Abstract
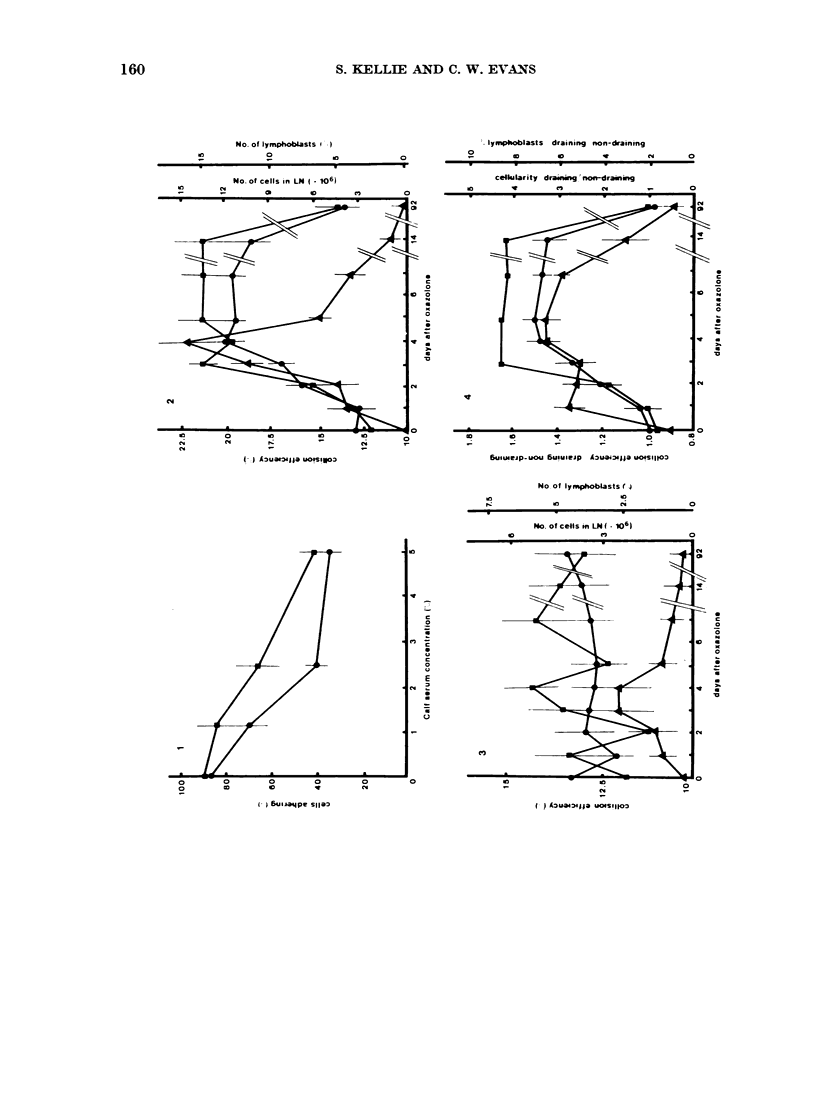
Lymphoid cells from the draining lymph nodes of mice 3 days after oxazolone application were found to be more adhesive to each other and to glass than cells from unsensitized nodes. Examination of the temporal sequence of changes during contact sensitization showed that during the first 4 days after oxazolone application there was an increase in both the cellularity of the draining node and in the intercellular adhesiveness of cells from the draining node, which persisted for at least 14 days. There was also an increase in the lymphoblast content; however, this was transient, peaking at Day 4 before returning almost to normal by Day 7. The intercellular adhesiveness of a lymphoblast-enriched subpopulation from the draining node was greater than the adhesiveness of a small lymphocyte subpopulation from the same node. However, the adhesiveness of both these subpopulations were greater than that of normal, unsensitized lymphoid cells. The implications of a change in cellular adhesiveness on the migratory properties in vivo of lymphocytes are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson G. L., Allwood G. G. Inflammatory lymphoid cells. Cells in immunized lymph nodes that move to sites of inflammation. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):493–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Barnes R. M. Contact sensitivity in the mouse. IX. The role of immunological and non-immunological inflammation in the movement of lymphocytes to immunized lymph nodes. Immunology. 1973 May;24(5):885–894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Ptak W. Contact and delayed hypersensitivity in the mouse. I. Active sensitization and passive transfer. Immunology. 1968 Sep;15(3):405–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis A. S. The measurement of cell adhesiveness by an absolute method. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1969 Nov;22(3):305–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J., Carter R. L., Leuchars E., Wallis V. The morphology of immune reactions in normal, thymectomized and reconstituted mice. II. The response to oxazolone. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):111–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. W., Davies M. D. The influence of cell adhesiveness on the migratory behavior of murine thymocytes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Parry D. M., Smith M. E. The distribution and differentiation of lymph-borne immunoblasts after intravenous injection into syngeneic recipients. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1972 May;5(3):269–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1972.tb00365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H. Localization of afferent lymph cells within the draining node during a primary immune response. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):510–513. doi: 10.1038/227510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A. R., Hall J. G. Nonspecific entry of thoracic duct immunoblasts into intradermal foci of antigens. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jul;8(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski W. L., Kupiec-Weglinski J. Whole body localization of intravenously injected lymphoblasts in normal rats. Lymphology. 1978 Dec;11(4):222–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRENDERGAST R. A. CELLULAR SPECIFICITY IN THE HOMOGRAFT REACTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:377–388. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Ferguson A. Selective migration of lymphocytes within the mouse small intestine. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):571–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., de Sousa M. A. Changes in the thymus-dependent areas of lymph nodes after immunological stimulation. Nature. 1966 Dec 17;212(5068):1316–1317. doi: 10.1038/2121316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Byrd W., Williams N., Brunner K. T., Cerottini J. C. The separation of different cell classes from lymphoid organs. The relationship between the adherence properties and the buoyant density of sub-populations of "B" and "T" lymphocytes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1972 Jun;50(3):323–336. doi: 10.1038/icb.1972.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


