Abstract
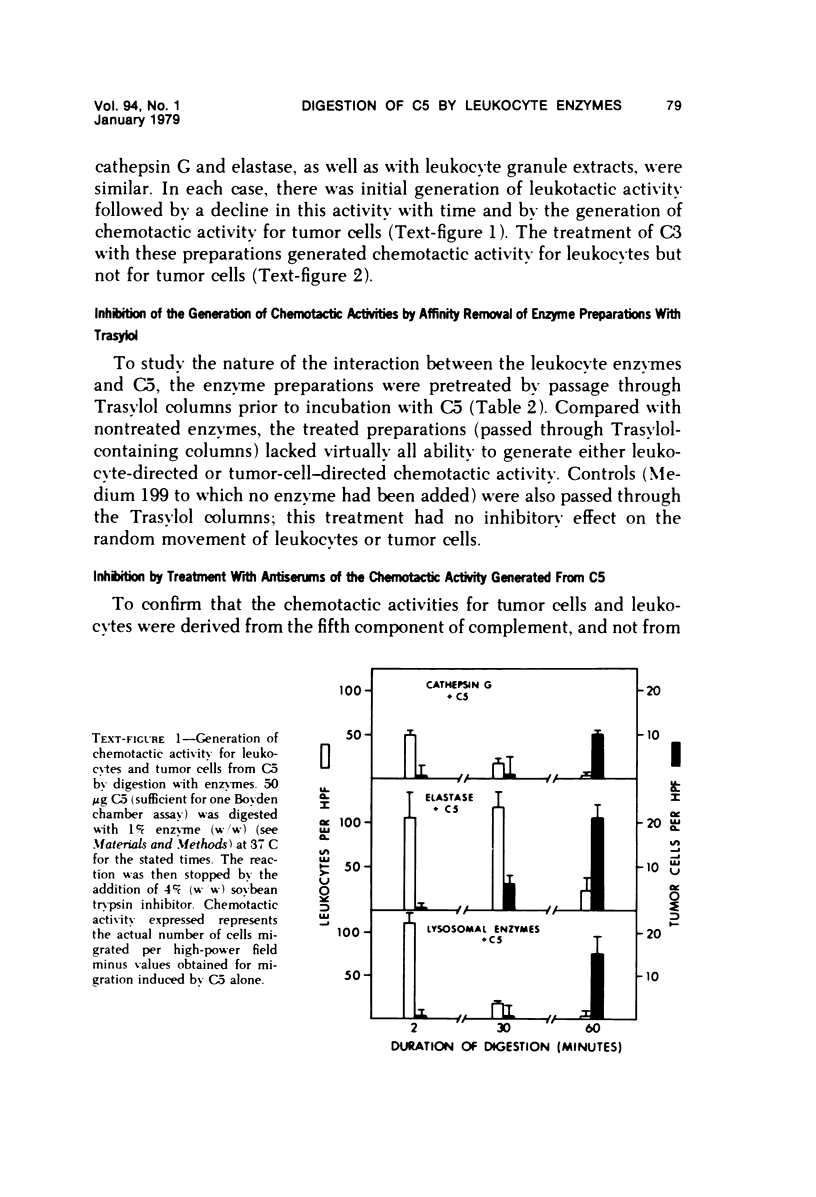
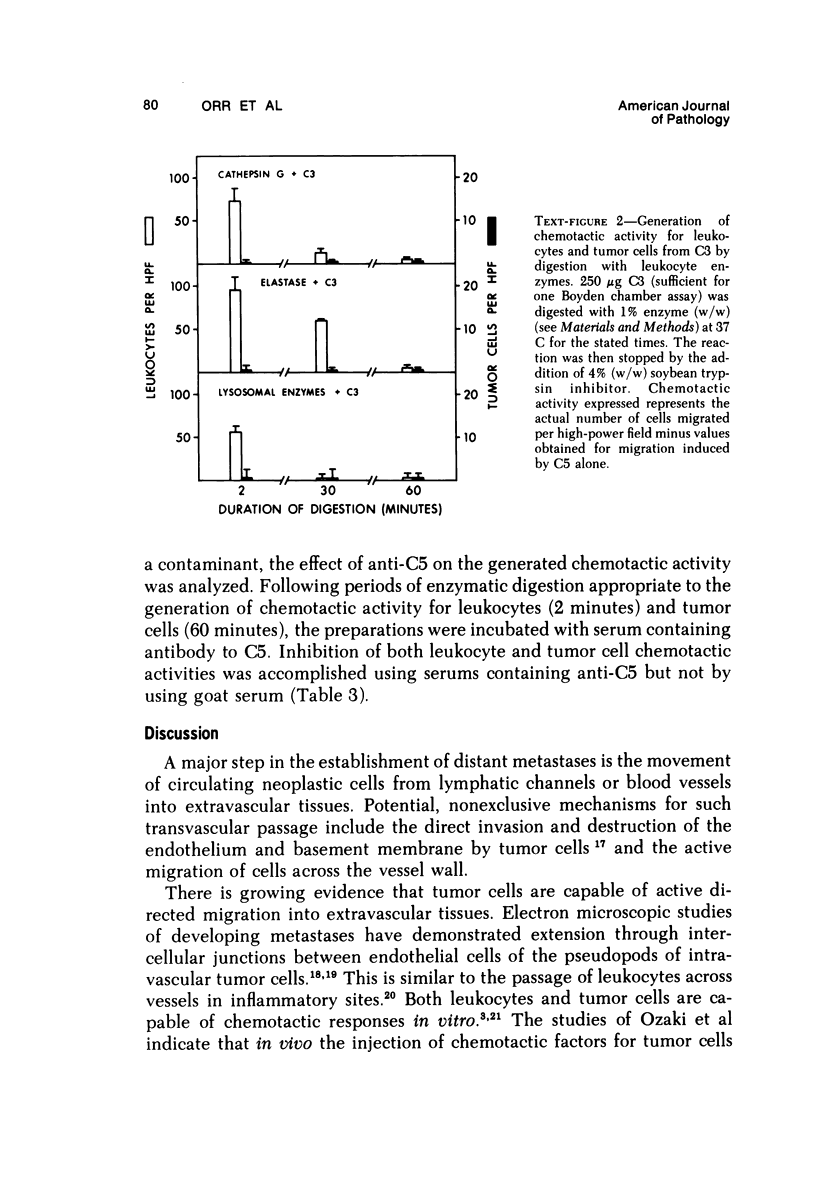
Leukocytes contain within their lysosomal granules enzymatic activity that will generate from C5 chemotactic activity for leukocytes (neutrophils) and tumor (Walker carcinosarcoma) cells. Similar activity has been found in phagocytic supernatant fluids from neutrophils and in purified preparations of the leukocyte neutral proteases elastase and cathepsin G. White leukotactic activities can be generated from either the third (C3) or the fifth (C5) components of complement, only C5 serves as a source for generation of the chemotactic activity for tumor cells. As has been previously shown with trypsin, the C5-related chemotactic activities generated by leukocyte proteases are time-dependent: leukotactic activity appears early, then disappears, and is replaced by chemotactic activity for tumor cells. The generation of these chemotactic activities from C5 is blocked by prior treatment of leukocyte preparations with the neutral protease inhibitor Trasylol. The demonstration that enzyme activities from leukocytes have the ability to generate tumor cell chemotactic factors from C5 suggests a possible mechanism by which the development of metastatic lesions may be promoted at sites of tissue injury or inflammation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOSTINO D., CLIFFTON E. E. TRAUMA AS A CAUSE OF LOCALIZATION OF BLOOD-BORNE METASTASES: PREVENTIVE EFFECT OF HEPARIN AND FIBRINOLYSIN. Ann Surg. 1965 Jan;161:97–102. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196501000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALEXANDER J. W., ALTEMEIER W. A. SUSCEPTIBILITY OF INJURED TISSUES TO HEMATOGENOUS METASTASES: AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY. Ann Surg. 1964 Jun;159:933–944. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196406000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozna J. P., Senior R. M., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor inactivators of human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1280–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI108887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., MORSE S. I. Interactions between rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes and staphylococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:419–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemans K. P. Invasion of liver tissue by blood-borne mammary carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Dec;53(6):1813–1824. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.6.1813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER B., FISHER E. R. Experimental studies of factors influencing hepatic metastases. II. Effect of partial hepatectomy. Cancer. 1959 Sep-Oct;12:929–932. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195909/10)12:5<929::aid-cncr2820120512>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Yoshida K., Ozaki T., Ushijima K. Chemotactic factor associated with invasion of cancer cells. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):174–175. doi: 10.1038/226174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T. The site of leucocyte emigration during inflammation. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1961 Apr;46:115–118. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1961.sp001522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Tomar R. H., Taylor F. B., Jr Additional studies on human C5: development of a modified purification method and characterization of the purified product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jul;9(7):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Varani J., Ward P. A. Characteristics of the chemotactic response of neoplastic cells to a factor derived from the fifth component of complement. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):405–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Ward P. A. Quantitation of leukotaxis in agarose by three different methods. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki T., Yoshida K., Ushijima K., Hayashi H. Studies on the mechanisms of invasion in cancer. II. In vivo effects of a factor chemotactic for cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jan 15;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romualdez A. G., Jr, Ward P. A. A unique complement derived chemotactic factor for tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romualdez A. G., Ward P. A., Torikata T. Relationship between the C5 peptides chemotactic for leukocytes and tumor cells. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1762–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindelar W. F., Tralka T. S., Ketcham A. S. Electron microscopic observations on formation of pulmonary metastases. J Surg Res. 1975 Feb;18(2):137–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(75)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. A plasmin-split fragment of C'3 as a new chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):189–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Hill J. H. C5 chemotactic fragments produced by an enzyme in lysosomal granules of neutrophils. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Zvaifler N. J. Complement-derived leukotactic factors in inflammatory synovial fluids of humans. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):606–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI106531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


