine structure of peritoneal tumors produced in animals by injections of asbestos. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1823–1837. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M. The long term fibrogenic effects of chrysotile and crocidolite asbestos dust injected into the pleural cavity of experimental animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Dec;51(6):617–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P., De Treville R. T. Experimental asbestosis. Studies on the progressiveness of the pulmonary fibrosis caused by chrysotile dust. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Nov;15(5):638–649. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOURIHANE D. O. THE PATHOLOGY OF MESOTHELIOMATA AND AN ANALYSIS OF THEIR ASSOCIATION WITH ASBESTOS EXPOSURE. Thorax. 1964 May;19:268–278. doi: 10.1136/thx.19.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaughey W. T. Asbestos and neoplasia: diffuse mesothelial tumors. Criteria for diagnosis of diffuse mesothelial tumors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER J. C., SLEGGS C. A., MARCHAND P. Diffuse pleural mesothelioma and asbestos exposure in the North Western Cape Province. Br J Ind Med. 1960 Oct;17:260–271. doi: 10.1136/oem.17.4.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G. Mesotheliomas in rats following inoculation with asbestos. Br J Cancer. 1969 Sep;23(3):567–581. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1969.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G., Skidmore J. W., Timbrell V. The effects of the inhalation of asbestos in rats. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):252–269. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G., Timbrell V. Mesotheliomata in rats after inoculation with asbestos and other materials. Br J Cancer. 1973 Aug;28(2):173–185. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]